From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Infobox drug/sandbox (edit · t · history · diff · links · /test · Source · e · t · hist · links · /subpages · /doc · /doc edit )
/testcases2 -- titles, licence, EMA/testcases3 -- pregcat, legal, licence, PLLR, ATC; Wikidata/testcases4 -- chem formula, mab/testcases5 -- identifiers, second id's/testcases6 -- all up/testcases7images -- images/testcases8 -- type, titles/testcases9 -- order variants, container_only/testcases10 -- pharmacokinetic, localINN (2017) has (data page) -- is a redirect/testcases11 -- hormone, gene therapy (2018) , has (data page)/testcases-FDA -- FDA 2023/testcases-warning -- warning box(es)
vaccine_type [ edit ] PubChem PID, SID [ edit ] Purge PID |PubChem=3007
Purge SID |PubChem=7003 (?)
Purge FA
Side by side comparison {{Infobox drug }} {{Infobox drug/sandbox }}
Amfetamine Pronunciation Trade names Adderall, Dyanavel XR, Evekeo, others Other names α-methylphenethylamine AHFS /Drugs.com amphetamine License data Dependence Physical : nonePsychological : moderateAddiction Moderate Routes of Medical: oral (ingestion) , nasal inhalation , intravenous oral , nasal inhalation , insufflation , rectal , intravenous ATC code Legal status Bioavailability Oral 75–100% Protein binding 15–40% Metabolism Amphetamine only:CYP2D6 , DBH , FMO3 Metabolites 4-hydroxyamphetamine 4-hydroxynorephedrine 4-hydroxyphenylacetone benzoic acid , hippuric acid , norephedrine , phenylacetone Onset of action IR dosing: 30–60 minutes[1] XR dosing: 1.5–2 hours[2] [3] Elimination half-life D-amph :9–11 hoursL-amph :11–14 hourspH -dependent: 8–31 hoursDuration of action IR dosing: 3–7 hours[4] XR dosing: 12 hoursExcretion Primarily renal ;pH -dependent range: 1–75%
(RS )-1-phenylpropan-2-amine
CAS Number PubChem CID IUPHAR/BPS DrugBank ChemSpider UNII KEGG ChEBI ChEMBL NIAID ChemDB PDB ligand Formula C 9 H 13 N Molar mass 135.20622 g/mol g·mol−1 3D model (JSmol ) Chirality 1:1 mixture (racemate ) Density 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 Melting point 11.3 °C (52.3 °F) (predicted)[5] Boiling point 203 °C (397 °F) at 760 mmHg
InChI=1S/C9H13N/c1-8(10)7-9-5-3-2-4-6-9/h2-6,8H,7,10H2,1H3
Key:KWTSXDURSIMDCE-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Amfetamine Pronunciation Trade names Adderall, Dyanavel XR, Evekeo, others Other names α-methylphenethylamine AHFS /Drugs.com amphetamine License data Dependence Physical : nonePsychological : moderateAddiction Moderate Routes of Medical: oral (ingestion) , nasal inhalation , intravenous oral , nasal inhalation , insufflation , rectal , intravenous ATC code Legal status Bioavailability Oral 75–100% Protein binding 15–40% Metabolism Amphetamine only:CYP2D6 , DBH , FMO3 Metabolites 4-hydroxyamphetamine 4-hydroxynorephedrine 4-hydroxyphenylacetone benzoic acid , hippuric acid , norephedrine , phenylacetone Onset of action IR dosing: 30–60 minutes[1] XR dosing: 1.5–2 hours[2] [3] Elimination half-life D-amph :9–11 hoursL-amph :11–14 hourspH -dependent: 8–31 hoursDuration of action IR dosing: 3–7 hours[4] XR dosing: 12 hoursExcretion Primarily renal ;pH -dependent range: 1–75%
(RS )-1-phenylpropan-2-amine
CAS Number PubChem CID IUPHAR/BPS DrugBank ChemSpider UNII KEGG ChEBI ChEMBL NIAID ChemDB PDB ligand Formula C 9 H 13 N Molar mass 135.20622 g/mol g·mol−1 3D model (JSmol ) Chirality 1:1 mixture (racemate ) Density 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 Melting point 11.3 °C (52.3 °F) (predicted)[5] Boiling point 203 °C (397 °F) at 760 mmHg
InChI=1S/C9H13N/c1-8(10)7-9-5-3-2-4-6-9/h2-6,8H,7,10H2,1H3
Key:KWTSXDURSIMDCE-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Purge
Side by side comparison {{Infobox drug }} {{Infobox drug/sandbox }}
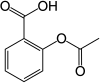
Aspirin Pronunciation acetylsalicylic acid Other names 2-acetoxybenzoic acid AHFS /Drugs.com Monograph MedlinePlus a682878 License data Pregnancy Routes of Most commonly oral, also rectal, lysine acetylsalicylate may be given intravenously or intramuscularly ATC code Legal status
AU :S2 (Pharmacy medicine) except when given intravenously (in which case it is schedule 4), used in animal medicine (schedule 5/6) or when the dose is higher than usual.UK :General sales list (GSL, OTC)US :OTC
Bioavailability 80–100%[6] Protein binding 80–90%[7] Metabolism Hepatic , (CYP2C19 and possibly CYP3A ), some is also hydrolysed to salicylate in the gut wall.[7] Elimination half-life Dose-dependent; 2–3 hours for low doses, 15–30 hours for large doses.[7] Excretion Urine (80–100%), sweat, saliva, feces[6] CAS Number PubChem CID IUPHAR/BPS DrugBank ChemSpider UNII KEGG ChEBI ChEMBL PDB ligand Formula C 9 H 8 O 4 Molar mass 180.157 g/mol g·mol−1 3D model (JSmol ) Density 1.40 g/cm3 Melting point 135 °C (275 °F) Boiling point 140 °C (284 °F) (decomposes) Solubility in water 3 mg/mL (20 °C)
InChI=1S/C9H8O4/c1-6(10)13-8-5-3-2-4-7(8)9(11)12/h2-5H,1H3,(H,11,12)
Key:BSYNRYMUTXBXSQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Aspirin Pronunciation acetylsalicylic acid Other names 2-acetoxybenzoic acid AHFS /Drugs.com Monograph MedlinePlus a682878 License data Pregnancy Routes of Most commonly oral, also rectal, lysine acetylsalicylate may be given intravenously or intramuscularly ATC code Legal status
AU :S2 (Pharmacy medicine) except when given intravenously (in which case it is schedule 4), used in animal medicine (schedule 5/6) or when the dose is higher than usual.UK :General sales list (GSL, OTC)US :OTC
Bioavailability 80–100%[6] Protein binding 80–90%[7] Metabolism Hepatic , (CYP2C19 and possibly CYP3A ), some is also hydrolysed to salicylate in the gut wall.[7] Elimination half-life Dose-dependent; 2–3 hours for low doses, 15–30 hours for large doses.[7] Excretion Urine (80–100%), sweat, saliva, feces[6] CAS Number PubChem CID IUPHAR/BPS DrugBank ChemSpider UNII KEGG ChEBI ChEMBL PDB ligand Formula C 9 H 8 O 4 Molar mass 180.157 g/mol g·mol−1 3D model (JSmol ) Density 1.40 g/cm3 Melting point 135 °C (275 °F) Boiling point 140 °C (284 °F) (decomposes) Solubility in water 3 mg/mL (20 °C)
InChI=1S/C9H8O4/c1-6(10)13-8-5-3-2-4-7(8)9(11)12/h2-5H,1H3,(H,11,12)
Key:BSYNRYMUTXBXSQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Purge Side by side comparison {{Infobox drug }} {{Infobox drug/sandbox }}
Infobox drug/testcases9 Pronunciation Trade names Desoxyn Other names N -methylamphetamine N ,α-dimethylphenethylamine AHFS /Drugs.com Monograph License data Dependence Physical Psychological Addiction Very high Routes of Medical: oral (ingestion) , intravenous [8] oral , intravenous , intramuscular , subcutaneous , smoke inhalation , insufflation , rectal , vaginal ATC code Legal status Bioavailability Oral: 70%[9] [9] Protein binding Varies widely[10] Metabolism CYP2D6 ,[11] DBH ,[12] FMO3 ,[13] XM-ligase ,[14] ACGNAT [15] Onset of action Rapid[16] Elimination half-life 5–30 hours[17] Duration of action 10–20 hours[16] Excretion Primarily renal CAS Number PubChem CID IUPHAR/BPS DrugBank ChemSpider UNII KEGG ChEBI ChEMBL Formula C 10 H 15 N Molar mass −1 3D model (JSmol ) Chirality 1:1 mixture (racemate ) Melting point 3 °C (37 °F) (predicted)[5] Boiling point 212 °C (414 °F) at 760 mmHg [18]
InChI=1S/C10H15N/c1-9(11-2)8-10-6-4-3-5-7-10/h3-7,9,11H,8H2,1-2H3
Y Key:MYWUZJCMWCOHBA-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Y
Infobox drug/testcases9 Pronunciation Trade names Desoxyn Other names N -methylamphetamine N ,α-dimethylphenethylamine AHFS /Drugs.com Monograph License data Dependence Physical Psychological Addiction Very high Routes of Medical: oral (ingestion) , intravenous [8] oral , intravenous , intramuscular , subcutaneous , smoke inhalation , insufflation , rectal , vaginal ATC code Legal status Bioavailability Oral: 70%[9] [9] Protein binding Varies widely[10] Metabolism CYP2D6 ,[11] DBH ,[12] FMO3 ,[13] XM-ligase ,[14] ACGNAT [15] Onset of action Rapid[16] Elimination half-life 5–30 hours[17] Duration of action 10–20 hours[16] Excretion Primarily renal CAS Number PubChem CID IUPHAR/BPS DrugBank ChemSpider UNII KEGG ChEBI ChEMBL Formula C 10 H 15 N Molar mass −1 3D model (JSmol ) Chirality 1:1 mixture (racemate ) Melting point 3 °C (37 °F) (predicted)[5] Boiling point 212 °C (414 °F) at 760 mmHg [18]
InChI=1S/C10H15N/c1-9(11-2)8-10-6-4-3-5-7-10/h3-7,9,11H,8H2,1-2H3
Y Key:MYWUZJCMWCOHBA-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Y
Order of sections [ edit ]
Container only [ edit ]
^ "Pharmacology" . amphetamine/dextroamphetamine . WebMD. Retrieved 21 January 2016 . Onset of action: 30–60 min ^ Millichap JG (2010). "Chapter 9: Medications for ADHD". In Millichap JG (ed.). Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder Handbook: A Physician's Guide to ADHD (2nd ed.). New York, USA: Springer. p. 112. ISBN 9781441913968 ^ Brams M, Mao AR, Doyle RL (September 2008). "Onset of efficacy of long-acting psychostimulants in pediatric attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder". Postgrad. Med . 120 (3): 69–88. doi :10.3810/pgm.2008.09.1909 . PMID 18824827 . ^ Mignot EJ (October 2012). "A practical guide to the therapy of narcolepsy and hypersomnia syndromes" . Neurotherapeutics . 9 (4): 739–752. doi :10.1007/s13311-012-0150-9 . PMC 3480574 PMID 23065655 . ^ a b "Properties: Predicted – EP|Suite" . Amphetamine . Retrieved 6 November 2013 .^ a b "Zorprin, Bayer Buffered Aspirin (aspirin) dosing, indications, interactions, adverse effects, and more" . Medscape Reference . WebMD. Retrieved 3 April 2014 .^ a b c Brayfield, A, ed. (14 January 2014). "Aspirin" . Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference . Pharmaceutical Press. Retrieved 3 April 2014 . ^ United States Congress Senate Committee on the Judiciary Subcommittee to Investigate Juvenile Delinquincy (1 January 1972). Amphetamine legislation 1971: Hearings, Ninety-second Congress, first session, pursuant to S. Res. 32, section 12, investigation of juvenile delinquency in the United States (PDF) . U.S. Govt. Print. Off. p. 161. Retrieved 1 January 2016 . We made a decision in January of 1969 to cease the manufacture of injectable methamphetamines. ^ a b Rau T, Ziemniak J, Poulsen D (2015). "The neuroprotective potential of low-dose methamphetamine in preclinical models of stroke and traumatic brain injury". Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry . 64 : 231–6. doi :10.1016/j.pnpbp.2015.02.013 . PMID 25724762 . In humans, the oral bioavailability of methamphetamine is approximately 70% but increases to 100% following intravenous (IV) delivery (Ares-Santos et al., 2013). ^ "Toxicity" . Methamphetamine . National Center for Biotechnology Information. Retrieved 31 December 2013 .^ "Adderall XR Prescribing Information" (PDF) . United States Food and Drug Administration . December 2013. pp. 12–13. Retrieved 30 December 2013 .^ Lemke TL, Williams DA, Roche VF, Zito W (2013). Foye's Principles of Medicinal Chemistry (7th ed.). Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 648. ISBN 1609133455 Alternatively, direct oxidation of amphetamine by DA β-hydroxylase can afford norephedrine. {{cite book }}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link )^ Krueger SK, Williams DE (June 2005). "Mammalian flavin-containing monooxygenases: structure/function, genetic polymorphisms and role in drug metabolism" . Pharmacol. Ther . 106 (3): 357–387. doi :10.1016/j.pharmthera.2005.01.001 . PMC 1828602 PMID 15922018 . ^ "Substrate/Product" . butyrate-CoA ligase . Technische Universität Braunschweig. Archived from the original on 22 June 2017. Retrieved 5 October 2017 .^ "Substrate/Product" . glycine N-acyltransferase . Technische Universität Braunschweig. Archived from the original on 23 June 2017. Retrieved 5 October 2017 .^ a b Riviello, Ralph J. (2010). Manual of forensic emergency medicine : a guide for clinicians ISBN 9780763744625 ^ Schep LJ, Slaughter RJ, Beasley DM (August 2010). "The clinical toxicology of metamfetamine". Clinical Toxicology . 48 (7): 675–694. doi :10.3109/15563650.2010.516752 . ISSN 1556-3650 . PMID 20849327 . S2CID 42588722 . ^ "Chemical and Physical Properties" . Methamphetamine . National Center for Biotechnology Information. Retrieved 31 December 2013 .