User:Mr. Ibrahem/Pulmonary valve stenosis
| Pulmonary valve stenosis | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Valvular pulmonary stenosis, pulmonic stenosis |
 | |
| Specialty | Cardiology |
| Symptoms | Few symptoms initially, may develop syncope, chest pain, and shortness of breath |
| Causes | Congenital heart disease, carcinoid syndrome[1] |
| Diagnostic method | Suspected based on a systolic murmur, confirmed by ultrasound of the heart[1] |
| Treatment | Balloon valvuloplasty, valve replacement[1] |
| Prognosis | Generally good[1] |
| Frequency | 0.4% at birth[2] |
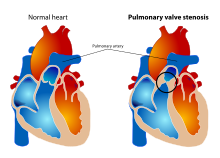
Pulmonary valve stenosis (PVS) is a type of heart valve disease in which there is narrowing of the pulmonary valve opening.[3] Affected children often have no symptoms.[1] When symptoms develop these may include syncope, chest pain, or shortness of breath.[1]
The most common cause is congenital heart disease such as tetralogy of Fallot and Noonan syndrome.[1] Other causes include carcinoid syndrome.[1] Diagnosis may be suspected based on a systolic murmur and confirmed by ultrasound of the heart.[1]
Treatment may may include balloon valvuloplasty and valve replacement.[1] Outcomes are generally good.[1] At birth it affected about 4 per 1,000 people.[2] Initial descriptions of the condition at birth date from 1761 by John Baptist Morgagni.[4] Surgical repair was first carried out in 1953.[4]
References[edit]
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k "Pulmonic Stenosis - Cardiovascular Disorders". Merck Manuals Professional Edition. Retrieved 23 December 2020.
- ^ a b Benjamin, Ivor; Griggs, Robert C.; Fitz, J. Gregory (2015). Andreoli and Carpenter's Cecil Essentials of Medicine E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 72. ISBN 978-0-323-35236-9.
- ^ "Congenital heart disease - Types". nhs.uk. 19 October 2017. Retrieved 24 December 2020.
- ^ a b Satpathy, M. (2015). Clinical Diagnosis of Congenital Heart Disease. JP Medical Ltd. p. 197. ISBN 978-93-5152-912-5.
