User:Yakoove/sandbox
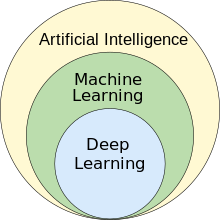

As of 2020, many sources continue to assert that machine learning remains a subfield of AI.[3][4][5] The main disagreement is whether all of ML is part of AI as shown in Fig-x. This would mean that anyone using ML could claim they are using AI, as all of ML is a subfield of AI.
Others have the view that not all of ML is part of AI[6][7][8] as shown in Fig-y where only a subset of ML is part of AI or a subset of AI is part of ML.[9]
The question to what is the difference between ML and AI is answered by Judea Pearl in The Book of Why.[10] Accordingly ML learns and predicts based on passive observations, whereas AI implies an agent interacting with the environment to learn and take actions that maximize its chance of successfully achieving its goals.[13]
References[edit]
- ^ "AN EMPIRICAL SCIENCE RESEARCH ON BIOINFORMATICS IN MACHINE LEARNING – Journal". Retrieved 28 October 2020.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ "rasbt/stat453-deep-learning-ss20" (PDF). GitHub.
- ^ Garbade, Dr Michael J. (14 September 2018). "Clearing the Confusion: AI vs Machine Learning vs Deep Learning Differences". Medium. Retrieved 28 October 2020.
- ^ "AI vs. Machine Learning vs. Deep Learning vs. Neural Networks: What's the Difference?". www.ibm.com. Retrieved 28 October 2020.
- ^ "AN EMPIRICAL SCIENCE RESEARCH ON BIOINFORMATICS IN MACHINE LEARNING – Journal". Retrieved 28 October 2020.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ "Chapter 1: Introduction to Machine Learning and Deep Learning". Dr. Sebastian Raschka. 5 August 2020. Retrieved 28 October 2020.
- ^ August 2011, Dovel Technologies in (15 May 2018). "Not all Machine Learning is Artificial Intelligence". CTOvision.com. Retrieved 28 October 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ "AI Today Podcast #30: Interview with MIT Professor Luis Perez-Breva -- Contrary Perspectives on AI and ML". Cognilytica. 28 March 2018. Retrieved 28 October 2020.
- ^ "rasbt/stat453-deep-learning-ss20" (PDF). GitHub. Retrieved 28 October 2020.
- ^ Pearl, Judea; Mackenzie, Dana. The Book of Why: The New Science of Cause and Effect (2018 ed.). Basic Books. ISBN 9780465097609. Retrieved 28 October 2020.
- ^ Poole, Mackworth & Goebel 1998, p. 1.
- ^ Russell & Norvig 2003, p. 55.
- ^ Definition of AI as the study of intelligent agents: * Poole, Mackworth & Goebel (1998), which provides the version that is used in this article. These authors use the term "computational intelligence" as a synonym for artificial intelligence.[11] * Russell & Norvig (2003) (who prefer the term "rational agent") and write "The whole-agent view is now widely accepted in the field".[12] * Nilsson 1998 * Legg & Hutter 2007
