User:Amarchais/RsaOG RNA
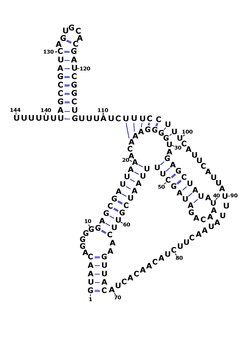
RsaOG (acronym for RNA S. aureus Orsay G) is a non-coding RNA that was discovered in the pathogenic bacteria Staphylococcus aureus N315 using a large scale computational screening based on phylogenetic profiling[1]. It was subsequently identified in other strains under the name of RsaI[2]. The rsaOG gene is conserved in all Staphylococcaceae sequenced genomes. Northern blot experiments show that RsaOG is expressed in several S. aureus strains[1],[2]. Mapping of RsaOG ends indicates a size of 146 nucleotides in S. aureus[2]. The rsaOG function is unknown.
References[edit]
- ^ a b Marchais A, Naville M, Bohn C, Bouloc P, Gautheret D (April 2009). "Single-pass classification of all noncoding sequences in a bacterial genome using phylogenetic profiles". Genome Res. 19 (6): 1084–1092. doi:10.1101/gr.089714.108. PMC 2694484. PMID 19237465.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: date and year (link) CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b c Geissmann T, Chevalier C, Cros MJ; et al. (September 2009). "A search for small noncoding RNAs in Staphylococcus aureus reveals a conserved sequence motif for regulation". Nucleic Acids Res. 37 (21): 7239–7257. doi:10.1093/nar/gkp668. PMC 2790875. PMID 19786493.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help)CS1 maint: date and year (link) CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
External links[edit]
RsaOG Alignment [1]
