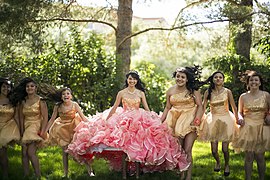User:Bstrait/sandbox
 | This is a user sandbox of Bstrait. You can use it for testing or practicing edits. This is not the sandbox where you should draft your assigned article for a dashboard.wikiedu.org course. To find the right sandbox for your assignment, visit your Dashboard course page and follow the Sandbox Draft link for your assigned article in the My Articles section. |
Intro[edit]
A ball gown or ballgown is a type of evening gown worn to a ball or a formal event. Most versions are cut off the shoulder with a low décolletage, exposed arms, and long bouffant styled skirts.[6] Such gowns are typically worn with a stole (a formal shawl in expensive fabric), cape or cloak in lieu of a coat, "good" (couture or vintage) jewelry and opera-length gloves. Where "state decorations" are to be worn, they are on a bow pinned to the chest, and married women wear a tiara if they have one. Although artificial fabrics are now sometimes used, the most common fabrics are satin, silk, taffeta and velvet with trimmings of lace, pearls, sequins, embroidery, ruffles, ribbons, rosettes and ruching.[6]
Events[edit]
The first forms of the 21rst century term “Debutante ball” or “Cotillion” emerged in the mid 19th century with what was called a “coming out ball”. These events were meant to show off the women who were now of marriageable age. Traditionally the debutantes will wear all white, but with varying styles of dress.[5] While the style of dress can vary, strapless and sleeveless variations are popular and are typically worn with long white gloves and can be accessorized with bouquets, and sometimes a fan. For most of the 19th century, a headdress with veiling was a popular style as well as a full train attached at the waist and in later years it would attach to the shoulders.
The traditional ideals of the debutante ball vary based on location in the USA. The debutantes in New Orleans could be seen wearing jeweled crowns and dresses with Medici collars with elongated trains. Texas has variations within its various regions. In Laredo, middle class debutantes wear beaded suede garments. In San Antonio, the dresses are of elaborate colors and covered in beads of different designs. The beads add extensive weight having some dresses weigh in at about 75 lbs.[5] Another coming of age event is the Quinceanera, an event in Latin American cultures when a girl turns 15. Their gowns are often very brightly colored and resemble traditional ball gowns with very full ruffled or ruched skirts.[5]
First Lady's Collection[edit]
In 1912, Hellen Taft along with collection founders Cassie Mason Myers Julian-James, Rose Gouverneur Hoes, and the Smithsonian Institution started the “First Ladies Collection.” It is customary for the first lady of a new president to donate the dress she wears to the inauguration ball but it is not required. Every first lady is represented in the collection although they are not all inaugural dresses. [7] Mrs. Taft started this tradition when she donated her dress that she wore during President Taft’s inauguration. Typically the dresses were added to the collection after the first lady had left office but in 1955 the publics uproar to see Mamie Eisenhower’s inaugural dress was so strong that the Smithsonian changed their policy and added her dress immediately, not waiting until she left office.[7]
History[edit]
1850s[edit]

In previous years, the same type of dress might have been called an evening dress, having very similar features; low-cut neckline, a tight bodice, a large skirt and sometimes-bare arms.[8] The ball gown at this time had similar features, a full skirt supported by a petticoat, a tight waist achieved by a corset or bodice with a stay to keep the subject upright and with perfect posture, off the shoulder style and with bare arms.[9]
In the coming years, the introduction of the sewing machine changed the dress market. Middle class people could now produce their own dresses and with more quality and efficiency than before when they were made by hand. Upper class members of society might still have had their dresses made by a designer but with the turn around time decreased.[9] Around this time was also the introduction of chemical dyes.[9] This dramatically changed the range of colors that dresses could be produced in. This time was encompassed within the Romantic period, which coincided with the Victorian era. During this time the crinoline was introduced as well as demure sleeves, which puffed up around the arm.[9]
1860-1864[edit]
Skirts had developed an overall bell shape but with extra fullness at the back.[9]

1865-1867[edit]

Skirts lost their front shape and were altered to lay more flat against the body while the sides and back gained fullness with pleating techniques. Often times a long train was attached to the back of the skirt.[9]

1868-1878[edit]
For the next 10 years the fullness in the back of the skirts increased further with the use of the bustle.[9]


1878-1884[edit]
The bustle went out of style because it was not needed anymore for the fullness in the back of the dress. The material instead was gathered and fell down the back which ended with a long train.[9]
1890-1900[edit]
The hourglass shape emerged which was known for a narrow waist. It was achieved by having a cone-shaped skirt that was narrow at the waist and gained fullness near the bottom.[9]

1950s[edit]
Previously, Ball gowns were worn for private events and parties, but as we move into the mid-20th century, private events turned into public ones. As the century progressed, traditional events become less important while ones like charity events took its place. In 21st century culture, galas and red carpet events are showcases for extravagant gowns to be in the public eye. In Britain, when Elizabeth II terminated formal court events in 1957, the more public events, like a charity ball, arose in popularity because it was open to anyone who could afford to buy a ticket.[3]
Designer dresses were typically part of a designer’s collection, having it altered for the wearer. Designers need to know where the dress will be worn to avoid two people from matching.[3] But if the original wearer decides to wear the dress to another event afterwards, the possibility of matching is increased. In modern times, designers must understand that their pieces of work will be criticized and also praised as a result of the internet and paparazzi. — Preceding unsigned comment added by Bstrait (talk • contribs) 18:49, 12 November 2017 (UTC)
-
The gown on the far right is an accurate representation of one that would be worn in 1880.
-
"Hourglass" shape of 1900
- ^ Laver, James; De La Haye, Amy; Tucker, Andrew (2012). Costume and Fashion : a concise history.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help) - ^ Boucher, Francois; Deslandres, Yvonne (1987). 20,000 Years of Fashion: the history of fashion and personal adornment.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help) - ^ a b c "Ballgowns: About the Exhibition". Victoria and Albert Museum. Retrieved 1 November 2017.
- ^ Hegland, Jane; Steele, Valerie (2010). The Berg Companion to Fashion. Bloomsbury Academicpage=45-47.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help) - ^ a b c d Haynes, Michaele (2010). The Berg Companion to Fashion. Bloomsbury Academic. p. 204-206.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help) - ^ a b Hegland, Jane; Steele, Valerie (2010). The Berg Companion to Fashion. Bloomsbury Academicpage=45-47.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help) - ^ a b "- The Tradition of the Gowns". National Museum of American History. Retrieved 2017-11-16.
- ^ Hegland, Jane (2010). Evening Dress. Oxford: Bloomsbury Academic. pp. 265–267.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Schwartz, Jessica (2016). Clothing and Fashion: American Fashion from Head. ABC-CLIO.