User:Super Cyclonic Storm Corona/PAC

Typhoon Goni, known in the Philippines as Super Typhoon Rolly, was an extremely powerful tropical cyclone that made landfall as a Category 5–equivalent super typhoon on Catanduanes in the Philippines and in Vietnam as a tropical storm, and became the strongest landfalling tropical cyclone on record by 1-minute winds, eclipsing the previous record held by Haiyan and Meranti. The nineteenth named storm, ninth typhoon, and second super typhoon of the 2020 Pacific typhoon season, Goni originated as a tropical depression south of Guam on October 26. It was then named as Tropical Storm Goni on October 27. On the next day, Goni explosively intensified over the Philippine Sea, becoming a Category 5–equivalent super typhoon on October 30. Goni maintained Category 5 strength for over a day, before making landfall on Catanduanes at peak intensity, with 10-minute sustained winds of 220 km/h (140 mph),[1] and 1-minute sustained winds of 315 km/h (195 mph), with a minimum central pressure of 905 hPa (mbar; 26.72 inHg). It was the second-most intense tropical cyclone observed worldwide in 2020, after Cyclone Yasa, and one of the most intense tropical cyclones on record.[2]
Following its first landfall, Goni rapidly weakened while it moved over the Philippines. The storm brought severe flash flooding to Legazpi, as well as lahar flow from the nearby Mayon Volcano. There were widespread power outages as well as damaged power and transmission lines in Bicol. Crops were also heavily damaged. Over 390,000 out of 1 million evacuated individuals have been displaced in the region. Due to the extreme wind speed of the typhoon, two evacuation shelters had their roofing lost. Debris and lahars had also blocked various roads, as well as rendering the Basud Bridge impassible. In Vietnam, where Goni made landfall as a tropical depression, there was flooding in numerous areas, as well as eroded and damaged roads. This exacerbated the 2020 Central Vietnam floods, causing an estiamted ₫543 billion (US$23.5 million). In all, the typhoon killed at least 32 people and caused at least ₱20 billion (US$415 million) worth of damage.[3] The COVID-19 pandemic was also a concern for people in evacuation centers.[4]
After Goni moved into the West Philippine Sea, it subsequently weakened into a tropical storm. It started to move generally westward towards Vietnam. It eventually reached the country late on November 5 as a tropical depression, bringing heavy rain and gusty winds. International relief from several countries as well as the United Nations followed soon after the typhoon moved away from the Philippines.[5] The relief included donations totaling up to $11.48 million and protection from the pandemic, among other items. Due to the damages caused by the typhoon, the name Rolly will be retired and will be replaced with a new name for a future typhoon season.

Typhoon Hagibis, known in Japan as Reiwa 1 East Japan Typhoon (令和元年東日本台風, Reiwa Gannen Higashi-Nihon Taifū), was an extremely violent and large tropical cyclone that caused widespread destruction across its path. The thirty-eighth depression, ninth typhoon, and third super typhoon of the 2019 Pacific typhoon season, it was the strongest typhoon in decades to strike mainland Japan, and one of the largest typhoons ever recorded, with a peak gale-force diameter of 825 nautical miles (950 mi; 1529 km). Hagibis was also the deadliest typhoon to strike Japan since Typhoon Tip in 1979. Its death toll is marginally higher than that of Typhoon Bess in 1982 and Typhoon Tokage in 2004.
Hagibis developed from a tropical disturbance located a couple hundred miles north of the Marshall Islands on October 2, 2019. The Joint Typhoon Warning Center issued a red tropical cyclone formation alert - noting that the disturbance could undergo rapid intensification upon being identified as a tropical depression. On the next day, October 3, both the Japan Meteorological Agency and the Joint Typhoon Warning Center began issuing advisories on Tropical Depression 20W. The depression stayed at the same intensity as it travelled west toward the Mariana Islands on October 4, but on October 5, 20W began undergoing rapid intensification and early that day, the system was issued with the name "Hagibis" by the JMA, which means speed in Filipino. Sea surface temperatures and wind shear became extremely favourable for tropical cyclogenesis and Hagibis started extremely rapid intensification on October 6, and became a Category 5 super typhoon in under 12 hours - the second of the 2019 Pacific typhoon season. Edging closer to the uninhabited areas of the Mariana Islands, Hagibis displayed excellent convection as well as a well-defined circulation. The system developed a pinhole eye and made landfall on the Northern Mariana Islands at peak intensity, with 10-minute sustained winds of 195 km/h (120 mph) and a central pressure of 915 hPa (27.02 inHg).
Land interaction did not affect Hagibis much, but as the system continued to move westward, it underwent an eyewall replacement cycle, which is usual for all tropical cyclones of a similar intensity. The inner eyewall was robbed of its needed moisture and Hagibis began to weaken, but it formed a large and cloud-filled eye, which then became clear, and Hagibis reached its second peak. Travelling toward Japan, Hagibis encountered high vertical wind shear and its inner eyewall began to degrade, and the outer eyewalls rapidly eroded as its center began to be exposed. On October 12, Hagibis made landfall on Japan at 19:00 p.m JST (10:00 UTC) on the Izu Peninsula near Shizuoka. Then, an hour later at 20:00 p.m. JST, (11:00 UTC), Hagibis made its second landfall on Japan in the Greater Tokyo Area. Wind shear was now at 60 knots (69 mph; 111 km/h), and Hagibis' structure became torn apart as it sped at 34 knots (39 mph; 63 km/h) north-northeast toward more hostile conditions. On October 13, Hagibis became an extratropical low and the JMA and JTWC issued their final advisories on the system. However, the extratropical remnant of Hagibis persistent for more than a week, before dissipating on October 22. Hagibis caused catastrophic destruction across much of eastern Japan. Hagibis spawned a large tornado on October 12, which struck the Ichihara area of Chiba Prefecture during the onset of Hagibis,; the tornado, along with a 5.7 magnitude earthquake off the coast, caused additional damage those areas that were damaged by Hagibis. Hagibis caused $15 billion (2019 USD), making it the costliest typhoon on record.

Severe Tropical Cyclone Winston was the most intense tropical cyclone in the Southern Hemisphere on record, as well as the strongest to make landfall in the Southern Hemisphere, with the possible exception of 1899's Cyclone Mahina in both regards. Winston is also the costliest tropical cyclone on record in the South Pacific basin. The system was first noted as a tropical disturbance on 7 February 2016, when it was located to the northwest of Port Vila, Vanuatu. Over the next few days, the system gradually developed as it moved southeast, acquiring gale-force winds by 11 February. The following day, it underwent rapid intensification and attained ten-minute maximum sustained winds of 175 km/h (110 mph). Less favourable environmental conditions prompted weakening thereafter. After turning northeast on 14 February, Winston stalled to the north of Tonga on 17 February. Due to a change in higher level steering, the storm drifted back to the west. In the process, Winston again rapidly intensified, reaching Category 5 intensity on both the Australian tropical cyclone scale and the Saffir–Simpson hurricane wind scale on 19 February. The storm passed directly over Vanua Balavu, where a national record wind gust of 306 km/h (190 mph) was observed.
The cyclone reached its peak intensity on 20 February, with ten-minute sustained winds of 280 km/h (175 mph) and a pressure of 884 hPa (mbar; 26.10 inHg), shortly before making landfall on Viti Levu, Fiji. Thereafter, the storm slowly weakened within a less favourable environment; the system turned southeast during this time, though remained well away from Fiji. It later degenerated into a remnant low, with some subtropical characteristics, on 24 February as it turned to the west and later northwest. The system persisted for more than a week over the Coral Sea before ultimately moving over Queensland, Australia and dissipating on 3 March, 26 days after being classified a tropical disturbance.
In advance of the storm's arrival in Fiji, numerous shelters were opened, and a nationwide curfew was instituted during the evening of 20 February. Striking Fiji at Category 5 intensity on 20 February, Winston inflicted extensive damage on many islands and killed 44 people. Communications were temporarily lost with at least six islands, with some remaining isolated more than two days after the storm's passage. A total of 40,000 homes were damaged or destroyed and approximately 350,000 people—roughly 40 percent of Fiji's population—were significantly impacted by the storm. Total damage from Winston amounted to FJ$2.98 billion (US$1.4 billion). The nation's government declared a state of emergency on 20 February, which remained in place for 60 days. Immediately following the cyclone, the governments of Australia and New Zealand provided logistical support and relief packages. In the following weeks, a coalition of international support, including intergovernmental agencies, brought tens of millions of dollars in aid and hundreds of tons of supplies to residents in Fiji.

Hurricane Patricia was an exceptionally powerful tropical cyclone that became the strongest on record worldwide in terms of wind speed and the second-most intense on record worldwide in terms of pressure, behind Typhoon Tip in 1979, with a minimum atmospheric pressure of 872 mbar (hPa; 25.75 inHg). Originating from a sprawling disturbance near the Gulf of Tehuantepec, south of Mexico, in mid-October 2015, Patricia was first classified a tropical depression on October 20. Initial development was slow, with only modest strengthening within the first day of its classification. The system later became a tropical storm and was named Patricia, the twenty-fourth named storm of the annual hurricane season. Exceptionally favorable environmental conditions fueled explosive intensification on October 22. A well-defined eye developed within an intense central dense overcast and Patricia grew from a tropical storm to a Category 5 hurricane in just 24 hours—a near-record pace. On October 23, the hurricane achieved its record peak intensity with maximum sustained winds of 215 mph (345 km/h). This made it the most intense tropical cyclone on record in the Western Hemisphere and the strongest globally in terms of one-minute maximum sustained winds.
Late on October 23, dramatic weakening ensued and Patricia made landfall near Cuixmala, Jalisco, with winds of 150 mph (240 km/h). This made it the strongest landfalling hurricane on record along the Pacific coast of Mexico. Patricia continued to weaken extremely quickly, faster than it had intensified, as it interacted with the mountainous terrain of Mexico. Within 24 hours of moving ashore, Patricia weakened into a tropical depression and dissipated soon thereafter, late on October 24.
The precursor to Patricia produced widespread flooding rains in Central America. Hundreds of thousands of people were directly affected by the storm, mostly in Guatemala. At least six fatalities were attributed to the event: four in El Salvador, one in Guatemala, and one in Nicaragua. Torrential rains extended into southeastern Mexico, with areas of Quintana Roo and Veracruz reporting accumulations in excess of 19.7 in (500 mm). Damage in Chetumal reached MX$1.4 billion (US$85.3 million).
As a tropical cyclone, Patricia's effects in Mexico were tremendous; however, the affected areas were predominantly rural, lessening the number of people directly impacted. Violent winds tore roofs from structures and stripped coastal areas of their vegetation. Preliminary assessments indicated hundreds of homes to be destroyed; seven fatalities were linked to the hurricane directly or indirectly, including one during evacuations. Total damage from Patricia was estimated to be at least $462.8 million (2015 USD); the damage in Mexico alone was estimated to be in excess of MX$5.4 billion (US$325 million), with agriculture and infrastructure comprising the majority of losses. Flooding partially associated with remnant moisture from Patricia inflicted US$52.5 million in damage across Southern Texas.
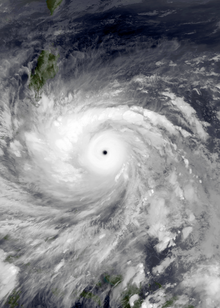
Typhoon Haiyan, known in the Philippines as Super Typhoon Yolanda, was one of the most powerful tropical cyclones ever recorded. On making landfall, Haiyan devastated portions of Southeast Asia, particularly the Philippines. It is one of the deadliest Philippine typhoons on record, killing at least 6,300 people in that country alone. In terms of JTWC-estimated 1-minute sustained winds, Haiyan is tied with Meranti in 2016 for being the second strongest landfalling tropical cyclone on record. In January 2014, bodies were still being found.
The thirtieth named storm, thirteenth typhoon, and fifth super typhoon of the 2013 Pacific typhoon season, Haiyan originated from an area of low pressure several hundred kilometers east-southeast of Pohnpei in the Federated States of Micronesia on November 2, 2013. Tracking generally westward, environmental conditions favored tropical cyclogenesis and the system developed into a tropical depression on the following day. After becoming a tropical storm and being named Haiyan at 00:00 UTC on November 4, the system began a period of rapid intensification that brought it to typhoon intensity by 18:00 UTC on November 5. By November 6, the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) assessed the system as a Category 5-equivalent super typhoon on the Saffir–Simpson hurricane wind scale (SSHWS); the storm passed over the island of Kayangel in Palau shortly after attaining this strength.
Thereafter, Haiyan continued to intensify; at 12:00 UTC on November 7, the Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) upgraded the storm's maximum ten-minute sustained winds to 230 km/h (145 mph), the highest in relation to the storm. The Hong Kong Observatory put the storm's maximum ten-minute sustained winds at 285 km/h (180 mph) prior to landfall in the central Philippines, while the China Meteorological Administration estimated the maximum two-minute sustained winds at the time to be around 78 m/s (280 km/h or 175 mph). At the same time, the JTWC estimated the system's one-minute sustained winds at 315 km/h (195 mph), unofficially making Haiyan the strongest tropical cyclone ever observed based on wind speed, a record which would later be surpassed by Hurricane Patricia in 2015 at 345 km/h (215 mph). Haiyan is also tied with Meranti in 2016 and Goni in 2020 as the most intense tropical cyclone in the Eastern Hemisphere by 1-minute sustained winds; several others have recorded lower central pressure readings. At 20:40 UTC on November 7, the eye of the typhoon made its first landfall in the Philippines at Guiuan, Eastern Samar at peak strength. Gradually weakening, the storm made five additional landfalls in the country before emerging over the South China Sea. Turning northwestward, the typhoon eventually struck northern Vietnam as a severe tropical storm on November 10. Haiyan was last noted as a tropical depression by the JMA on the following day.
The typhoon caused catastrophic destruction in the Visayas, particularly on Samar and Leyte. According to UN officials, about 11 million people were affected and many were left homeless. People are still missing because of this powerful storm.
- ^ "Typhoon 202019 (GONI) – Detailed Wind Information (Japan Meteorological Agency Best Track Data)". Digital Typhoon. National Institute of Informatics. Archived from the original on November 1, 2020.
- ^ Samenow, Jason. "Super Typhoon Goni explodes into 2020s strongest storm on Earth, moves toward Philippines". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on October 31, 2020. Retrieved October 31, 2020.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
AONwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Ratcliffe, Rebecca (November 2, 2020). "Typhoon Goni: thousands of homes in Philippines feared destroyed". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Archived from the original on November 2, 2020. Retrieved November 2, 2020.
- ^ "SitRep No.07 re Preparedness Measures for Super Typhoon Rolly" (PDF). NDRRMC. November 5, 2020.
