Portal:Yemen
Yemen Portal


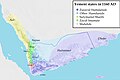
Yemen (/ˈjɛmən/ ⓘ; Arabic: ٱلْيَمَنْ, romanized: al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen, is a sovereign state in West Asia. Located in the southern Arabian Peninsula, it borders Saudi Arabia to the north, Oman to the northeast, and the Indian Ocean to the south, sharing maritime borders with Eritrea, Djibouti and Somalia across the Horn of Africa. Covering roughly 528,000 square kilometres (203,861 square miles), with a coastline of approximately 2,000 kilometres (1,200 miles), Yemen is the second largest country on the Arabian Peninsula. Sanaa is its constitutional capital and largest city. Yemen's estimated population is 34.7 million, comprised mostly of Arab Muslims. It is a member of the Arab League, the United Nations, the Non-Aligned Movement and the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation.
Owing to its geographic location, Yemen has been at the crossroads of many civilisations for over 7,000 years. In 1200 BCE, the Sabaeans formed a thriving commercial kingdom that included parts of modern Ethiopia and Eritrea. In 275 CE, it was succeeded by the Himyarite Kingdom, which spanned much of Yemen's present-day territory and was heavily influenced by Judaism. Christianity arrived in the fourth century, followed by the rapid spread of Islam in the seventh century. Yemenite troops playing a crucial role in early Islamic conquests. Various dynasties emerged between the 9th and 16th centuries. During the 19th century, the country was divided between the Ottoman and British empires. After World War I, the Mutawakkilite Kingdom of Yemen was established, which in 1962 became the Yemen Arab Republic (North Yemen) following a coup. In 1967, the British Aden Protectorate became the independent People's Democratic Republic of Yemen (South Yemen), the first and only officially socialist state in the Arab world. In 1990, the two Yemeni states united to form the modern Republic of Yemen (al-Jumhūrīyah al-Yamanīyah), with Ali Abdullah Saleh serving as the first president until his resignation in 2012 in the wake of the Arab Spring.
Since 2011, Yemen has been enduring a political crisis, marked by street protests against poverty, unemployment, corruption, and President Saleh's plan to amend Yemen's constitution and eliminate the presidential term limit. By 2015, the country became engulfed by an ongoing civil war with multiple entities vying for governance, including the Presidential Leadership Council of the internationally recognized government, the Houthi movement's Supreme Political Council, and the separatist Southern Movement's Southern Transitional Council. This conflict, which has escalated to involve various foreign powers, has led to a severe humanitarian crisis. (Full article...)
Selected article -
The Yemeni revolution (or Yemeni intifada) followed the initial stages of the Tunisian Revolution and occurred simultaneously with the 2011 Egyptian revolution and other Arab Spring protests in the Middle East and North Africa. In its early phase, protests in Yemen were initially against unemployment, economic conditions and corruption, as well as against the government's proposals to modify Yemen's constitution. The protesters' demands then escalated to calls for the resignation of Yemeni President Ali Abdullah Saleh. Mass defections from the military, as well as from Saleh's government, effectively rendered much of the country outside of the government's control, and protesters vowed to defy its authority.
A major demonstration of over 16,000 protesters took place in Sanaʽa, Yemen's capital, on 27 January. On 2 February, Saleh announced he would not run for reelection in 2013 and that he would not pass power to his son. On 3 February, 20,000 people protested against the government in Sanaʽa, while others protested in Aden, a southern Yemeni seaport city, in a "Day of Rage" called for by Tawakel Karman, while soldiers, armed members of the General People's Congress and many protesters held a pro-government rally in Sanaʽa. In a "Friday of Anger" on 18 February, tens of thousands of Yemenis took part in anti-government demonstrations in Taiz, Sanaʽa and Aden. On a "Friday of No Return" on 11 March, protesters called for Saleh's ousting in Sanaʽa where three people were killed. More protests were held in other cities, including Mukalla, where one person was killed. On 18 March, protesters in Sanaʽa were fired upon, resulting in 52 deaths and ultimately culminating in mass defections and resignations. (Full article...)List of selected articles
|
|---|
Selected biography -
General images -
Selected city -
Thula (Arabic: ثُلَاء, romanized: Thulāʾ) or Thila (Arabic: ثِلَاء, romanized: Thilāʾ) is a town in west-central Yemen. It is located in the 'Amran Governorate.
Thula is one of five towns in Yemen on the UNESCO World Heritage Tentative List. Dating to the Himyarite period, the town is very well preserved and includes traditional houses and mosques. Archaeological investigation discovered Sabaean period ruins with massive stone architecture beneath the Himyarite. Restoration between 2004 and 2011, restored the Bab al Mayah gate, several
watch towers, paths, the traditional cistern, and other portions of the Sabaean fort. (Full article...)Selected picture -
Selected cuisines, dishes and foods -
List of articles
|
|---|
Related portals
Religions in Yemen
Arab states
Categories
Topics
Related portals
Religions in Yemen
Arab states
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus