Portal:Asia

 Asia (/ˈeɪʒə/ AY-zhə, UK also /ˈeɪʃə/ AY-shə) is the largest continent in the world by both land area and population. It covers an area of more than 44 million square kilometers, about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8% of Earth's total surface area. The continent, which has long been home to the majority of the human population, was the site of many of the first civilizations. Its 4.7 billion people constitute roughly 60% of the world's population. Asia shares the landmass of Eurasia with Europe, and of Afro-Eurasia with both Europe and Africa. In general terms, it is bounded on the east by the Pacific Ocean, on the south by the Indian Ocean, and on the north by the Arctic Ocean. The border of Asia with Europe is a historical and cultural construct, as there is no clear physical and geographical separation between them. It is somewhat arbitrary and has moved since its first conception in classical antiquity. The division of Eurasia into two continents reflects East–West cultural, linguistic, and ethnic differences, some of which vary on a spectrum rather than with a sharp dividing line. A commonly accepted division places Asia to the east of the Suez Canal separating it from Africa; and to the east of the Turkish Straits, the Ural Mountains and Ural River, and to the south of the Caucasus Mountains and the Caspian and Black seas, separating it from Europe. China and India traded places as the largest economies in the world from 1 to 1800 CE. China was a major economic power for much of recorded history, with the highest GDP per capita until 1500. The Silk Road became the main east–west trading route in the Asian hinterlands while the Straits of Malacca stood as a major sea route. Asia has exhibited economic dynamism as well as robust population growth during the 20th century, but overall population growth has since fallen. Asia was the birthplace of most of the world's mainstream religions including Hinduism, Zoroastrianism, Judaism, Jainism, Buddhism, Confucianism, Taoism, Christianity, Islam, Sikhism, as well as many other religions. (Full article...) Featured articleThe Battle for Henderson Field, also known as the Battle of Guadalcanal or Battle of Lunga Point by the Japanese, took place from 23 to 26 October 1942 on and around Guadalcanal in the Solomon Islands. The battle was a land, sea, and air battle of the Pacific campaign of World War II and was fought between the Imperial Japanese Army and Navy and Allied forces, mainly U.S. Marines and Army. The battle was the last of three major land offensives conducted by the Japanese during the Guadalcanal campaign. In the battle, U.S. Marine and Army forces repulsed an attack by the Japanese 17th Army under the command of Lieutenant General Harukichi Hyakutake. The American forces were defending the Lunga perimeter that guarded Henderson Field on Guadalcanal, which the Allies had captured from the Japanese in landings on Guadalcanal on 7 August 1942. Hyakutake's force was sent to Guadalcanal in response to the Allied landings with the mission of recapturing the airfield and driving the Allied forces off the island. His soldiers conducted numerous assaults over three days at various locations around the Lunga perimeter, all repulsed with heavy Japanese losses. At the same time, Allied aircraft operating from Henderson Field successfully defended American positions on Guadalcanal from attacks by Japanese naval air and sea forces. (Full article...)Selected Country Japan is an island country in East Asia. It is in the northwest Pacific Ocean and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north toward the East China Sea, Philippine Sea, and Taiwan in the south. Japan is a part of the Ring of Fire, and spans an archipelago of 14,125 islands, with the four main islands being Hokkaido, Honshu (the "mainland"), Shikoku, and Kyushu. Tokyo is the country's capital and largest city, followed by Yokohama, Osaka, Nagoya, Sapporo, Fukuoka, Kobe, and Kyoto. The Japanese archipelago has been inhabited since the Upper Paleolithic (30,000 BC). Between the fourth and ninth centuries AD, the kingdoms of the region became unified under an emperor and the imperial court based in Heian-kyō. Beginning in the 12th century, political power was held by a series of military dictators (shōgun) and feudal lords (daimyō), and enforced by a class of warrior nobility (samurai). After a century-long period of civil war, the country was reunified in 1603 under the Tokugawa shogunate, which enacted an isolationist foreign policy. In 1854, a United States fleet forced Japan to open trade to the West, which led to the end of the shogunate and the restoration of imperial power in 1868. In the Meiji period, the Empire of Japan adopted a Western-modeled constitution, and pursued a program of industrialization and modernization. Amidst a rise in militarism and overseas colonization, Japan invaded China in 1937 and entered World War II as an Axis power in 1941. After suffering defeat in the Pacific War and two atomic bombings, Japan surrendered in 1945 and came under a seven-year Allied occupation, during which it adopted a new constitution. (Full article...)Featured biographyAbū Bakr Muḥammad ibn Ṭughj ibn Juff ibn Yiltakīn ibn Fūrān ibn Fūrī ibn Khāqān (8 February 882 – 24 July 946), better known by the title al-Ikhshīd (Arabic: الإخشيد) after 939, was an Abbasid commander and governor who became the autonomous ruler of Egypt and parts of Syria (Levant) from 935 until his death in 946. He was the founder of the Ikhshidid dynasty, which ruled the region until the Fatimid conquest of 969. The son of Tughj ibn Juff, a general of Turkic origin who served both the Abbasids and the autonomous Tulunid rulers of Egypt and Syria, Muhammad ibn Tughj was born in Baghdad but grew up in Syria and acquired his first military and administrative experiences at his father's side. He had a turbulent early career: he was imprisoned along with his father by the Abbasids in 905, was released in 906, participated in the murder of the vizier al-Abbas ibn al-Hasan al-Jarjara'i in 908, and fled Iraq to enter the service of the governor of Egypt, Takin al-Khazari. Eventually he acquired the patronage of several influential Abbasid magnates, chiefly the powerful commander-in-chief Mu'nis al-Muzaffar. These ties led him to being named governor first of Palestine and then of Damascus. In 933, he was briefly named governor of Egypt, but this order was revoked after the death of Mu'nis, and Ibn Tughj had to fight to preserve even his governorship of Damascus. In 935, he was re-appointed to Egypt, where he quickly defeated a Fatimid invasion and stabilized the turbulent country. His reign marks a rare period of domestic peace, stability and good government in the annals of early Islamic Egypt. In 938 Caliph al-Radi granted his request for the title of al-Ikhshid, which had been borne by the rulers of his ancestral Farghana Valley. It is by this title that he was known thereafter. (Full article...)General imagesThe following are images from various Asia-related articles on Wikipedia. Featured picture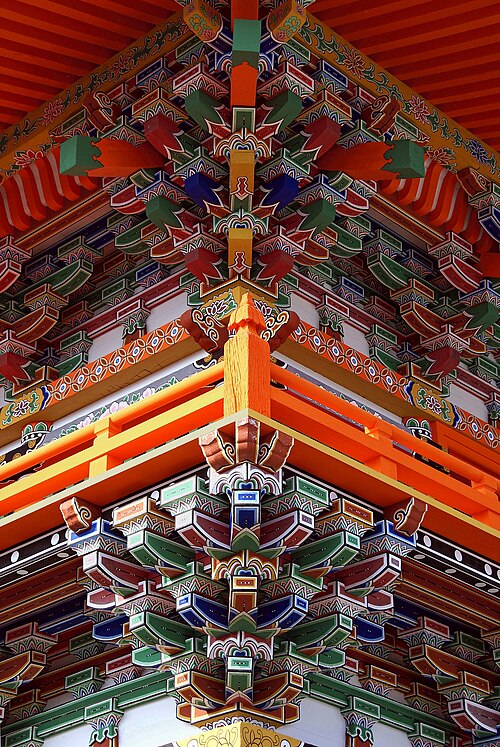 Credit: 663highland A colorful dougong supporting a structure at Sagami Temple, Kasai, Hyōgo, Japan. Dougong is a structural element of interlocking wooden brackets, one of the most important elements in traditional Chinese, Japanese, and Korean architecture. The use of dougong first appeared in buildings of the late centuries BC and evolved into a structural network that joined pillars and columns to the frame of the roof. The pieces are fit together by joinery alone without glue or fasteners, due to the precision and quality of the carpentry.
Did you know...
Updated: 6:33, 14 February 2024 In the news
Related portalsMajor Religions in Asia Middle East Central Asia and Surroundings Indian Subcontinent Southeast Asia East Asia Selected panorama
A panoramic view of the Hiroshima Peace Memorial, the site of the first atomic bomb to be used in warfare on August 6, 1945, during the final stages of World War II. Over 70,000 people were killed immediately, and another 70,000 suffered fatal injuries from the radiation, after the U.S. Army Air Force bomber Enola Gay dropped the bomb, codenamed "Little Boy". The Genbaku ("A-bomb") Dome (center) was directly beneath the blast, but managed to survive mostly intact. TopicsCategoriesAssociated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
More portalsShortcuts to this page: Asia portal • P:ASIA Purge server cache |





























































































