User:Tom29739/The EU
The European Union (EU) is a union of countries, located mostly in Europe.
European Union | |
|---|---|
| Motto: United in diversity | |
| Anthem: Ode to Joy | |
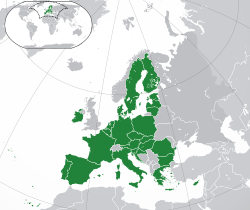 | |
| Capital | Brussels |
| Largest city | Paris and London |
| Internet TLD | .eu |
Website europa.eu | |

Evolution[edit]
The EU has not always been the European Union. It has had several incarnations, shown in the diagram below:Since the end of World War II, sovereign European countries have entered into treaties and thereby co-operated and harmonised policies (or pooled sovereignty) in an increasing number of areas, in the European integration project or the construction of Europe (French: la construction européenne). The following timeline outlines the legal inception of the European Union (EU)—the principal framework for this unification. The EU inherited many of its present responsibilities from the European Communities (EC), which were founded in the 1950s in the spirit of the Schuman Declaration.
| Legend: S: signing F: entry into force T: termination E: expiry de facto supersession Rel. w/ EC/EU framework: de facto inside outside |
[Cont.] | ||||||||||||||||
| (Pillar I) | |||||||||||||||||
| European Atomic Energy Community (EAEC or Euratom) | [Cont.] | ||||||||||||||||
| European Economic Community (EEC) | |||||||||||||||||
| Schengen Rules | European Community (EC) | ||||||||||||||||
| 'TREVI' | Justice and Home Affairs (JHA, pillar II) | ||||||||||||||||
| [Cont.] | Police and Judicial Co-operation in Criminal Matters (PJCC, pillar II) | ||||||||||||||||
Anglo-French alliance |
[Defence arm handed to NATO] | European Political Co-operation (EPC) | Common Foreign and Security Policy (CFSP, pillar III) | ||||||||||||||
| [Tasks defined following the WEU's 1984 reactivation handed to the EU] | |||||||||||||||||
| [Social, cultural tasks handed to CoE] | [Cont.] | ||||||||||||||||
- ^ a b c d e Although not EU treaties per se, these treaties affected the development of the EU defence arm, a main part of the CFSP. The Franco-British alliance established by the Dunkirk Treaty was de facto superseded by WU. The CFSP pillar was bolstered by some of the security structures that had been established within the remit of the 1955 Modified Brussels Treaty (MBT). The Brussels Treaty was terminated in 2011, consequently dissolving the WEU, as the mutual defence clause that the Lisbon Treaty provided for EU was considered to render the WEU superfluous. The EU thus de facto superseded the WEU.
- ^ Plans to establish a European Political Community (EPC) were shelved following the French failure to ratify the Treaty establishing the European Defence Community (EDC). The EPC would have combined the ECSC and the EDC.
- ^ The European Communities obtained common institutions and a shared legal personality (i.e. ability to e.g. sign treaties in their own right).
- ^ The treaties of Maastricht and Rome form the EU's legal basis, and are also referred to as the Treaty on European Union (TEU) and the Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union (TFEU), respectively. They are amended by secondary treaties.
- ^ Between the EU's founding in 1993 and consolidation in 2009, the union consisted of three pillars, the first of which were the European Communities. The other two pillars consisted of additional areas of cooperation that had been added to the EU's remit.
- ^ The consolidation meant that the EU inherited the European Communities' legal personality and that the pillar system was abolished, resulting in the EU framework as such covering all policy areas. Executive/legislative power in each area was instead determined by a distribution of competencies between EU institutions and member states. This distribution, as well as treaty provisions for policy areas in which unanimity is required and qualified majority voting is possible, reflects the depth of EU integration as well as the EU's partly supranational and partly intergovernmental nature.
How the EU benefits the UK[edit]
The EU benefits the UK because we can trade with Europe and the rest of the World easily. It allows free movement of citizens of the EU in and out of the UK and other EU countries.
Disadvantages of the EU[edit]
The EU sets limits on how many people a member state must take per year. This means that the UK has to take in benefit-scrounging, good for nothing scum migrants that take all the jobs from native-born British people and take all the money out of the national pot for themselves.
Member states of the EU[edit]
The following countries are member states of the EU:
| Name | Capital | Accession | Population | Area (km2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vienna | 1 January 1995 | 8,584,926 | 83,855 | |
| Brussels | Founder | 11,258,434 | 30,528 | |
| Sofia | 1 January 2007 | 7,202,198 | 110,994 | |
| Zagreb | 1 July 2013 | 4,225,316 | 56,594 | |
| Nicosia | 1 May 2004 | 847,008 | 9,251 | |
| Prague | 1 May 2004 | 10,538,275 | 78,866 | |
| Copenhagen | 1 January 1973 | 5,659,715 | 43,075 | |
| Tallinn | 1 May 2004 | 1,313,271 | 45,227 | |
| Helsinki | 1 January 1995 | 5,471,753 | 338,424 | |
| Paris | Founder | 66,352,469 | 640,679 | |
| Berlin | Founder | 81,174,000 | 357,021 | |
| Athens | 1 January 1981 | 10,812,467 | 131,990 | |
| Budapest | 1 May 2004 | 9,849,000 | 93,030 | |
| Dublin | 1 January 1973 | 4,625,885 | 70,273 | |
| Rome | Founder | 60,795,612 | 301,338 | |
| Riga | 1 May 2004 | 1,986,096 | 64,589 | |
| Vilnius | 1 May 2004 | 2,921,262 | 65,200 | |
| Luxembourg City | Founder | 562,958 | 2,586 | |
| Valletta | 1 May 2004 | 429,344 | 316 | |
| Amsterdam | Founder | 16,900,726 | 41,543 | |
| Warsaw | 1 May 2004 | 38,005,614 | 312,685 | |
| Lisbon | 1 January 1986 | 10,374,822 | 92,390 | |
| Bucharest | 1 January 2007 | 19,861,408 | 238,391 | |
| Bratislava | 1 May 2004 | 5,421,349 | 49,035 | |
| Ljubljana | 1 May 2004 | 2,062,874 | 20,273 | |
| Madrid | 1 January 1986 | 46,439,864 | 504,030 | |
| Stockholm | 1 January 1995 | 9,747,355 | 449,964 | |
| London | 1 January 1973 | 64,767,115 | 243,610 |
Culture[edit]
This is a selection of pictures of the culture of the EU:
-
A typical Schengen border crossing.
-
A European Court of Justice courtroom.
-
The outside of the European Central Bank.
-
The European Court of Auditors.
-
The EU flags in front of the main office of the European Commission.
-
The inside of the Louise Weiss building of the European Parliament in Strasbourg.
-
A European Council room.
-
The European Council.
-
A bird protected under EU laws.
-
A protected area under EU laws.
-
The European coastline in Cyprus.
-
Mont Blanc in the Alps, the highest peak in the EU.
-
The fall of the Berlin Wall in 1989.
-
The European flag in 2004 after EU enlargements.
-
The European Central Bank building in Frankfurt, Germany, under construction in this picture.
-
The Öresund bridge.
-
A vineyard in Romania
-
A view of Madrid, from a downtown building.
-
The view of Berlin.
-
A panorama of Paris.
-
London from a hot air balloon.
-
The Colosseum in Rome at night.
-
The Acropolis in Athens.






















