User:Mr. Ibrahem/Vaginal discharge
| Vaginal discharge | |
|---|---|
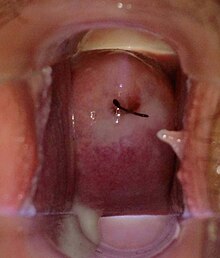 | |
| Normal vagina and cervix during a medical speculum exam demonstrating IUD strings at the opening of the cervix and normal milky white vaginal discharge on the vaginal walls, cervix, and pooled in vaginal fornix. | |
| Specialty | Gynecology |
| Symptoms | Normal: Thin, watery, thick, sticky, clear or white[1][2] Abnormal: Change in color, increase in amount, foul smell, itching, burning, pelvic pain, abnormal vaginal bleeding, pain during sex[2][3] |
| Types | Normal, abnormal[2] |
| Differential diagnosis | Normal, bacterial vaginosis, yeast infection, trichomoniasis, chlamydia, gonorrhea, herpes[2] |
Vaginal discharge can be normal or abnormal.[2] Normal vaginal discharge occurs in most women and girls.[2] The amount, quality, and composition of discharge varies between individuals, throughout the menstrual cycle, and throughout the stages of sexual and reproductive development.[4] Normal vaginal discharge may have a thin, watery consistency or a thick, sticky consistency, and it may be clear or white in color.[1][2] Normal vaginal discharge typically does not have a strong smell, nor is it typically associated with itching or pain.[4] It may be large in volume, which occurs more often during pregnancy, when sexually active, or when taking birth control.[4][2]
Normal vaginal discharge is a mixture of liquid, cells, and bacteria that lubricate and protect the vagina.[1] This mixture is produced by the cells of the vagina and cervix, and it exits the body through the vaginal opening.[3] Normal vaginal discharge cannot be prevented and douching is specifically not recommended.[2]
While most discharge represents normal functioning of the body, some changes in discharge can reflect infection or other problems.[5] Infections that may cause changes in vaginal discharge include vaginal yeast infections, bacterial vaginosis, and certain sexually transmitted infections.[6] Non infectious causes may include bubble bath or foreign objects.[3] The characteristics of abnormal vaginal discharge vary depending on the cause, with common features including a change in color, increase in amount, foul smell, or associated symptoms such as itching, burning, pelvic pain, abnormal vaginal bleeding, or pain during sex.[2][3]
References[edit]
- ^ a b c Beckmann, R.B. (2014). Obstetrics and Gynecology (7th ed.). Baltimore, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 260. ISBN 9781451144314.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j "Vaginal discharge". nhs.uk. 18 October 2017. Archived from the original on 23 September 2020. Retrieved 24 September 2020.
- ^ a b c d "Vaginal Discharge - Women's Health Issues". Merck Manuals Consumer Version. Archived from the original on 24 December 2020. Retrieved 24 September 2020.
- ^ a b c Hacker, Neville F. (2016). Hacker & Moore's Essentials of Obstetrics and Gynecology (6th ed.). Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier. p. 276. ISBN 9781455775583.
- ^ Richardson, Ania; Robinson, Angela J. (1 May 2022). "Vaginal discharge". Medicine. 50 (5): 254–258. doi:10.1016/j.mpmed.2022.02.002. ISSN 1357-3039.
- ^ Rice, Alexandra (2016). "Vaginal Discharge". Obstetrics, Gynaecology & Reproductive Medicine. 26 (11): 317–323. doi:10.1016/j.ogrm.2016.08.002.
