User:MSGJ/Ezcema
| MSGJ/Ezcema |
|---|
from ancient Greek ἔκζεμα ékzema,[1]
from ἐκζέ-ειν ekzé-ein,
from ἐκ ek "out" + ζέ-ειν zé-ein "to boil"
(OED)
Eczema is a form of dermatitis,[2] or inflammation of the epidermis (the outer layer of the skin).[3] In England, an estimated 5,773,700 or about one in every nine people have been diagnosed with the disease by a clinician at some point in their lives.[4]
Terminology[edit]
The term eczema is broadly applied to a range of persistent skin conditions. These include dryness and recurring skin rashes that are characterized by one or more of these symptoms: redness, skin edema (swelling), itching and dryness, crusting, flaking, blistering, cracking, oozing, or bleeding. Areas of temporary skin discoloration may appear and are sometimes due to healed injuries. Scratching open a healing lesion may result in scarring and may enlarge the rash.
Eczema may be confused with urticaria. In contrast to psoriasis, eczema is often likely to be found on the flexor aspect of joints.[citation needed]
In some languages, dermatitis and "eczema" are synonymous, while in other languages "dermatitis" implies an acute condition and "eczema" a chronic one.[5] The two conditions are often classified together.
Classification[edit]
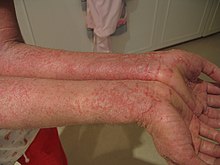
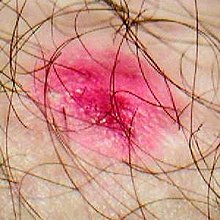
The term eczema refers to a set of clinical characteristics. Classification of the underlying diseases has been haphazard and unsystematic, with many synonyms used to describe the same condition. A type of eczema may be described by location (e.g., hand eczema), by specific appearance (eczema craquele or discoid), or by possible cause (varicose eczema). Further adding to the confusion, many sources use the term eczema for the most common type of eczema (atopic dermatitis) interchangeably.
The European Academy of Allergology and Clinical Immunology (EAACI) published a position paper in 2001 which simplifies the nomenclature of allergy-related diseases including atopic and allergic contact eczemas.[6] Non-allergic eczemas are not affected by this proposal.
The classification below is ordered by incidence frequency.
Common[edit]
- Atopic eczema (aka infantile e., flexural e., atopic dermatitis) is an allergic disease believed to have a hereditary component and often runs in families whose members also have asthma. Itchy rash is particularly noticeable on head and scalp, neck, inside of elbows, behind knees, and buttocks. Experts are urging doctors to be more vigilant in weeding out cases that are, in actuality, irritant contact dermatitis. It is very common in developed countries, and rising. (L20)
- Contact dermatitis is of two types: allergic (resulting from a delayed reaction to some allergen, such as poison ivy or nickel), and irritant (resulting from direct reaction to a detergent, such as sodium lauryl sulfate, for example). Some substances act both as allergen and irritant (wet cement, for example). Other substances cause a problem after sunlight exposure, bringing on phototoxic dermatitis. About three quarters of cases of contact eczema are of the irritant type, which is the most common occupational skin disease. Contact eczema is curable, provided the offending substance can be avoided and its traces removed from one’s environment. (L23; L24; L56.1; L56.0)
- Xerotic eczema (aka asteatotic e., e. craquele or craquelatum, winter itch, pruritus hiemalis) is dry skin that becomes so serious it turns into eczema. It worsens in dry winter weather, and limbs and trunk are most often affected. The itchy, tender skin resembles a dry, cracked, river bed. This disorder is very common among the older population. Ichthyosis is a related disorder. (L30.8A; L85.0)
- Seborrhoeic dermatitis or Seborrheic dermatitis ("cradle cap" in infants) is a condition sometimes classified as a form of eczema that is closely related to dandruff. It causes dry or greasy peeling of the scalp, eyebrows, and face, and sometimes trunk. The condition is harmless except in severe cases of cradle cap. In newborns it causes a thick, yellow crusty scalp rash called cradle cap, which seems related to lack of biotin and is often curable. (L21; L21.0)
Less common[edit]
- Dyshidrosis (aka dyshidrotic e., pompholyx, vesicular palmoplantar dermatitis, housewife’s eczema) only occurs on palms, soles, and sides of fingers and toes. Tiny opaque bumps called vesicles, thickening, and cracks are accompanied by itching, which gets worse at night. A common type of hand eczema, it worsens in warm weather. (L30.1)
- Discoid eczema (aka nummular e., exudative e., microbial e.) is characterized by round spots of oozing or dry rash, with clear boundaries, often on lower legs. It is usually worse in winter. Cause is unknown, and the condition tends to come and go. (L30.0)
- Venous eczema (aka gravitational e., stasis dermatitis, varicose e.) occurs in people with impaired circulation, varicose veins and edema, and is particularly common in the ankle area of people over 50. There is redness, scaling, darkening of the skin and itching. The disorder predisposes to leg ulcers. (I83.1)
- Dermatitis herpetiformis (aka Duhring’s Disease) causes intensely itchy and typically symmetrical rash on arms, thighs, knees, and back. It is directly related to celiac disease, can often be put into remission with appropriate diet, and tends to get worse at night. (L13.0)
- Neurodermatitis (aka lichen simplex chronicus, localized scratch dermatitis) is an itchy area of thickened, pigmented eczema patch that results from habitual rubbing and scratching. Usually there is only one spot. Often curable through behavior modification and anti-inflammatory medication. Prurigo nodularis is a related disorder showing multiple lumps. (L28.0; L28.1)
- Autoeczematization (aka id reaction, autosensitization) is an eczematous reaction to an infection with parasites, fungi, bacteria or viruses. It is completely curable with the clearance of the original infection that caused it. The appearance varies depending on the cause. It always occurs some distance away from the original infection. (L30.2)
- There are also eczemas overlaid by viral infections (e. herpeticum, e. vaccinatum), and eczemas resulting from underlying disease (e.g. lymphoma). Eczemas originating from ingestion of medications, foods, and chemicals, have not yet been clearly systematized. Other rare eczematous disorders exist in addition to those listed here.
Cause[edit]
The hygiene hypothesis postulates that the cause of asthma, eczema and other allergic diseases, is an unusually clean environment. It is supported by epidemiologic studies for asthma.[7] The hypothesis is that exposure to bacteria and other immune system modulators is important during development, and missing out on this exposure increases risk for asthma and allergy.
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis of eczema is based mostly on history and physical examination. However, in uncertain cases, skin biopsy may be useful.
Prevention[edit]
Those with a family history of eczema are advised not to accept the smallpox vaccination, or anything else that contains live vaccinia virus due to risk of developing eczema vaccinatum, a potentially severe and sometimes fatal complication.[8]
Treatment[edit]
There is no known cure for eczema; therefore, treatments aim to control the symptoms by reducing inflammation and relieving itching.
Medications[edit]
Corticosteroids[edit]
Dermatitis is often treated with corticosteroids. They do not cure eczema, but are highly effective in controlling or suppressing symptoms in most cases.[9] For mild-moderate eczema a weak steroid may be used (e.g. hydrocortisone or desonide), while more severe cases require a higher-potency steroid (e.g. clobetasol propionate, fluocinonide). Medium-potency corticosteroids such as clobetasone butyrate (Eumovate), Betamethasone Valerate (Betnovate) or triamcinolone are also available. Generally medical practitioners will prescribe the less potent ones first before trying the more potent ones. In many countries, weak steroids can be purchased 'over the counter' (e.g., hydrocortisone in UK, United States, Germany, Czech Republic, Australia, Norway, Iceland), while the more potent ones require a prescription.
Side effects[edit]
Prolonged use of topical corticosteroids is thought to increase the risk of possible side effects, the most common of which is the skin becoming thin and fragile (atrophy).[10] Because of this, if used on the face or other delicate skin, only a low-strength steroid should be used. Additionally, high-strength steroids used over large areas, or under occlusion, may be significantly absorbed into the body, causing hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis suppression (HPA axis suppression).[11] Finally by their immunosuppressive action they can, if used without antibiotics or antifungal drugs, lead to some skin infections (fungal or bacterial). Care must be taken to avoid the eyes, as topical corticosteroids applied to the eye can cause glaucoma [12] or cataracts.
Because of the risks associated with this type of drug, a steroid of an appropriate strength should be sparingly applied only to control an episode of eczema. Once the desired response has been achieved, it should be discontinued and replaced with emollients as maintenance therapy. Corticosteroids are generally considered safe to use in the short- to medium-term for controlling eczema, with no significant side effects differing from treatment with non-steroidal ointment.[13]
However, recent research has shown that topically applied corticosteroids did not significantly increase the risk of skin thinning, stretch marks or HPA axis suppression (and where such suppression did occur, it was mild and reversible where the corticosteroids were used for limited periods of time). Further, skin conditions are often under-treated because of fears of side effects. This has led some researchers to suggest that the usual dosage instructions should be changed from "Use sparingly" to "Apply enough to cover affected areas," and that specific dosage directions using "fingertip units" or FTU's be provided, along with photos to illustrate FTU's.[14]
Other forms[edit]
In severe cases, oral cortisosteroids such as prednisolone or injections such as triamcinolone injections may also be prescribed. While these usually bring about rapid improvements, they should not be taken for any length of time and the eczema often returns to its previous level of severity once the medication is stopped. In the case of triamcinolone injections, a waiting period between treatments may be required.
Skin barrier emulsions[edit]
In a clinical study led by Jeffrey L. Sugarman of the Department of Dermatology at the University of California in San Francisco and Lawrence Charles Parish of the Department of Dermatology and Cutaneous Biology at the Jefferson Medical College of Thomas Jefferson University in Philadelphia, skin barrier emulsion Epiceram was shown to have comparable efficacy to a mid-potent steroid in a clinical study after 28 days of treatment, reducing disease severity, improvement in pruritus and improving sleep habits.[15]
Immunomodulators[edit]

Topical immunomodulators like pimecrolimus (Elidel and Douglan) and tacrolimus (Protopic) were developed after corticosteroid treatments, effectively suppressing the immune system in the affected area, and appear to yield better results in some populations. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has issued a public health advisory about the possible risk of lymph node or skin cancer from use of these products,[16] but many professional medical organizations disagree with the FDA's findings;
- The postulation is that the immune system may help remove some pre-cancerous abnormal cells which is prevented by these drugs. However, any chronic inflammatory condition such as eczema, by the very nature of increased metabolism and cell replication, has a tiny associated risk of cancer (see Bowen's disease).
- Current practice by UK dermatologists is not to consider this a significant real concern and they are increasingly recommending the use of these new drugs.[17] The dramatic improvement on the condition can significantly improve the quality of life of sufferers (and families kept awake by the distress of affected children). The major debate, in the UK, has been about the cost of such newer treatments and, given only finite NHS resources, when they are most appropriate to use.[18]
- In addition to cancer risk, there are other potential side effects with this class of drugs. Adverse reactions including severe flushing,headaches, flu-like syndrome, photosensitive reactivity and possible drug interactions with a variety of medications, alcohol and grapefruit.[19][20]
Antibiotics[edit]
When the normal protective barrier of the skin is disrupted (dry and cracked), it allows easy entry for bacteria. Scratching by the patient both introduces infection and spreads it from one area to another. Any skin infection further irritates the skin and a rapid deterioration in the condition may ensue; the appropriate antibiotic should be given.
Immunosuppressants[edit]
When eczema is severe and does not respond to other forms of treatment, immunosuppressant drugs are sometimes prescribed. These dampen the immune system and can result in dramatic improvements to the patient's eczema. However, immunosuppressants can cause side effects on the body. As such, patients must undergo regular blood tests and be closely monitored by a doctor. In the UK, the most commonly used immunosuppressants for eczema are ciclosporin, azathioprine and methotrexate. These drugs were generally designed for other medical conditions but have been found to be effective against eczema.
Itch relief[edit]
Anti-itch drugs, often antihistamine, may reduce the itch during a flare up of eczema, and the reduced scratching in turn reduces damage and irritation to the skin (the itch cycle).[citation needed] However, in eczema, the itch relief is often due to the sedative side effects of these drugs, rather than their specific antihistamine effect. Hence, sedating antihistamines such as promethazine (Phenergan) or diphenhydramine (Benadryl) are more effective at relieving itch than the newer, nonsedating antihistamines.[citation needed]
Capsaicin applied to the skin acts as a counter irritant (see gate control theory of nerve signal transmission).
Hydrocortisone applied to the skin aids in temporary itch relief.
Temporary yet significant and fast-acting relief can be found by cooling the skin via water (swimming, cool water bath or wet washcloth), air (direct output of an air conditioning vent), or careful use of an ice pack (can substitute bags of frozen vegetables).
Moisturizers[edit]
Eczema can be exacerbated by dryness of the skin. Moisturizing is one of the most important self-care treatments for sufferers of eczema. Keeping the affected area moistened can promote skin healing and relief of symptoms.
Soaps and harsh detergents should not be used on affected skin because they can strip natural skin oils and lead to excessive dryness. Instead, the use of moisturizing body wash, or an emollient like aqueous cream, will maintain natural skin oils and may reduce some of the need to moisturize the skin. Another option is to try bathing using colloidal oatmeal bath treatments. In addition to avoiding soap, other products that may dry the skin such as powders or perfume should also be avoided. Even water can cause a severe reddening of the skin and cause irritation.
Moistening agents are called 'emollients'. In general, it is best to match thicker ointments to the driest, flakiest skin. Light emollients like aqueous cream may not have any effect on severely dry skin. Some common emollients for the relief of eczema include Oilatum, Balneum, Medi Oil, Diprobase, bath oils and aqueous cream. Sebexol, Epaderm ointment, Exederm and Eucerin lotion or cream may also be helpful with itching. Lotions or creams may be applied directly to the skin after bathing to lock in moisture. Moisturizing gloves (gloves which keep emollients in contact with skin on the hands) can be worn while sleeping. Generally, twice-daily applications of emollients work best. While creams are easy to apply, they are quickly absorbed into the skin, and therefore need frequent reapplication. Ointments, with less water content, stay on the skin for longer and need fewer applications, but they can be greasy and inconvenient. Steroids may also be mixed in with ointments.
For unbroken skin, direct application of waterproof tape with or without an emollient or prescription ointment can improve moisture levels and skin integrity which allows the skin to heal. This treatment regimen can also help prevent the skin from cracking, as well as put a stop to the itch cycle. The end result is reduced lichenification (the roughening of skin from repeated scratching). Taping works best on skin away from joints.
There is a disagreement whether baths are desirable or a necessary evil. For example, the Mayo Clinic advises against daily baths to avoid skin drying.[21] On the other hand, the American Academy of Dermatology claims "it is a common misconception that bathing dries the skin and should be kept to a bare minimum" and recommends bathing to hydrate skin. They even suggest up to 3 short baths a day for people with severe eczema. According to them, a moisturizer should be applied within 3 minutes to trap the moisture from bath in the skin.[22] U.S. National Eczema Association and the Eczema Society of Canada make similar recommendations.[23] [24]
Regardless of more or less frequent bathing, the hardness of the bathing water is a major factor. Soft water can have therapeutic effects for people with eczema currently using hard water. An ion exchange water softener can be installed (plumbing required) to reduce the hardness of the water supply.[25] [26]
Recently, ceramides, which are the major lipid constituent of the stratum corneum, have been used in the treatment of eczema.[27][28][29] They are often one of the ingredients of modern moisturizers. These lipids were also successfully produced synthetically in the laboratory.[30]
However, detergents are so ubiquitous in modern environments in items like tissues, and so persistent on surfaces, "safe" soaps are necessary to remove them from the skin in order to control eczema. Although most eczema recommendations use the terms "detergents" and "soaps" interchangeably, and tell eczema sufferers to avoid both, detergents and soaps are not the same and are not equally problematic to eczema sufferers. Detergents, often made from petrochemicals, increase the permeability of skin membranes in a way that soaps and water alone do not. Sodium lauryl sulfate, the most common household detergent, has been shown to amplify the allergenicity of other substances ("increase antigen penetration").[31]
Unfortunately there is no one agreed-upon best kind of skin cleanser for eczema sufferers. Different clinical tests, sponsored by different personal product companies, unsurprisingly tout various brands as the most skin-friendly based on specific properties of various products and different underlying assumptions as to what really determines skin friendliness. The terms "hypoallergenic" and "doctor tested" are not regulated,[32] and no research has been done showing that products labeled "hypoallergenic" are in fact less problematic than any others. It may be best to avoid soaps and detergent cleansers altogether, except for the armpits, groin and perianal areas, and use cheap bland emolients in the bath or shower, for example aqueous cream.
Lifestyle[edit]
While it has been suggested that eczema may sometimes be an allergic reaction to the excrement from house dust mites,[33] with up to 5% of people showing antibodies to the mites,[34] the overall role this plays awaits further corroboration.[35]
Various measures may reduce the amount of mite antigens, in particular swapping carpets for hard surfaces.[36] Effectiveness of vacuum cleaners is dependent upon the characteristics of the carpet pile,[37] but in other studies daily vacuuming did not affect levels of mites.[38] However it is not clear whether such measures actually help patients with eczema. A controlled study suggested that a number of environmental factors such as air exchange rates, relative humidity and room temperature (but not the level of house dust mites) might have an effect on the condition.[39]
Staphylococcus aureus colonies are developed by overly scratching eczema. In a 2009 study from Northwestern University, children with moderate or severe eczema were given diluted bleach baths and this reduced the severity of the disease.[40] Diluted bleach has been known to have antibacterial qualities. In the study, diluted meant a half cup of bleach to a full tub of water and a bath meant soaking for 5–10 minutes. Antibacterial bath oils containing agents such as triclosan or benzalkonium chloride are available to both moisturise the skin and suppress Staphylococcus aureus. Brand names include Oilatum Plus and QV Flareup Oil.
Light therapy[edit]
Light therapy (or deep penetrating light therapy) using ultraviolet light can help control eczema.[41] UVA is mostly used, but UVB and Narrow Band UVB are also used. Overexposure to ultraviolet light carries its own risks, particularly potential skin cancer from exposure.[42]
When light therapy alone is found to be ineffective, the treatment is performed with the application (or ingestion) of a substance called psoralen. This PUVA (Psoralen + UVA) combination therapy is termed photo-chemotherapy. Psoralens make the skin more sensitive to UV light, thus allowing lower doses of UVA to be used. However, the increased sensitivity to UV light also puts the patient at greater risk for skin cancer.[43]
Diet[edit]
Recent studies provide hints that food allergy may trigger atopic dermatitis. For these people, identifying the allergens could lead to an avoidance diet to help minimize symptoms, although this approach is still in an experimental stage.[44] Dietary elements that have been reported to trigger eczema include dairy products, coffee (both caffeinated and decaffeinated), soybean products, eggs, nuts, wheat and maize (sweet corn), though food allergies may vary from person to person.[citation needed] However, in 2009, researchers at National Jewish Medical and Research Center found that eczema patients were especially prone to misdiagnosis of food allergies.[45][46]
A study led by researchers at the University of California, San Diego School of Medicine suggests that use of oral vitamin D3 supplements bolsters production of a protective chemical normally found in the skin, and may help prevent skin infections that are a common result of atopic dermatitis, the most common form of eczema.[47] It can be noted that the production of vitamin D3 is catalyzed by UV radiation and may influence histocompatibility expression, correlating with both the seasonality of eczema and its relation to the immune system.
Margitta Worm et al. discovered that a diet rich in omega-3 (and low in omega-6) polyunsaturated fatty acids may be able to reduce symptoms.[48]
Alternative therapies[edit]
Non-conventional medical approaches include traditional Chinese medicine and Western herbalism. There are a wide variety of treatments, each of which may vary from individual to individual as to efficacy or harm. Patients should inform their doctor/allergist/dermatologist if they are pursuing one of these treatment routes.
Alleged remedies include:
- Oatmeal is a common remedy to relieve itching, and can be applied topically as a cream or, as a colloid, in the bath. It is also part of many commercially available products intended for eczema treatment and for other skin conditions. But some recent studies say that oat can provoke a flare-up on some patients.[citation needed]
- Sea water: According to the British Association of Dermatologists, there is considerable anecdotal evidence that salt water baths may help some children with atopic eczema.[49] One reason might be that seawater has antiseptic properties. The Dead sea is popular for alleviating skin problems including eczema. The benefit of this treatment must be weighed against the extreme discomfort and burning sensations suffered as the salt water contacts raw skin.
- Sulfur has been used for many years as a topical treatment in the alleviation of eczema, although this could be suppressive. It was fashionable in the Victorian and Edwardian eras. However, there is currently no scientific evidence for the claim that sulfur treatment relieves eczema.[50]
- Probiotics are live microorganisms taken orally, such as the Lactobacillus bacteria found in yogurt. They are not effective for treating eczema in older populations, but some research points to some strains of beneficial microorganisms having the ability to prevent the triad of allergies, eczema and asthma, although in rare cases they have a very small risk of infection in those with poor immune system response.[51][52]
- Traditional Chinese medicine: According to American Academy of Dermatology, while certain blends of Chinese herbal medicines have been proven effective in controlling eczema, they have also have proven toxic with severe consequences.[53] In Chinese Medicine diagnosis, eczema is often considered a manifestation of underlying ill health. Treatment aims to improve the overall health of the individual, therefore not only resolving the eczema but improving quality of life (energy level, digestion, disease resistance, etc.).[54] A recent study published in the British Journal of Dermatology describes improvements in quality of life and reduced need for topical corticosteroid application.[55] Another British trial with ten different plants traditionally used in Chinese medicine for eczema treatment suggest a benefit with herbal remedy, but reviewers noted that the blinding was not maintained, leaving the results invalid.[56]
- Other remedies lacking scientific evidence include chiropractic spinal manipulation.[57]
Patients can also wear clothing designed specifically to manage the itching, scratching and peeling associated with eczema.[58]
Behavioural approach[edit]
In the 1980s, Swedish dermatologist Peter Noren developed a behavioural approach to the treatment of long term atopic eczema. This approach has been further developed by dermatologist Richard Staughton and psychiatrist Christopher Bridgett at the Chelsea and Westminster Hospital in London.[59][60] Patients undergo a six-week monitored program involving scratch habit reversal and self awareness of scratching levels. For long term eczema sufferers, scratching can become habitual. Sometimes scratching becomes a reflex, resulting in scratching without conscious awareness, rather than from the feeling of itchiness itself. The habit reversal program is done in conjunction with the standard applied emollient/corticosteroid treatments so that the skin can heal. It also reduces future scratching, as well as reduces the likelihood of further flareups. The behavioural approach can give an eczema sufferer some control over the degree of severity of eczema.
Epidemiology[edit]
The lifetime clinician-recorded prevalence of eczema has been seen to peak in infancy, with female predominance of eczema presentations occurring during the reproductive period of 15–49 years.[61] Although little data on the trend of eczema prevalence over time exists prior to the Second World War (1939–45), the prevalence of eczema has been found to have increased substantially in the latter half of the 20th Century, with eczema in school-aged children being found to increase between the late 1940s and 2000.[62] A review of epidemiological data in the UK has also found an inexorable rise in the prevalence of eczema over time.[63] Further recent increases in the incidence and lifetime prevalence of eczema in England have also been reported, such that an estimated 5,773,700 or about one in every nine people have been diagnosed with the disease by a clinician at some point in their lives.[4]
Research[edit]
Other than direct treatments of the symptoms, no cure is presently known for most types of dermatitis; even cortisone treatments and immunomodulation may often have only minor effects on what may be a complex problem. As the condition is often related to family history of allergies (and thus heredity), it is probable that gene therapy or genetic engineering might help.
Damage from the enzymatic activity of allergens is usually prevented by the body's own protease inhibitors, such as, LEKTI, produced from the gene SPINK5. Mutations in this gene are known to cause Netherton’s syndrome, which is a congenital erythroderma. These patients nearly always develop atopic disease, including hay fever, food allergy, urticaria and asthma. Such evidence supports the hypothesis that skin damage from allergens may be the cause of eczema, and may provide a venue for further treatment.[64]
Another study identified a gene that the researchers believe to be the cause of inherited eczema and some related disorders. The gene produces the protein filaggrin, the lack of which causes dry skin and impaired skin barrier function.[65]
A recent study indicated that two specific chemicals found in the blood are connected to the itching sensations associated with eczema. The chemicals are Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and Substance P.[66]
Eczema has increased dramatically in England as a study showed a 42% rise in diagnosis of the condition between 2001 and 2005, by which time it was estimated to affect 5.7 million adults and children. A paper in the Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine says Eczema is thought to be a trigger for other allergic conditions. GP records show over 9 million patients were used by researchers to assess how many people have the skin disorder.[67]
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^ Henry George Liddell, Robert Scott. "Ekzema". A Greek-English Lexicon. Tufts University: Perseus.
- ^ Eczema at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- ^ "eczema" at Dorland's Medical Dictionary
- ^ a b Simpson CR, Newton J, Hippisley-Cox J, Sheikh A (March 2009). "Trends in the epidemiology and prescribing of medication for eczema in England". Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine. 102 (3): 108–17. doi:10.1258/jrsm.2009.080211. PMC 2746851. PMID 19297652.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: date and year (link) CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Johannes Ring; Bernhard Przybilla; Thomas Ruzicka (2006). Handbook of atopic eczema. Birkhäuser. p. 4. ISBN 9783540231332. Retrieved 4 May 2010.
- ^ Johansson SG, Hourihane JO, Bousquet J; et al. (September 2001). "A revised nomenclature for allergy. An EAACI position statement from the EAACI nomenclature task force". Allergy. 56 (9): 813–24. doi:10.1034/j.1398-9995.2001.t01-1-00001.x. PMID 11551246.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help)CS1 maint: date and year (link) CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Bufford, Jeremy D.; Gern, James E. (2005). "The hygiene hypothesis revisited". Immunology and Allergy Clinics of North America. 25 (2): 247–262. doi:10.1016/j.iac.2005.03.005. PMID 15878454.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: date and year (link) - ^ "CDC Smallpox | Smallpox (Vaccinia) Vaccine Contraindications (Info for Clinicians)". Emergency.cdc.gov. 2007-02-07. Retrieved 2010-02-07.
- ^ Hoare C, Li Wan Po A, Williams H (2000). "Systematic review of treatments for atopic eczema". Health Technology Assessment. 4 (37): 1–191. doi:10.3310/hta4370. PMC 4782813. PMID 11134919.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Atherton DJ (October 2003). "Topical corticosteroids in atopic dermatitis". BMJ. 327 (7421): 942–3. doi:10.1136/bmj.327.7421.942. PMC 259155. PMID 14576221.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: date and year (link) - ^ Lee NP, Arriola ER (1999). "Topical corticosteroids: back to basics". The Western Journal of Medicine. 171 (5–6): 351–3. PMC 1308757. PMID 10639873.
- ^ "neomycin and polymyxin b sulfates and bacitracin zinc with hydrocortisone acetate (Neomycin sulfate and Polymyxin B Sulfate, Bacitracin zinc and Hydrocortisone Acetate) ointment -- Warnings". U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
- ^ Van Der Meer JB, Glazenburg EJ, Mulder PG, Eggink HF, Coenraads PJ (June 1999). "The management of moderate to severe atopic dermatitis in adults with topical fluticasone propionate. The Netherlands Adult Atopic DermatitisStudy Group". British Journal of Dermatology. 140 (6): 1114–21. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2133.1999.02893.x. PMID 10354080.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: date and year (link) CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Bewley A; Dermatology Working, Group (May 2008). "Expert consensus: time for a change in the way we advise our patients to use topical corticosteroids". The British Journal of Dermatology. 158 (5): 917–20. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2008.08479.x. PMID 18294314.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: date and year (link) - ^ Sugarman, Jeffrey L. (2009). "Efficacy of a lipid-based barrier repair formulation in moderate-to-severe pediatric atopic dermatitis". Journal of Drugs in Dermatology.
- ^ "FDA Issues Public Health Advisory Informing Health Care Providers of Safety Concerns Associated with the Use of Two Eczema Drugs, Elidel and Protopic". FDA. March 10, 2005. Archived from the original on 2007-09-17. Retrieved 2007-10-16.
- ^ N H Cox and Catherine H Smith (December 2002). "Advice to dermatologists re topical tacrolimus" (DOC). Therapy Guidelines Committee. British Association of Dermatologists.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: date and year (link) - ^ "Pimecrolimus cream for atopic dermatitis". Drug and Therapeutics Bulletin. 41 (5): 33–6. May 2003. doi:10.1136/dtb.2003.41533. PMID 12789846.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: date and year (link) - ^ http://www.astellas.us/docs/protopic.pdf
- ^ Martins, Gladys Aires; Arruda, Lucia (2004). "Tratamento sistêmico da psoríase - Parte I: metotrexato e acitretina". Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia. 79 (3): 263–278. doi:10.1590/S0365-05962004000300002.
- ^
"Atopic dermatitis (eczema) - Prevention at [[Mayoclinic]]'s website". Retrieved 2008-05-07.
{{cite web}}: URL–wikilink conflict (help) - ^
"Daily Skin Care Essential to Control Atopic Dermatitis article at [[American Academy of Dermatology]]'s EczemaNet website". Retrieved 2009-03-24.
{{cite web}}: URL–wikilink conflict (help) - ^ "Bathing and Moisturizing at National Eczema Association's EASE website". Retrieved 2008-05-07.
- ^ "Treating Eczema at The Eczema Society of Canada's website". Retrieved 2008-05-07.
- ^ "Water softener eczema relief hope". BBC News. 2009-01-11. Retrieved 2009-12-19.
- ^ "Softened Water Eczema Trial, A clinical trial to see if water softeners help children with eczema". Retrieved 2009-12-19.
- ^ Coderch L, López O, de la Maza A, Parra JL (2003). "Ceramides and skin function". American Journal of Clinical Dermatology. 4 (2): 107–29. doi:10.2165/00128071-200304020-00004. PMID 12553851.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Bouwstra JA, Ponec M (2006). "The skin barrier in healthy and diseased state". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes. 1758 (12): 2080–95. doi:10.1016/j.bbamem.2006.06.021. PMID 16945325.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: date and year (link) - ^ Choi MJ, Maibach HI (2005). "Role of ceramides in barrier function of healthy and diseased skin". American Journal of Clinical Dermatology. 6 (4): 215–23. doi:10.2165/00128071-200506040-00002. PMID 16060709.
- ^ "New Skin-healing Chemicals". Science Daily. August 30, 2007. Retrieved 2007-10-06.
- ^ Corazza M, Virgili A (May 2005). "Allergic contact dermatitis from ophthalmic products: can pre-treatment with sodium lauryl sulfate increase patch test sensitivity?". Contact Dermatitis. 52 (5): 239–41. doi:10.1111/j.0105-1873.2005.00606.x. PMID 15898995.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: date and year (link) - ^ Murphy LA, White IR, Rastogi SC (May 2004). "Is hypoallergenic a credible term?". Clinical and Experimental Dermatology. 29 (3): 325–7. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2230.2004.01521.x. PMID 15115531.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: date and year (link) CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Carswell F, Thompson S (1986). "Does natural sensitisation in eczema occur through the skin?". Lancet. 2 (8497): 13–5. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(86)92560-2. PMID 2873316.
- ^ Henszel Ł, Kuźna-Grygiel W (2006). "[House dust mites in the etiology of allergic diseases]". Annales Academiae Medicae Stetinensis (in Polish). 52 (2): 123–7. PMID 17633128.
- ^ Atopic Dermatitis at eMedicine
- ^ Mihrshahi S, Marks G, Vanlaar C, Tovey E, Peat J (2002). "Predictors of high house dust mite allergen concentrations in residential homes in Sydney". Allergy. 57 (2): 137–42. doi:10.1034/j.1398-9995.2002.5720999.x. PMID 11929416.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Causer SM, Lewis RD, Batek JM, Ong KH (April 2004). "Influence of wear, pile height, and cleaning method on removal of mite allergen from carpet". Journal of Occupational and Environmental Hygiene. 1 (4): 237–42. doi:10.1080/15459620490432169. PMID 15204862.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: date and year (link) CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Wassenaar DP (February 1988). "Effectiveness of vacuum cleaning and wet cleaning in reducing house-dust mites, fungi and mite allergen in a cotton carpet: a case study". Experimental & Applied Acarology. 4 (1): 53–62. doi:10.1007/BF01213841. PMID 3378462.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: date and year (link) - ^ Beck HI, Bjerring P, Harving H (1989). "Atopic dermatitis and the indoor climate. The effect from preventive measures". Acta Dermato-venereologica. 69 (2): 162–5. PMID 2564236.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Berman, Jillian (2009-06-29). "Bath in diluted bleach relieves kids' eczema". Usatoday.Com. Retrieved 2010-02-07.
- ^ Polderman MC, Wintzen M, le Cessie S, Pavel S (2005). "UVA-1 cold light therapy in the treatment of atopic dermatitis: 61 patients treated in the Leiden University Medical Center". Photodermatology, Photoimmunology & Photomedicine. 21 (2): 93–6. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0781.2005.00150.x. PMID 15752127.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Stöppler MC (31 May 2007). "Psoriasis PUVA Treatment Can Increase Melanoma Risk". MedicineNet. Retrieved 2007-10-17.
- ^ Stern RS; Puva Follow Up, Study (May 2001). "The risk of melanoma in association with long-term exposure to PUVA". Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. 44 (5): 755–61. doi:10.1067/mjd.2001.114576. PMID 11312420.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: date and year (link) - ^ Kanny G (January 2005). "[Atopic dermatitis in children and food allergy: combination or causality? Should avoidance diets be initiated?]". Annales de Dermatologie et de Vénéréologie (in French). 132 (Spec No 1): 1S90–103. PMID 15984300.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: date and year (link) - ^ "Food allergies commonly misdiagnosed, especially among eczema patients" (Press release). National Jewish Medical and Research Center. 16 March 2009. Retrieved 2009-03-20.
- ^ Atkins D (March 2008). "Food allergy: diagnosis and management". Primary Care. 35 (1): 119–40, vii. doi:10.1016/j.pop.2007.09.003. PMID 18206721.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: date and year (link) - ^ "Oral Vitamin D May Help Prevent Some Skin Infections". University of California, San Diego. October 6, 2008. Retrieved 2010-11-29.
- ^ Fleming Nic (March 27, 2008). "Omega-3 can help eczema". London: The Daily Telegraph. Retrieved 2009-04-28., citing Koch C, Dölle S, Metzger M; et al. (April 2008). "Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) supplementation in atopic eczema: a randomized, double-blind, controlled trial". The British Journal of Dermatology. 158 (4): 786–92. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2007.08430.x. PMID 18241260.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help)CS1 maint: date and year (link) CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Atopic Eczema - British Association of Dermatologists". Archived from the original on 2008-08-02.
- ^ "Sulfur". University of Maryland Medical Center. 4/1/2002. Retrieved 2007-10-15.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Boyle RJ, Bath-Hextall FJ, Leonardi-Bee J, Murrell DF, Tang ML (2008). "Probiotics for treating eczema". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (Online) (4): CD006135. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD006135.pub2. PMID 18843705.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Flohr C, Pascoe D, Williams HC (February 2005). "Atopic dermatitis and the 'hygiene hypothesis': too clean to be true?". The British Journal of Dermatology. 152 (2): 202–16. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2004.06436.x. PMID 15727630.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: date and year (link) CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Complementary Therapies". American Academy of Dermatology. Retrieved 2008-08-01.
- ^ http://www.acupuncturetoday.com/archives2005/mar/03glick.html [dubious ]
- ^ "Chinese medicine 'eases eczema'". BBC News. 13 March 2008.
- ^ Armstrong NC, Ernst E (August 1999). "The treatment of eczema with Chinese herbs: a systematic review of randomized clinical trials". British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 48 (2): 262–4. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2125.1999.00004.x. PMC 2014284. PMID 10417508.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: date and year (link) - ^ Eldred DC, Tuchin PJ (November 1999). "Treatment of acute atopic eczema by chiropractic care. A case study". Australasian Chiropractic & Osteopathy. 8 (3): 96–101. PMC 2051093. PMID 17987197.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: date and year (link) - ^ Ricci G, Patrizi A, Bellini F, Medri M (2006). "Use of textiles in atopic dermatitis: care of atopic dermatitis". Current Problems in Dermatology. 33: 127–43. doi:10.1159/000093940. PMID 16766885.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Bridgett, C. (2000). "Psychodermatology and Atopic Skin Disease in London 1989–1999 – Helping Patients to Help Themselves". Dermatology and Psychosomatics / Dermatologie und Psychosomatik. 1 (4): 183. doi:10.1159/000057975.
- ^ Bridgett C (2004). "Psychocutaneous medicine". Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology. 3 (2): 116. doi:10.1111/j.1473-2130.2004.00047.x. PMID 17147570.
- ^ Osman M, Hansell AL, Simpson CR, Hollowell J, Helms PJ (February 2007). "Gender-specific presentations for asthma, allergic rhinitis and eczema in primary care". Primary Care Respiratory Journal. 16 (1): 28–35. doi:10.3132/pcrj.2007.00006. PMC 6634172. PMID 17297524.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: date and year (link) CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Taylor B, Wadsworth J, Wadsworth M, Peckham C (December 1984). "Changes in the reported prevalence of childhood eczema since the 1939-45 war". Lancet. 2 (8414): 1255–7. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(84)92805-8. PMID 6150286.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: date and year (link) CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Gupta R, Sheikh A, Strachan DP, Anderson HR (April 2004). "Burden of allergic disease in the UK: secondary analyses of national databases". Clinical and Experimental Allergy. 34 (4): 520–6. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2222.2004.1935.x. PMID 15080802.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: date and year (link) CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Walley AJ, Chavanas S, Moffatt MF; et al. (2001). "Gene polymorphism in Netherton and common atopic disease". Nat. Genet. 29 (2): 175–8. doi:10.1038/ng728. PMID 11544479.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Palmer CN; et al. (2006). "Common loss-of-function variants of the epidermal barrier protein filaggrin are a major predisposing factor for atopic dermatitis". Nature Genetics. 38 (4): 441–6. doi:10.1038/ng1767. PMID 16550169.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help) - ^ "'Blood chemicals link' to eczema -- Scientists have identified two blood chemicals linked to itchy eczema, offering new treatment possibilities". BBC News. 26 August 2007. Retrieved 2007-10-16.
- ^ Wilkinson Emma (23 March 2009). "Eczema cases rise dramatically". BBC News.
External links[edit]
- MedlinePlus: Dermatitis
- Mayo Clinic: Dermatitis and Eczema - Overview, Treatment, Causes, Prevention, Self-Care
- National Eczema Society (UK)
- National Eczema Association (US)
- Eczema Zones Online resource for people with eczema from Schering-Plough (UK)
