History of Afragola

The history of Afragola covers a time span of several millennia. The exact place where the city arose, namely the Regi Lagni plain in ancient Campania Felix, was frequented/occupied between the Final Late Neolithic/Chalcolithic and the Early Bronze Age, evidenced by the discovery of the Early Bronze Age village of Afragola and various artifacts found during the construction of the Naples Afragola station.[1][2]
Origin of the name[edit]
The first mention of the name (Afraore) dates back to the year 1131.[3] Other variants in later charters are "Afragone," "Afraone," "Fragola," "Frabola," "Afraole," "Afraolla," "Fraolla," "Aufrangola," and "Afrangola."[4]
The medieval name of the casale is recorded in documents of the Angevin and Aragonese periods as "Villa Fragorum"; the toponym underwent, then, changes due to the vernacular spoken by the inhabitants until it became the present Afragola.[5]
Foundation between history and legend[edit]

According to legend, Afragola was founded in 1140 by Roger II of Sicily, an event painted in 1886 by the painter Augusto Moriani, depicting Roger, surrounded by his soldiers and in the act of granting them land; Friar Domenico de Stelleopardis stated in his work Relatione historica della fondazione della chiesa di San Marco della selvetella, that ten families founded Afragola: Castaldo, Fusconi, Iovini, Muti, Tuccillo, Commeneboli, Fortini, del Furco, Cerbone, de Stelleopardis, of which only eight resided in the future city; the last two moved to Naples.[6]
However, the event is considered false by historians, such as Castaldi, since Roger I of Sicily had already died in 1101, and Roger II in 1154, and, moreover, earlier settlements already existed; therefore, a foundation of the city by them seems unlikely.[6]
Prehistory and protohistory[edit]
Neolithic period[edit]
The area where Afragola stands today was inhabited as early as during the Final Late Neolithic/Chalcolithic and Bronze Age, where small villages sprang up, for example, the Early Bronze Age village of Afragola (where Mycenaean-age artifacts were found), which was destroyed by the eruption of the Avellino Pumices, whose volcanic material covered the area causing the villages to silt up and the ground to rise by more than a meter, which is why communities were forced to flee.[1][7]
Ancient Era[edit]
Opici and Samnite settlements[edit]
In the 7th century BC. the territory was inhabited by the Opici, attracted by the fertile vegetation, consisting of ferns, hollies, maples, elms, poplars, sycamores and pines,[8] evidenced by a series of tomb finds at Arena and Camposantiello Vecchio and in 1882, during the construction of labor houses in Via Sicilia, the year in which excavations were made of the mother chapel of the present cemetery, as well as 4 Greek tombs, composed of large pieces of tuff, found in the Padula locality in the 19th century.[6][8]
From the 4th century B.C., populations of Osco-Samnite background lived there, evidenced by the discovery in 1961 of several tombs dating to the 3rd century B.C, including a double-chest tomb found in the Cantariello locality, exhibited in room LXVII of the National Archaeological Museum of Naples and depicting two women, arranged facing each other; the woman on the left holds an oinochoe in one hand and a situla in the other, while the woman on the right holds a bread and a kantharos, and in the center is depicted a pomegranate, a symbol of death and life.[8][9]
During preliminary investigations for the construction of the Porta station, on the railway line of the Naples Afragola station, a fragment of bucchero (4.5 cm in length and 2.3 cm in height) was found, dating from the late 6th century BCE. B.C. and the early 5th century B.C. and part of a keeled basin and the wall of an open-form vessel, a chalice or kantharos, bearing on the final portion a 0.02-cm-high inscription in the Etruscan alphabet ([---]ias) and possibly part of a funerary equipment.[10]
Romans[edit]

Between the 4th and 3rd centuries BC the territory was conquered by the Romans, evidenced by the discovery in 1929 of an Augustan altar, probably from the 1st century BC, consisting of a travertine capital with the carved dedication "AVG SACR" (Augustus Sacrum), which measured 1.17 m in height and 0.55 m in width, later used as a drinking trough and destroyed to obtain road metal for road reconstruction,[6] two Roman villas between Caivano and Afragola, three Roman columns, a tomb, found in the Cantariello locality, several rustic villas, and remains of a branch of the Roman aqueduct of the Serino.[9][11]
Objects of daily use were also found such as: a wine press, a small olpe, an Hadrianic coin, the Stone of St. Mark in Sylvis, remains of an altar, an amphora tomb, covered by layers of lapilli and found in Contrada Sarricchione during work for the construction of the Naples-Cancello railway line variant, probably part of a Christian necropolis datable between the fourth and seventh centuries AD. C. and of the pit or amphora type, in which the body of a woman with a broken neck was found (probably because the amphora was smaller and pressure was applied to allow the woman to enter), and, finally, an epigraph in the Salicelle area bearing the following text:[9][11][12][13][14]
Cam(illus) vil(licus) i(us) l(ibertorum) h(abeus) v(otum) p(osuit) L(ibero)
In about 133 B.C., during the time of the Gracchi, the territory was subjected to centuriation (Ager Campanus I), continued in the Augustan age with the Acerrae-Atella I centuriation, traces of which still remain in the present road layout, particularly of the former.[15]
In addition, there was an epigraph, named after Clodius Celsinus Adelphius, set into a wall of the Church of St. John and bearing the following text:[16]
Adelfi Clodio Celsino insigni et. c. v. praestanti benivolentia avctoritate ivstitia corr. regionvm dvarvm memorabili et praeteritorvm ivdicvm exempla virtvtibvs omnibvs svpergresso ordo splendidissimvs Beneventanae civitatis patrono dignissimo
— Epigraph of Clodius Celsinus Adelphius
There was also an epigraph (dated 30 B.C.-20 A.D.), named after Aulus Vitellius and preserved in the National Archaeological Museum in Naples, and a tile with a vignette, found in 1983 near USL 25 on Highway 87 Sannitica, bearing the following text:[17]
When alive Aulus Vitellius Crestus, freedman of Aulus Quintus, [built this tomb] for his mother Trolia Antemius and for his freedwoman Prima Vitellia, 12 feet in front and 12 feet deep (Latin: V(ivit) A(ulus) Vitellius Q(inti) A(uli) l(ibertus) Chrestus Troliae Anthemio matri svae et Vitelliae Primae libert(ae) svae in fr(onte) p(edes) XII in agr(o) p(edes) XII)
— Epigraph of Aulus Vitellius, National Archaeological Museum of Naples, CIL, X, 3117.
CAMVILILVD
— Epigraph, tile with vignette
Also, probably between Caivano and Afragola, a branch of the Pisonians settled, and in order to repopulate Atella, Augustus founded a colony.[6]
Middle Ages[edit]
Early Middle Ages[edit]
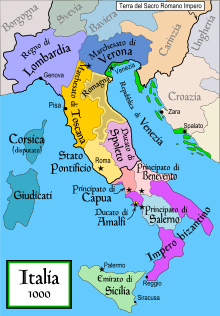
Following the fall of the Western Roman Empire, the territory was gradually invaded by the Vandals, Visigoths, Ostrogoths, Lombards, and, finally, the Byzantines in the 9th century (Duchy of Naples), a period during which the conquered lands were entrusted to soldiers.[8]
The territory was also part of the diocese of Atella, but with the arrival of the Lombards it then passed to the archdiocese of Naples.[15]
Around 1000, the villages of Arcopinto, Cantarello, San Salvatore delle Monache (which took its name from the church of San Salvatore, dependent on the monastery of San Gregorio Maggiore), Salice, Arcora, Contrada Regina, San Marco and San Martino, as well as Casa aurea (Casoria) and Paternum ad sanctum Petrum (San Pietro a Patierno) developed, while nearby were located a forest, a swamp, the "campus" of San Severino and the remains of an old Roman aqueduct.[6][18]
Among the first inhabitants of Arcopinto and Casoria were respectively two farmers, Cicino Russo del fu Palumbo and Gregorio Capuburria del fu Leone, Russo's brother-in-law, mentioned in a document of 1025.[6]
Due to the overflow of the Clanio River, the territory became swampy and inhospitable.[11]
Late Middle Ages[edit]
Norman and Swabian occupation[edit]
Between the 11th and 12th centuries the territory was conquered respectively by the Normans, following the Norman conquest of southern Italy completed by Roger II of Sicily, and then by the Swabians.[19]
In a document of 1130/1131, written in Lombard characters, Afragola (Afraore) is mentioned for the first time, according to Bartolommeo Capasso, and in which various country estates are listed, granted to the abbot of the monastery of Saints Severino and Sossio, such as: Licignano, Sant'Arcangelo (near Caivano) and Cantarello etc.[6]
A document from August 1143 mentions "Pagano, son of the late Nicola, de la Frahola" and his wife Mansa, who donated a plot of land of 22 quarts, in the district of Cupolo, while the Norman Diplomatic Codex of Alfonso Gallo also mentions Afragola.[6]
The first inhabitants of Arco Pinto erected a small church dedicated to St. Martin, visited in 1619 by Cardinal Decio Carafa and destroyed in 1768 by order of the Governor of Afragola.[6]
Angevin occupation[edit]

During the Angevin period, some documents report a "Villa Arcus pinti," of a "Casale Arcus pinti," "loco ubi dicitur Arcus pintus," and the village Canterello, and among the feudal lords are mentioned in the documents: Paolo Scotto, who owned a fief in the place called "a la Fracta," Pandolfo Gennaro, feudatory of Arcopinto, Ermigaldo de Lupian and Raimondo di Odiboni, physician of Charles II of Anjou and feudatory of the Cesine, sold to Giovanni Protomedico and, later, to Guglielmo de Brusato.[6]
On Feb. 24, 1265 Afragola was visited by King Charles I of Anjou, on his way to Naples, who was welcomed by 18 knights and M. Francesco Loffredo, Elected of the Government, who presented the keys of the City to the king.[6]
In 1284 the "barony" of Afragola was created, when the Curia invested Pierre de Lamanon with all rights over the city, with the exception of the lands already belonging to the archdiocese of Naples; the fief passed from hand to hand numerous times over the following centuries.[6]
During the reign of Charles II of Naples and Robert of Anjou, many fiefs and lands in the city were owned by the archiepiscopal curia of Naples, particularly by Archbishop Bernardo Caracciolo, cultivated by vassals in the service of the same curia, including the Salerno man Tommaso Mansella and Robert of Capua, count of Altavilla.[6][20]
In 1355 Louis of Durazzo camped there with Count Lando's German minions.[21]
In July 1380, the city was involved in the clash between the Durazzeschi and Angevins, and Otto IV of Brunswick-Grubenhagen, husband of Joanna I of Naples, camped there. He ordered that "all farmsteads be evacuated and moved to the fort for the arrival of Sir Charles in the kingdom."[21]
In 1385, Pope Urban VI, besieged by King Charles III of Naples in the castle of Nocera, asked for help from Raimondo Orsini del Balzo, who, accompanied by Francesco della Ratta, count of Caserta, Carlo d'Artus, count of Sant'Agata de' Goti, and 1,200 horsemen, took possession of Afragola, clashing with the enemy troops near Nocera in March of that year, suffering, however, a heavy defeat.[22]
In 1386 Villanuccio di Brunforte camped there with his troops.[23]
In January 1388, Domenico Ruffaldi of Siena encamped in Afragola with Berardo da Recanati and 500 horses, damaging the territory as far as Casalnuovo di Napoli; however, Francesco Della Ratta and his brother Sandolo, accompanied by Teutonic and Breton soldiers, clashed with Ruffaldi, forcing him to retreat.[24]
In addition, on January 26, Queen Margaret of Durazzo's troops encamped near Carluccio Minutolo's tower in a vain attempt to besiege Naples.[24]
However, in April 1389, Otto, in the service of Louis II of Anjou and in the company of Giovanni Acuto, clashed with enemy troops at Casalnuovo in an attempt to repel them, deciding, despite everything, to fall back between Aversa and Afragola.[25]
In May 1392, Ruffaldi, accompanied by Giacomo Stendardo, count of Alife, again attacked Afragola and the aforementioned tower, raiding the territory.[24]
Around 1398 and 1399 Alberico da Barbiano camped there to face the Angevin troops, besieging Naples and forcing the troops to surrender.[26]
In 1423, a clash took place near the city between the troops of King Alfonso V of Aragon with those of Giacomo Sforza, captain of Queen Joanna II of Naples.[6]
Aragonese and Spanish occupation[edit]
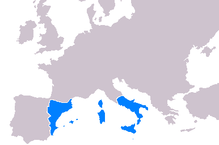
From 1442 Afragola was part of the Aragonese territories, and then passed to the Spanish during the Spanish viceroyalty of Naples.[27]
In 1575, Paolo Capece-Bozzuto, feudatory of Afragola, offered the reigning authority 7000 ducats to buy the demanial part of the barony; the universitas of Afragola appealed to the Royal Court, asking to be allowed to buy both the demanial part (for 7000 ducats) and the odal part (for 20000 ducats), owned by the Capece-Bozzuto family for almost two centuries. On 22 December of that year, the Royal Collateral Council, while accepting the Baron's offer, granted the universitas a month to collect the money, and on 12 January 1576, following the deposit of the sum by the municipal authority, obliged Paolo Capece-Bozzuto to sell the fief to the universitas.[28] Ludovico Capece-Bozzuto, Paolo's son, appealed, referring to his great-uncle Troiano's fideicommissum that prevented the alienability of the fief, but all attempts were in vain and the barony ceased to exist forever.[6][21]
Lords of Afragola (1284-1576)[edit]
| Name | Period | Notes |
| Pierre de Lamanon | 1284 - 1291 | Was invested with all the rights of the Curia over Afragola, with the exception of the lands belonging to the archdiocese of Naples.[21] |
| Eneca or Agneta de Lamanon | 1291 - 1292 | Daughter of Pierre de Lamanon; she inherited the fief following the death of her father.[21] |
| Public domain | 1292 - 1299 | The fiefdom returned to the Royal Court following Eneca's death.[21] |
| Guglielmo Grappino | 1299 - c. 1313 | Husband of Eneca; he was invested with the fief by Charles II of Naples on 24 August 1299; three quarters of the fief, however, constituted the dowry of his second wife, Giovanna de Glisis.[21] |
| Giovanna de Glisis | c. 1313 - ? | Inherited the fief following the death of her husband.[21] |
| Giovanni Grappino | ? - ? | Son of Guglielmo and Giovanna; he may have inherited the fief following the death of his mother.[21] |
| Public domain | ? - 1330 approx. | The fiefdom returned to the Royal Court possibly following the revocation against Giovanni Grappino.[21] |
| Roberto de Lagonessa | c. 1330 - post 1333 | Was invested with the fief by the Royal Court.[21] |
| Marino de Martano | post c. 1333 - 1336 | Took over from Roberto de Lagonessa, possibly by purchasing his rights.[21] |
| Enrico Dentice | c. 1336 | Uterine brother of Marino de Martano; he inherited the fief upon the death of his brother, who died without direct heirs.[21] |
| Tommaso Mansella | c. 1336 | Son of Niccolò Mansella, armed knight in 1332 and accountant in the service of King Robert of Anjou; he succeeded Enrico Dentice.[21] |
| Roberto di Capua | c. 1336 - c. 1337 | Count of Altavilla; bought the fief from Mansella.[21] |
| Nicola d'Eboli | c. 1337 | Count of Trivento; he was invested with the fiefdom by the Curia, with the exception of a part of Afragola that was definitively returned to the State and the Cesine.[21] |
| Charles of Durazzo | 1337 - 1346 | Duke of Durazzo; he bought the fiefdom with his brothers Ludovico and Roberto from Nicola di Eboli, who, however, kept part of it for himself, and sold it in 1340 to Gualtiero Galeota; in 1346 Charles was sentenced to death for treason by order of King Louis I of Hungary.[21] |
| Robert of Durazzo | 1346 | Charles' brother; he inherited the rights to the fiefdom upon his brother's death, but was in turn stripped of all property through treason, dying in prison in 1364.[21] |
| Public domain | 1346 - 1370 | The fiefdom possibly reverted to the State following the betrayal of the Durazzo family.[21] |
| Charles of Durazzo | before 1370 - 1381 | Son of Louis; he regained possession of his father's fiefdom, with the exception of the lands belonging to the Church of Naples.[21] |
| Giacomo, Giordano and Giovannello Capece-Bozzuto | c. 1381 - 1401 | Acquired the feudal part of Afragola from Charles and Margaret of Durazzo.[21] |
| Giovannello Tomacelli | c. 1401 - 1407 | Brother of Pope Boniface IX; he was invested with the fief probably after Giovannello Capece-Bozzuto fell into disgrace or exchanged it for another possession.[21] |
| Public domain | 1407 - 1419 | The fief probably returned to the Royal Court.[21] |
| Giovannello Capece-Bozzuto | 1419 - post 1423 | Together with his son Nicola Maria, he regained possession of the fief and in 1419 obtained for himself and his descendants the captaincy of Afragola and other places.[21] |
| Nicola Maria Capece-Bozzuto | post 1423 - 1477 | Son of Giovannello; he inherited the fief upon the death of his father.[21] |
| Cesare Maria Capece-Bozzuto | 1477 - 1495 | Son of Nicola Maria; he was stripped of the fief upon the return of the Aragonese to Naples, as he had sided with Charles VIII of France in the Italian War.[21] |
| Public domain | 1495 - 1497 | The fiefdom returned to the State following the betrayal of Cesare Maria Capece-Bozzuto.[21] |
| Fabrizio I Colonna | 1497 - 1507 | Count of Albe and Tagliacozzo; he was invested with the fief by King Frederick I of Naples.[21] |
| Cesare Maria Capece-Bozzuto | 1507 - 1513 | Regained the fief on 12 June 1507 following the agreement between Ferdinand II of Aragon and Louis XII of France.[21] |
| Scipione Capece-Bozzuto | 1513 - 1548 | Eldest son of Cesare Maria; he inherited the feud upon his father's death. However, according to historian Giuseppe Castaldi, the successor would have been Giovanni Capece-Bozzuto, another son of Cesare Maria, although it does not appear from any document that he was ever lord of Afragola.[21] |
| Troiano Capece-Bozzuto | 1548 - 1557 | Second son of Cesare Maria; he succeeded his brother.[21] |
| Ludovico Capece-Bozzuto | 1557 - 1571 | Son of Cesare Maria; he succeeded his brother.[21] |
| Paolo Capece-Bozzuto | 1571 - 1576 | Son of Troiano; he succeeded his uncle.[21] |
| Public domain | since 1576 | On 12 January 1576, the Royal Collateral Council forced Paolo Capece-Bozzuto to sell the fief to the universitas of Afragola.[28] |
Modern Age[edit]
17th century and the Thirty Years' War[edit]

During the seventeenth century, Afragola excelled in hat-making, textiles, hemp farming and agriculture.[29]
During the rule of Viceroy Pedro de Toledo, the inhabitants of Arcopinto moved to the new Spanish district, located near the church of Santa Maria d'Ajello, decimated by the eruption of Vesuvius in 1631 and the plague epidemic of 1656.[30]
In 1633, the construction of the Franciscan church and convent of St. Anthony of Padua (the current Basilica of St. Anthony of Padua) was begun.[31]
In 1639, Ramiro Felipe Núñez de Guzmán, Duke of Medina and Viceroy of Naples, sold the lands of Afragola to finance the Thirty Years' War, forcing the inhabitants to pay 18,000 ducats to be kept in state property.[32]
Revolt of Masaniello and the Neapolitan Republic[edit]

In 1647, Masaniello ordered Giovanni Bozzuto to burn Afragola, on the charge of remaining loyal to the viceroyal government;[33] however, after the revolutionary's death, soldiers arrested Bozzuto and imprisoned him in the Castel Nuovo.[33]
At the end of 1600, the city was administered by a viceregal governor.[20]
In 1737, a 'Code of Afragola' was also drafted, with nine rules engraved on a marble slab, preserved in the atrium of the Town Hall.[20]
Moreover, on 17 December 1796, an orphanage was founded by the priest Nicola Iengo, located in the castle of Afragola and run by oblate nuns.[34]

During the birth of the Neapolitan Republic, the French occupied the city, where, in the meantime, the tree of liberty was hoisted in Piazza dell'Arco (now Piazza Municipio).[35]
From May of the same year, however, the French were forced to leave Naples, encouraging the rise of anti-Jacobin revolts in various towns such as Caserta, Portici, Acerra, Teano, Campobasso and Afragola itself.[36]
According to the book Storia della Repubblica partenopea del 1799 e vite de' suoi uomini celebri by Clodomiro Perrone, Antonio La Rossa (or Della Rossa), a member of the Council of State, led a revolt on 3 June, knocking down the tree of liberty and calling soldiers from neighbouring towns, including Acerra, with the intention of attacking the Parthenopeans.[36]
In response, the Neapolitan Republic sent three hundred soldiers, who met the rebels at Capodichino and put them on the run towards Casoria.[36] The trees of liberty were then raised again to the rebel towns.[36]
However, La Rossa asked for help from the Marquis of Schiava and Cardinal Fabrizio Ruffo, who offered him three hundred and eight Sanfedists, led by the priest Pietro Moscia, and one hundred horsemen, led by Michele Rega, with the intention of breaking into Naples.[36]
Contemporary age[edit]
Austrian occupation and Napoleon's defeat[edit]
In 1809, the city was administered by an autonomous civic administration and a mayor, the notary Cesare Castaldo, for the first time.[20]
After Napoleon Bonaparte's defeat at the Battle of Waterloo (1815), the Austrians headed for the Kingdom of Naples and Afragola, which was occupied by them, as stated in the decree of the Treaty of Casalanza:
Article 3 paragraph 3 of the Military Conventions: On 22 May, the Austrian army will take up its position in the line of Aversa, Afragola, Melito and Giugliano[37]
From 1809 to 1860, Afragola was a municipality in the district of the same name, administered by a mayor, a decurionate of 30 officials, a royal judge (who administered justice), an inspector-commissioner (with police functions), two elected officials and a municipal chancellor.[38]
Unification of Italy[edit]
Between 1830 and 1889, the town again distinguished itself in the production of hemp, flax, pulses, wheat, maize, hats and fruit, especially melons.[29]
With the suppression of the district of Casoria in 1860 and, therefore, of all the districts in the province of Naples, Afragola became a municipality of the district of the same name.[39]
In 1873, the town was provided with a telegraph office, located in a house owned by the municipality, in Via Rosario, commissioned by the commissioner Giuseppe Arpa and the Compartmental Directorate of Telegraphs of Naples, and a civic hospital, located in the former Convent of St. Anthony, subsidised by the municipality and run by the monks of the convent.[40]
Despite everything, in 1878, the city was hit by a major flood, which caused extensive damage and forced the mayor to ask other nearby towns for help.[41]
Early 20th century and fascist period[edit]

During the First World War, the town suffered a hard time of poverty, particularly in 1918, caused mainly by the departure of young men for the war, for whom a memorial was erected, the Monument to the Fallen of the First World War.[29][42]
After the suppression of the Casoria district in 1926,[43] the territory was assigned to the district of Naples.[44]
Under the Fascist regime, like all Italian municipalities, the town was administered by a podestà, Luigi Ciaramella, in office from 1927 to 1943, who had the roads widened, the tramway runs strengthened and built sewers and a school, the current Marconi.[29]
On 5 October 1935, King Victor Emmanuel III, at the proposal of the mayor, conferred the title of "city" on the municipality.[45]
Nazi occupation[edit]

With the armistice of 8 September 1943, the city was occupied by the Germans, who on 2 October of the same year carried out a massacre, the so-called Afragola Massacre[46][47] and set up a prison camp inside the Casone Spena, in the Arcopinto area, a military hospital in the current Marconi school, while sentries were stationed on the bell tower of the church of Santa Maria d'Ajello, used as a watchtower.[48]
In honour of the sacrifice of the inhabitants, an epigraph was placed in verses dictated by Adolfo Omodeo on 11 October 1944:
To the memory of the XI victims of Nazi ferocity and of the XXX who were swept away in the battle, innocent of the common guilt of the ill-guarded civil liberty, as an everlasting warning for the present and for posterity, the citizens of Afragola place this marble on the first day of the Liberation by the hands of the Allies on 11 October MCMXLIV
— Epigraph[49]
According to Armando Izzo, the Casa del Fascio (House of the Fascist Party), located at the beginning of Via Gramsci, was sacked by the Germans, but without reprisals towards civilians.[48]
Moreover, in July of the same year the air-raid sirens sounded, due to two enemy planes dropping bombs near Via Arturo De Rosa, in particular on 18 July, during which four civilians perished and 10 were injured.[48][50]
Arrival of the Allies[edit]
On 2 October, the Allied armoured troops of the 7th Armoured Division, including the 1st Royal Tank Regiment (with its C Coy and 1 R.B. motorised companies), the 5th Regiment Royal Artillery (in particular the H Trp and Bty H.Q. of the CC Battery, commanded by Major Francis Brian Wyldbore-Smith) and the 11th Hussars Regiment, commanded by Lieutenant Colonel A. T. Smail (in particular, A Squadron, with Lieutenant Williamson's Troop 3Tp and Lieutenant Garrard's Troop 5Tp),[51][52][53] coming from Somma Vesuviana, together with some armoured cars from Casalnuovo di Napoli, headed towards Afragola, where the brigade's headquarters was located, the Brigade Tactical H.Q., with the intention of pushing on as far as Acerra, besieged by Nazi troops.[53][54] The Allies' objective was, in fact, to advance along the Regi Lagni, but on the way they found the only viable bridge, the Casolla bridge, still controlled by German soldiers.[54] The following day, the Allied troops put the Germans, coming from Cardito and Caivano, to flight after firefights in San Michele and near the lazaretto.[54] Moreover, while the British continued their advance towards Afragola, the state road 87 Sannitica along the Naples-Caivano tramway and the provincial road Afragola-Casolla was under fire from German troops.[54]

In a military report of 7 October, it is reported that on 3 October the 11 (StuG)Kp/PzRgt Hermann Göring, belonging to Captain Hans Sandrock's III Battalion and stationed near Cardito and Caivano,[55] with Captain Karl Roßmann's Abteilung, the 9th (Lieutenant Berger's) and 10th companies of the 1. Fallschirmjäger-Division and a unit of feldwebel Kuter, formed a line of defence with Sturmgeschütz III assault guns (including a Sturmhaubitze 42): two placed at the Cardito-Afragola-Casoria crossroads and commanded by Wachtmeister Kurt Boerner; two south of Cardito, under the command of stabswachtmeister Wilhelm Schulze-Oswald and, finally, another two 2 km south-east of Cardito, commanded by leutnant Karl-Heinz Wallhäuser (assisted by unteroffizier Bito and oberwachtmeister Tokk); in command of the Panzer-Aufklärungs-Abteilung was Captain Martin Lübke.[56][57][58] In addition to the latter, artillery batteries, machine guns, trenches and infantry units were also stationed at the Princess Caracciolo's farm and in the Porchiera.[54]
Leutnant Winkler of the Panzer-Aufklärungs-Abteilung reported the advance of enemy tanks from Afragola and, during the Allied attack, leutnant Adolf Roebig died from a blow to the head, while oberleutnant Jekosch (who had arrived on the spot together with Roebig in a sidecar to warn Boerner of the imminent danger) and gefreiter Rabitsch were wounded; Boerner then decided to set Cardito to fire and the German troops, under the command of Schulze-Oswald, destroyed three M4 Sherman tanks and two infantry trucks, managing to repel the Allied soldiers.[56][57][58]
In addition, Lieutenant Francesco de Fleury put up strenuous resistance with his unit until the arrival of the Anglo-Americans, managing to commandeer one truck, retreating north to join the Italian Social Republic military.[59]
After the Germans escaped, the Allies set up a prison camp, the so-called Camp 209, under the command of British soldiers.[60]
Post-war period and the birth of the Italian Republic[edit]
After the birth of the Italian Republic, Giuseppe Iazzetta was mayor from 1946 to 1953, a period during which the city experienced a strong economic boom.[29]
From 1953 to 1960, Armando Izzo was in charge, who built roads, sewers, two middle schools and started the construction of a scientific high school.[29]
During the 1960s, however, the city suffered an impoverishment of the population and the consequent emigration of inhabitants.[29]
On 9 July 1974, a serious air disaster occurred, the so-called TA-3B Skywarrior flight, in Arcopinto, on the border with Casoria, during which the aircraft, a Douglas TA-3B Skywarrior of the United States Navy, crashed in the Casoria countryside, disintegrating, causing the death of 5 passengers and 3 crew members and the wounding of 3 civilians.[61]
Moreover, in the 1980s, due to the 1980 Irpinia earthquake, the construction of the current Salicelle district was begun to house the earthquake victims and organised crime grew.[29]
On 6 June 2017, the Naples Afragola station, nicknamed 'The Gateway to the South', designed by architect Zaha Hadid and operational since 11 June 2017, was inaugurated in the presence of the then Prime Minister Paolo Gentiloni and Minister of Infrastructure and Transport Graziano Delrio.[62]
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^ a b Laforgia, pp. 1–12).
- ^ Nava, pp. 107–109).
- ^ Regii Neapolitani Archivi Monumenta (RNAM) (in Latin). Vol. VI.
in loco qui nominatur afraore had illu campu de sancti sebirinum. […] in suprascripto loco afraore
- ^ Castaldi, pp. 7–8).
- ^ Capasso, RRSC, 1970, p. 73).
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p RRSC, 2001, pp. 49–58).
- ^ Nava, pp. 101–126).
- ^ a b c d "Le origini di Afragola" (PDF). Il Salice Gioioso. Archived (PDF) from the original on 18 February 2020. Retrieved 23 August 2019.
- ^ a b c "Istituzione del Centro operativo di Afragola nell'ambito della soprintendenza per i beni archeologici di Napoli e Caserta". Camera dei deputati. 8 January 2014. Archived from the original on 18 February 2020. Retrieved 23 August 2019.
- ^ Mazzocchi, pp. 346–347).
- ^ a b c RRSC, 2009, pp. 101, 126–128).
- ^ "Scoperte nuove tombe sannitiche". Afragola Oggi. May 6, 1993. Archived from the original on February 18, 2020.
- ^ D'Angiò, Francesca (February 17, 2020). "Afragola tesoro storico: ritrovati numerosi altri reperti". Napoli Zon.it. Archived from the original on February 18, 2020.
- ^ Di Caterino, Marco (February 20, 2020). "Afragola, scavi dell'alta velocità: scoperta una necropoli cristiana". Il Mattino. Archived from the original on February 20, 2020. Retrieved February 20, 2020.
- ^ a b "Afragola". Istituto di Studi Atellani. Retrieved 5 February 2020.
- ^ Castaldi, p. 57).
- ^ RRSC, 2017, p. 68).
- ^ Capasso, pp. 11–28).
- ^ Carlo Cerbone, p. 8).
- ^ a b c d "Cenni Storici". Napoli: Rete Civica Metropolitana. Retrieved 5 November 2019.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag Carlo Cerbone, pp. 22–27).
- ^ Francesco della Ratta entry (in Italian) in the Enciclopedia italiana
- ^ Carlo Cerbone, p. 24).
- ^ a b c De Blasiis, pp. 73–74).
- ^ Leader, Marcotti, pp. 175–176).
- ^ Pagano, p. 500).
- ^ Carlo Cerbone, pp. 124–147, 181).
- ^ a b Raccolta Rassegna Storica dei Comuni, p. 57.)
- ^ a b c d e f g h Domenico Corcione (5 August 2014). "Storia di Afragola III - dall'Unità a un futuro incerto". Il Giornale di Casoria. Retrieved 10 September 2019.
- ^ "1602 – Dominio Domenicano". Comune di Afragola. Archived from the original on 16 July 2020. Retrieved 23 August 2019.
- ^ Castaldi, pp. 46–47).
- ^ A.S.N., Notai del XVII secolo, notaio Massimino Passero, 121/20, f. 159.
- ^ a b Capasso, RRSC, 1970, p. 74).
- ^ AA. VV., p. 11).
- ^ "3 giugno 1799: Afragola in rivolta". Alta Terra di Lavoro. 10 September 2018. Retrieved 23 August 2019.
- ^ a b c d e Perrone, pp. 326–329).
- ^ Colletta, p. 178).
- ^ Castaldi, p. 30).
- ^ Decreto Rattazzi, 1859.
- ^ Arpa, pp. 10, 21).
- ^ CE, p. 58).
- ^ "Monumento ai caduti della prima guerra mondiale". Ministero per i beni e le attività culturali. Retrieved 16 September 2019.
- ^ Regio Decreto 21 ottobre 1926, n. 1890, art. 1.
- ^ Regio Decreto 21 ottobre 1926, n. 1890, art. 2.
- ^ "ACS - Ufficio araldico - Fascicoli comunali". Archivio Centrale dello Stato. Archived from the original on April 19, 2016. Retrieved July 16, 2020.
- ^ Isabella Insolvibile. "Episodio di via Circonvallazione Afragola 2-10-1943" (PDF). Atlante delle stragi naziste e fasciste in Italia. Retrieved 25 July 2019.
- ^ Isabella Insolvibile. "Episodio della masseria D'Ambra Afragola 2-10-1943" (PDF). Atlante delle stragi naziste e fasciste in Italia. Retrieved 25 July 2019.
- ^ a b c Domenico Corcione (5 December 2015). "1943: Afragola nelle mani dei nazisti". Nuovacittà (32).
- ^ Omodeo, p. 530).
- ^ Comando supremo militare italiano, p. 590).
- ^ "War Diaries For The 11th Hussars, (Prince Albert's Own) September 1939 To March 1946". War Links. Archived from the original on March 11, 2021. Retrieved 11 March 2021.
- ^ "War Diaries of CC Battery, Royal Horse Artillery 1943". Desert Rats. Retrieved 4 August 2019.
- ^ a b Forty, pp. 165–167).
- ^ a b c d e Libertini, pp. 270–271).
- ^ Giuseppe Angelone. "Episodio di Orta di Atella 28-09-1943". Atlante delle stragi naziste e fasciste in Italia. Retrieved 20 November 2020.
- ^ a b Jentz, pp. 135–137).
- ^ a b Anderson, pp. 78–81).
- ^ a b Paterson, pp. 132–135).
- ^ ISSES, p. 134).
- ^ Di Fiore.
- ^ "Otto morti su un aereo americano precipitato nei pressi di Napoli" (PDF). L'Unità. 10 July 1974. p. 6. Archived from the original (PDF) on November 11, 2023. Retrieved 29 August 2019.
- ^ "L'inaugurazione della stazione di Napoli Afragola". FSNews. Ferrovie dello Stato Italiane. June 6, 2017. Retrieved November 5, 2019.
Bibliography[edit]
- Comando supremo militare italiano (1973). Bollettini di guerra del Comando supremo, 1940-1943. Ministero della difesa, Stato maggiore dell'Esercito, Ufficio storico.
- Istituto di studi storici economici e sociali (2006). Napoli nella Seconda guerra mondiale: atti del Convegno di studi storici tenutosi a Napoli il 5 marzo 2005. Istituto di studi storici economici e sociali.
- John Temple Leader; Giuseppe Marcotti (1889). Giovanni Acuto (Sir John Hawkwood): storia d'un condottiero. G. Barbera.
- Antonio Cassiano; Benedetto Vetere (2006). Dal giglio all'orso: i principi D'Angiò e Orsini del Balzo nel Salento. M. Congedo. ISBN 978-88-8086-683-1.
- AA. VV. (1970). Vol. 2 - Raccolta Rassegna Storica dei Comuni - Anno 1970. Istituto di Studi Atellani.
- AA. VV. (2001). Vol. 15 - Raccolta Rassegna Storica dei Comuni - Anno 2001. Istituto di Studi Atellani.
- AA. VV. (2009). Vol. 23 - Raccolta Rassegna Storica dei Comuni - Anno 2009. Istituto di Studi Atellani.
- AA. VV. (2018). Vol. 31 - Raccolta Rassegna Storica dei Comuni - Anno 2017. Istituto di Studi Atellani.
- Angelo Mazzocchi (2009). "Acerrae: Afragola (NA)". Rivista di Epigrafia Etrusca in Studi Etruschi (LXXIII–MMVII). Firenze: Istituto Nazionale di Studi Etruschi ed Italici.
- Elena Laforgia; Giuliana Boenzi; Tiziana Matarazzo; Monica Stanzione (7 October 2015). "18. Ambiente e biodiversità nella piana campana. Modalità di sfruttamento delle risorse vegetali in una comunità del Bronzo Antico. Il villaggio del Bronzo Antico di Afragola" (PDF). Istituto italiano di preistoria e protostoria.
- Maria Luisa Nava; Daniela Giampaola; Elena Laforgia; Giuliana Boenzi (2007) [2005]. "Tra il Clanis e il Sebeto: nuovi dati sull'occupazione della piana campana tra il Neolitico e l'età del Bronzo". Atti della XL Riunione Scientifica, Istituto Italiano di Preistoria e Protostoria, Strategie di insediamento fra Lazio e Campania in età preistorica e protostorica. Roma: Istituto italiano di preistoria e protostoria.
- Raccolta Rassegna Storica dei Comuni. Vol. 15. Istituto di Studi Atellani. 2010.
- Calendario ecclesiastico. Tipografia Centenari. 1884.
- Giuseppe de Blasiis, ed. (1887). Chronicon siculum incerti authori ab anno 340 ad annum 1396 in forma diary ex inedito codice Ottoboniano vaticano (in Latin). Napoli.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Clodomiro Perrone (1860). Storia della Repubblica partenopea del 1799 e vita de' suoi uomini celebri. Vol. 1. Napoli.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Giuseppe Arpa (1878). Relazione letta dal cav. Giuseppe Arpa regio delegato straordinario per il comune di Afragola nell'atto che il giorno 3 luglio 1873 insediava il nuovo consiglio comunale. Tipografia della Gazzetta di Napoli.
- Giuseppe Castaldi (1830). Memorie storiche del comune di Afragola raccolte da Giuseppe Castaldi. Sangiacomo.
- Filippo Maria Pagano (1835). Istoria del Regno di Napoli. Vol. 2. Marotta e Vanspadoch.
- Carlo Cerbone; Domenico De Stelleopardis (2004). Afragola feudale: per una storia degli insediamenti rurali del napoletano. Istituto di Studi Atellani.
- Thomas Anderson (2017). Sturmgeschütz: Panzer, Panzerjäger, Waffen-SS and Luftwaffe Units 1943–45. Bloomsbury Publishing.
- Gigi Di Fiore (2012). Controstoria della Liberazione. Biblioteca Universale Rizzoli.
- Gaetano Capasso (1976). Afragola, dieci secoli di storia. Aspetti e problemi. Napoli: Athena Mediterranea.
- Pietro Colletta (1861). Opere inedite or rare. Vol. I. Napoli.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Adolfo Omodeo (1960). Libertà e storia: scritti e discorsi politici. Giulio Einaudi Editore.
- George Forty (2014). Desert Rats at War: North Africa. Italy. Northwest Europe. Air Sea Media.
- Giacinto Libertini; Ludovico Migliaccio (2018). Quarto Volume Seconda Edizione Testimonianze per la memoria storica di Caivano raccolte da Ludovico Migliaccio e Collaboratori 2018 a cura di Giacinto Libertini. Istituto di Studi Atellani.
- AA. VV. (2000). Le suore Compassioniste ad Afragola. Afragola.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Domenico Corcione (2019). Il Caso Afragola. Per una rivalutazione della storia locale in ottica storiografica. Afragola.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Thomas L. Jentz (1997). Panzertruppen: The Complete Guide to the Creation and Combat Employment of Germany's Tank Force 1943-1945: The Complete Guide to the Creation & Combat. Combat Reports, Unit Strengths, Statistics. Vol. 2. Schiffer Publishing Ltd.
- Lawrence Paterson (2021). Fallschirm-Panzer-Division 'Hermann Göring' A History of the Luftwaffe's Only Armoured Division, 1933-1945. Greenhill Books.


