Wikipedia:Today's featured article/January 2007
| << | Today's featured articles for January 2007 | >> | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Su | Mo | Tu | We | Th | Fr | Sa |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
| 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 |
| 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 |
| 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 |
| 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 | |||
January 1
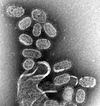
Influenza is an infectious disease of birds and mammals caused by an RNA virus of the family Orthomyxoviridae. Typically, influenza is transmitted from infected mammals through the air by coughs or sneezes, creating aerosols containing the virus, and from infected birds through their droppings. Infections occur through contact with these bodily fluids or with contaminated surfaces. Flu viruses can remain infectious for over 30 days at 0°C (32°F), about one week at human body temperature, and indefinitely at very cold temperatures. Flu spreads around the world in seasonal epidemics, killing millions of people in pandemic years and hundreds of thousands in non-pandemic years. Three influenza pandemics occurred in the 20th century—each following a major genetic change in the virus—and killed tens of millions of people. Often, these pandemics result from the spread of a flu virus between animal species. Since it first killed humans in Asia in the 1990s a deadly avian strain of H5N1 has posed the greatest influenza pandemic threat. Vaccinations against influenza are most common in high-risk humans in industrialised countries and farmed poultry. The most common human vaccine is the trivalent flu vaccine that contains purified and inactivated material from three viral strains. (more...)
Recently featured: Maraba Coffee – Kroger Babb – Redshift
January 2
Arthur Ernest Percival was a British Army officer and World War I hero. He built a successful military career during the interwar period but is most noted for his involvement in World War II, when he commanded the forces of the British Commonwealth during the Battle of Malaya and the subsequent Battle of Singapore. Percival's surrender to a smaller invading Imperial Japanese Army force was and remains the largest capitulation in British military history, and it fatally undermined Britain's prestige as an imperial power in the Far East. However, years of under-funding of Malaya's defences combined with the inexperienced, under-equipped nature of the Commonwealth army make it possible to hold a more sympathetic view of his command. (more...)
Recently featured: Influenza – Maraba Coffee – Kroger Babb
January 3
Yarralumla is a large suburb within Canberra, the capital city of Australia. Located approximately 3.5 kilometres south-west of the city centre, Yarralumla extends along the southern bank of Lake Burley Griffin. Europeans first settled the area in 1828, and it was named Yarralumla in 1834 from the Ngunnwal Indigenous Australian name for the area. Yarralumla is most noted for being the site of Government House, the official residence of the Governor-General of Australia, built in 1891. The suburb was officially gazetted in 1928 and today is home to approximately 3000 people and many diplomatic missions. In recent years, it has become one of Canberra's most desirable and expensive suburbs because of its leafy streets, attractive lakeside setting and central location. (more...)
Recently featured: Arthur Ernest Percival – Influenza – Maraba Coffee
January 4
John Brooke-Little was an influential and popular writer on heraldic subjects and a long-serving officer of arms at the College of Arms in London, England. In 1947, while still a student, Brooke-Little founded the "Society of Heraldic Antiquaries", now known as The Heraldry Society and recognized as one of the leading learned societies in its field. He served as the society's chairman for 50 years and then as its President from 1997 until his death in 2006. In addition to founding this group, Brooke-Little was involved in other heraldic groups and societies and worked for many years as an officer of arms. Having started his career as Bluemantle Pursuivant, Brooke-Little worked his way up to the second-highest heraldic office in England–Clarenceux King of Arms. (more...)
Recently featured: Yarralumla – Arthur Ernest Percival – Influenza
January 5
The Adventures of Tintin is a comic book series created by Belgian artist Hergé. The series first appeared in 1929 in a children's supplement to the French-language Belgian newspaper Le Vingtième Siècle. Set in a painstakingly researched world closely mirroring reality, The Adventures of Tintin presents colourful characters in distinctive, well-realised settings. The hero of the series is the eponymous Tintin, a young reporter and traveller aided in his adventures by his faithful dog Snowy. The success of the series saw serialised strips collected into albums, spun into a successful magazine, and adapted for both film and theatre. The series is one of the most popular European comics of the 20th century, with translations published in over 50 languages and more than 200 million copies of the books sold to date. The comic strip series has long been admired for its clean, expressive drawings, done in Hergé's signature ligne claire style. The Adventures of Tintin straddles a variety of genres, from mysteries to political thrillers to science fiction. Stories always feature slapstick humour, offset in later albums by sophisticated satire and political and cultural commentary. (more...)
Recently featured: John Brooke-Little – Yarralumla – Arthur Ernest Percival
January 6
Ahmose I (mummified head pictured) was a pharaoh of ancient Egypt and the founder of the Eighteenth dynasty. He was a member of the Theban royal house, the son of King Tao II Seqenenre, and brother of the last King of the Seventeenth dynasty, King Kamose. Ahmose I assumed the throne after the death of his brother. During his reign he completed the conquest and expulsion of the Hyksos from the delta region, restored Theban rule over the whole of Egypt, and successfully reasserted Egyptian power in its formerly subject territories of Nubia and Canaan. He then reorganized the administration of the country, reopened quarries, mines, and trade routes, and began massive construction projects of a type that had not been undertaken since the time of the Middle Kingdom. This building program culminated in the construction of the last pyramid built by native Egyptian rulers. Ahmose's reign laid the foundations for the New Kingdom, under which Egyptian power reached its peak. His reign is usually dated to about 1550-1525 BC. (more...)
Recently featured: The Adventures of Tintin – John Brooke-Little – Yarralumla
January 7
Genesis is an English progressive rock band formed in 1967. The band's notable members included Peter Gabriel and Phil Collins, both of whom achieved additional success as solo artists and in other ventures. With approximately 150 million albums sold worldwide, Genesis is one of the top 30 highest selling recording artists of all time. Between the 1970s and 1980s, Genesis changed from a progressive art rock band, with complex song structures, elaborate instrumentation, and theatrical live shows to a more pop-oriented band. Genesis' change of musical direction to accessible music with melodic hooks gave them their first UK #1 album, Duke, as well as their only U.S. #1 single, "Invisible Touch". Initially fronted by Peter Gabriel, Genesis has experienced several personnel changes over the years. Collins took over from Gabriel after the latter's departure from the group in 1975. After over two decades of being the band's frontman, Collins left the group in 1996 and was replaced by former Stiltskin singer Ray Wilson for the 1997 album Calling All Stations. Due to the commercial failure of the album, and after three decades of activity, the band announced that it was on an indefinite hiatus. On October 18 2006, the British Broadcasting Corporation announced that members of the band had agreed to reunite for a world tour and were exploring the possibility of recording new material. (more...)
Recently featured: Ahmose I – The Adventures of Tintin – John Brooke-Little
January 8
Operation Auca was an attempt by five Evangelical Christian missionaries from the United States to make contact with the Huaorani people of the rainforest of Ecuador. The Huaorani, also known as the Aucas, were an isolated tribe known for their violence, both against their own people and outsiders who entered their territory. With the intention of being the first Protestants to evangelize the Huaorani, the missionaries began making regular flights over Huaorani settlements in September 1955, dropping gifts. After several months of exchanging gifts, on January 2, 1956, the missionaries established a camp at "Palm Beach", a sandbar along the Curaray River, a few miles from Huaorani settlements. Their efforts culminated on January 8, 1956, when all five—Jim Elliot, Nate Saint, Ed McCully, Peter Fleming, and Roger Youderian—were attacked and speared by a group of Huaorani warriors. The news of their deaths was broadcast around the world, and Life magazine covered the event with a photo essay. The deaths of the men galvanized the missionary effort in the United States, sparking an outpouring of funding for evangelization efforts around the world. Their work is still frequently remembered in evangelical publications, and in 2006, was the subject of the film production End of the Spear. (more...)
Recently featured: Genesis – Ahmose I – The Adventures of Tintin
January 9
An invasion is a military action consisting of armed forces of one geopolitical entity entering territory controlled by another such entity, generally with the objective of conquering territory or altering the established government. An invasion can be the cause of a war, it can be used as a part of a larger strategy to end a war, or it can constitute an entire war in and of itself. The term usually connotes a strategic endeavor of substantial magnitude; because the goals of an invasion are usually large-scale and long-term, large forces are needed to hold territory and protect the interests of the invading entity. Smaller and lighter tactical infiltrations are not generally considered invasions, being more often classified as skirmishes, sorties, targeted killings, assassinations or reconnaissance in force. By definition, an invasion is an attack from outside forces. As such, rebellions, civil wars, coups d'etat, and internal acts of democide or other acts of oppression are generally not considered invasions. (more...)
Recently featured: Operation Auca – Genesis – Ahmose I
January 10
The fauna of Puerto Rico is similar to other island archipelago faunas, exhibiting high levels of endemism and low, skewed taxonomic diversity. Bats are the only extant native terrestrial mammals in Puerto Rico. Other terrestrial mammals are introduced species such as cats, goats, sheep, the Indian Mongoose, and escaped monkeys. Marine mammals include dolphins, manatees and whales. Of the 349 bird species, about 120 breed in the archipelago and 47.5% are accidental or rare. The most recognizable and famous animal of Puerto Rico is probably the coquí, a small endemic frog and one of the 85 species that comprise Puerto Rico's herpetofauna. No native freshwater fish occur in Puerto Rico, but some species, introduced by humans, have established populations in reservoirs and rivers. The low richness-high diversity pattern is also apparent among invertebrates, which constitute most of the archipelago's fauna. The arrival of indigenous people about 4,000 years ago and, to a larger extent, of Europeans more than 500 years ago had a significant impact on Puerto Rico's fauna. Hunting, habitat destruction, and the introduction of non-native species led to extinctions and extirpations. Conservation efforts, the most notable for the Puerto Rican Parrot, began in the second half of the 20th century. (more...)
Recently featured: Invasion – Operation Auca – Genesis
January 11
Half-Life 2 is a science fiction first-person shooter computer game and the sequel to Half-Life. It was developed by the Valve Software Corporation and was released on November 16 2004 following a protracted five-year development cycle during which the game's source code was leaked to the Internet. The game garnered near unanimous positive reviews and received critical acclaim, winning over 35 Game of the Year awards for 2005. Originally available only for Windows-based personal computers, the game has since been ported onto the Xbox console, and is due to be released additionally for the Xbox 360 and PlayStation 3 in 2007. Taking place in and around the fictional City 17 sometime in the near future, Half-Life 2 follows the scientist Gordon Freeman. Dr. Freeman is thrust into a dystopian environment in which the aftermath of the Black Mesa Incident has come to bear fully upon human society. The game uses the Source game engine, which includes a heavily modified version of the Havok physics engine. Overall, the Half-Life franchise, including Counter-Strike and Day of Defeat, has seen over 15 million sales. (more...)
Recently featured: Fauna of Puerto Rico – Invasion – Operation Auca
January 12
Richard III is a 1955 British film adaptation of William Shakespeare's historical play Richard III. The film also contains elements of Shakespeare's Henry VI, part 3. It was directed by Laurence Olivier, who also played Richard. The cast includes many noted Shakespearean actors of the time, including a quartet of acting knights. The film depicts Richard plotting and conspiring to grasp the throne from his brother, King Edward, played by Cedric Hardwicke. In the process, many are killed and betrayed, with Richard's evil leading to his own downfall. The prologue of the film states that history without its legends would be "a dry matter indeed", thus the film admits that it is not portraying the actual events of the time, but rather the legend. Many critics now consider Olivier's Richard III his best screen version of Shakespeare. As well, the British Film Institute has called Olivier's rendition of the play "definitive" and that it has done more to popularise Shakespeare than any other single piece of work. (more...)
Recently featured: Half-Life 2 – Fauna of Puerto Rico – Invasion
January 13
Alcibiades was a prominent Athenian statesman, orator, and general. The last famous member of an aristocratic family that fell from prominence after the Peloponnesian War, he played a major role in the second half of that conflict as a strategic advisor, military commander, and politician. During the course of the Peloponnesian War, Alcibiades changed his allegiance on several occasions. In his native Athens in the early 410s BC, he advocated for an aggressive foreign policy, and was a prominent proponent of the Sicilian Expedition, but fled to Sparta after his political enemies brought charges of sacrilege against him. In the years that he served Sparta, Alcibiades played a crucial role in Athens' undoing; the capture of Decelea and the revolts of several critical Athenian subjects occurred either at his suggestion or under his supervision. Once restored to his native city, however, he played a crucial role in a string of Athenian victories that eventually brought Sparta to seek a peace with Athens. He favored unconventional tactics, frequently winning cities over by treachery or negotiation rather than by siege. Alcibiades' military and political talents frequently proved valuable to whichever state currently held his allegiance, but his capacity for making powerful enemies ensured that he never remained in one place for long, and, by the end of the war that he had helped rekindle in the early 410s, his days of political relevance were a bygone memory. (more...)
Recently featured: Richard III – Half-Life 2 – Fauna of Puerto Rico
January 14
Shoshone National Forest spans nearly 2.5 million acres (10,000 km²) in the U.S. state of Wyoming and was the first federally protected forest in the United States. Originally a part of the Yellowstone Timberland Reserve, the forest was created by an act of Congress and signed into law by U.S. President Benjamin Harrison in 1891. A total of four wilderness areas are located within the forest, protecting more than half of the managed land area from development. From sagebrush plains through dense spruce and fir forest to craggy mountain peaks, Shoshone National Forest has a rich biodiversity rarely matched in any protected area. Three major mountain ranges are partially located in the forest including the Absaroka, the Beartooth and the Wind River Range. Yellowstone National Park forms part of the forest boundary to the west; while south of Yellowstone, the Continental Divide separates the forest from its neighbor, the Bridger-Teton National Forest, to the west. All of the forest is a part of the Greater Yellowstone Ecosystem, an unbroken expanse of federally protected lands encompassing an estimated 20 million acres (81,000 km²). (more...)
Recently featured: Alcibiades – Richard III – Half-Life 2
January 15
Kitsune are foxes in Japanese folklore. Stories depict them as intelligent beings who possess great magical abilities that increase with their age and wisdom. Foremost among these is the ability to assume human form. While some folktales speak of kitsune employing this ability to trick others — as foxes in folklore often do — others portray them as faithful guardians, friends, lovers, and wives. Foxes and human beings lived in close proximity in ancient Japan; this gave rise to legends about the creatures. Kitsune have become closely associated with Inari, a Shinto kami or spirit, and serve as his messengers. This role has reinforced the fox's supernatural significance. The more tails a kitsune has — they may have as many as nine — the older, wiser, and more powerful it is. Because of their potential power and influence, some people make offerings to them as to a deity. (more...)
Recently featured: Shoshone National Forest – Alcibiades – Richard III
January 16
Halloween is a 1978 American independent horror film set in the fictional Midwest town of Haddonfield, Illinois, on Halloween. The film was directed by John Carpenter and stars Donald Pleasence as Dr. Sam Loomis, Jamie Lee Curtis as Laurie Strode, and Nick Castle as Michael Myers. The film centers on Michael Myers' escape from a psychiatric hospital, his murdering of teenagers, and Sam Loomis's attempts to track and stop Myers. Halloween was produced on a budget of only $325,000 and grossed $47 million at the box office in the United States, making it one of the most successful independent films in American movie history. Many critics credit this film as the first in a long line of slasher films inspired by Alfred Hitchcock's Psycho (1960). The movie originated many of the clichés seen in low-budget horror films of the 1980s and 1990s, although first-time viewers of Halloween may be surprised by the fact that the film contains little actual graphic violence or gore. (more...)
Recently featured: Kitsune – Shoshone National Forest – Alcibiades
January 17
Sheffield Wednesday F.C. is one of the oldest football clubs in England; this season they play in the Football League. Based in Sheffield, South Yorkshire, England, Sheffield Wednesday's chief rivals are Sheffield United F.C. with whom they play in the Steel City Derby. As of 2006, The Owls have won four league titles, three FA Cups and one League Cup, but their League Cup triumph (secured in 1991) is their only major trophy since World War II. They did reach both domestic cup finals in 1993, but lost 2-1 to Arsenal each time. Sheffield Wednesday currently play in the Football League Championship. Home games are played at Hillsborough stadium in Sheffield, which had staged numerous FA Cup semi-finals prior to the 1989 Hillsborough disaster which claimed the lives of 96 Liverpool fans. (more...)
Recently featured: Halloween – Kitsune – Shoshone National Forest
January 18
Restoration literature is the literature written in English during the period commonly referred to as the English Restoration, corresponding with the last years of the direct Stuart reign in England, Scotland, Wales, and Ireland. In general, the term is used to denote roughly homogeneous styles of literature that centre on a celebration of or reaction to the restored court of Charles II. It is a literature that includes extremes, for it encloses both Paradise Lost and the Earl of Rochester's Sodom, the high-spirited sexual comedy of The Country Wife and the moral wisdom of Pilgrim's Progress. It saw Locke's Treatises on Government, the founding of the Royal Society, the experiments and holy meditations of Robert Boyle, the hysterical attacks on theatres from Jeremy Collier, and the pioneering of literary criticism from John Dryden and John Dennis. It saw news become a commodity, the essay develop into a periodical artform, the beginnings of textual criticism, and the emergence of the stock market. (more...)
Recently featured: Sheffield Wednesday F.C. – Halloween – Kitsune
January 19
El Greco was a prominent painter, sculptor and architect of the Spanish Renaissance. El Greco was born in Crete, which was at that time part of the Republic of Venice, and at 26 travelled to Venice to study. In 1570 he moved to Rome, where he opened a workshop and executed a series of works. During his stay in Italy, El Greco enriched his style with elements of Mannerism and of the Venetian Renaissance. In 1577 he emigrated to Toledo, Spain, where he lived and worked until his death. In Toledo El Greco received several major commissions and produced his best known paintings. El Greco's dramatic and expressionistic style was met with puzzlement by his contemporaries but found appreciation in the 20th century. El Greco is regarded as a precursor of both Expressionism and Cubism, while his personality and works were a source of inspiration for poets and writers such as Rainer Maria Rilke and Nikos Kazantzakis. El Greco has been characterized by modern scholars as an artist so individual that he belongs to no conventional school. He is best known for tortuously elongated figures and often fantastic or phantasmagorical pigmentation, marrying Byzantine traditions with those of Western civilization. (more...)
Recently featured: Restoration literature – Sheffield Wednesday F.C. – Halloween
January 20
Bacteria are unicellular microorganisms. They are typically a few micrometres long and have many different shapes including spheres, rods and spirals. The study of bacteria is bacteriology, a branch of microbiology. Bacteria are ubiquitous, living in every possible habitat on the planet including soil, underwater, deep in the earth's crust and even such environments as acidic hot springs and radioactive waste. In all, there are around five nonillion (5 × 1030) bacteria in the world. There are 10 times more bacterial cells than human cells in the human body, with large numbers of bacteria on the skin and in the digestive tract. Although the vast majority of these bacteria are harmless or beneficial, a few pathogenic bacteria cause infectious diseases, including cholera, syphilis, anthrax, leprosy and bubonic plague. The most common fatal bacterial disease is tuberculosis, which kills about 2 million people a year, mostly in sub-Saharan Africa. Bacteria are prokaryotes and, unlike animals and other eukaryotes, bacterial cells do not contain a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles. Although the term bacteria has traditionally been generally applied to all prokaryotes, the scientific nomenclature changed after the discovery that prokaryotic life consists of two very different groups of organisms that evolved independently from an ancient common ancestor. (more...)
Recently featured: El Greco – Restoration literature – Sheffield Wednesday F.C.
January 21
The music of the Lesser Antilles encompasses the musics of Martinique, Guadeloupe, Dominica, Trinidad and Tobago, Aruba and the Netherlands Antilles, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, Anguilla, Antigua and Barbuda, Barbados, Grenada, Virgin Islands, Saint Lucia, Saint Kitts and Nevis and Montserrat. The Lesser Antilles' musical cultures are largely based on the music of African slaves brought by European traders and colonizers. The African musical elements are a hybrid of instruments and styles from numerous West African tribes, while the European slaveholders added their own musics into the mix, as did immigrants from India. In many ways, the Lesser Antilles can be musically divided based on which nation colonized them. The ex-British colonies include Trinidad and Tobago, whose calypso style is an especially potent part of the music of the other former British colonies, which also share traditions like the Big Drum dance. The French islands of Martinique and Guadeloupe share the popular zouk style, and have also had extensive musical contact with the music of Haiti, itself once a French colony though not part of the Lesser Antilles. The Dutch colonies share the combined rhythm popular style. The islands also share a passion for kaseko, a genre of Surinamese music; Suriname and its neighbors Guyana and French Guiana share folk and popular styles that are connected enough to the Antilles and other Caribbean islands that both countries are studied in the broader context of Antillean or Caribbean music. (more...)
Recently featured: Bacteria – El Greco – Restoration literature
January 22
Indian Standard Time is the time observed throughout India, with a time offset of UTC+5:30. India does not observe daylight saving time (DST) or other seasonal adjustments, although DST was used briefly during the Sino–Indian War of 1962, and the Indo–Pakistani Wars of 1965 and of 1971. In military and aviation time, IST is designated E* = Echo*. Indian Standard Time is calculated on the basis of 82.5 °E longitude which is just west of the town of Mirzapur, near Allahabad in the state of Uttar Pradesh. The longitude difference between Mirzapur and the United Kingdom's Royal Observatory at Greenwich translates to an exact time difference of 5 hours and 30 minutes. Local time is calculated from a clock tower at the Allahabad Observatory though the official time-keeping devices are entrusted to the National Physical Laboratory, located in New Delhi. (more...)
Recently featured: Music of the Lesser Antilles – Bacteria – El Greco
January 23
The Battle of Cannae was a major battle of the Second Punic War, taking place on August 2, 216 BC near the town of Cannae in Apulia in southeast Italy. The Carthaginian army under Hannibal annihilated a numerically superior Roman army under command of the consuls Lucius Aemilius Paullus and Gaius Terentius Varro. Following the Battle of Cannae, Capua and several other Italian city-states defected from the Roman Republic. Although the battle failed to decide the outcome of the war in favour of Carthage, it is today regarded as one of the greatest tactical feats in military history. In terms of the number of lives lost within a single day, Cannae is among the costliest battles in all of recorded human history. (more...)
Recently featured: Indian Standard Time – Music of the Lesser Antilles – Bacteria
January 24
The United States Bill of Rights consists of the first ten amendments to the United States Constitution. These amendments limit the powers of the federal government, protecting the rights of the people by preventing Congress from abridging freedom of speech, freedom of the press, freedom of assembly, freedom of religious worship, the freedom to petition, and the right to keep and bear arms, preventing unreasonable search and seizure, cruel and unusual punishment, and self-incrimination, and guaranteeing due process of law and a speedy, public trial with an impartial jury. In addition, the Bill of Rights states that "the enumeration in the Constitution, of certain rights, shall not be construed to deny or disparage others retained by the people," and reserves all powers not granted to the federal government to the citizenry or States. The Bill of Rights plays a central role in American law and government, and remains a fundamental symbol of the freedoms and culture of the nation. (more...)
Recently featured: Battle of Cannae – Indian Standard Time – Music of the Lesser Antilles
January 25
Hasekura Tsunenaga was a Japanese samurai and retainer of Date Masamune, the daimyo of Sendai. He led an embassy to Mexico and then Europe between 1613 and 1620 (called the Keichō Embassy), after which he returned to Japan. He was the first-ever Japanese official ambassador to the Americas and arguably Europe, and became the key protagonist in the first recorded instance of Franco-Japanese relations. Although Hasekura's embassy created a strong impression in Europe, it happened at a time when Japan was moving towards the suppression of Christianity, so that European monarchs such as the King of Spain ultimately denied the trading agreements Hasekura had been seeking. Hasekura returned to Japan in 1620 and died of illness a year later, his embassy seemingly ending with few results in an increasingly isolationist Japan. (more...)
Recently featured: United States Bill of Rights – Battle of Cannae – Indian Standard Time
January 26
The history of saffron cultivation and use reaches back more than 3,000 years and spans many cultures, continents, and civilisations. Saffron, a spice derived from the dried stigmas of the saffron crocus, has remained among the world's most costly substances throughout history. With its bitter taste, hay-like fragrance, and slight metallic notes, saffron has been used as a seasoning, fragrance, dye, and medicine. Saffron is native to Southwest Asia, but was first cultivated in Greece. The wild precursor of domesticated saffron crocus is Crocus cartwrightianus. Human cultivators bred C. cartwrightianus specimens by selecting for plants with abnormally long stigmas. Thus, sometime in late Bronze Age Crete, a mutant form of C. cartwrightianus, C. sativus, emerged. Saffron was first documented in a 7th-century BC Assyrian botanical reference compiled under Ashurbanipal. Since then, documentation of saffron's use over a span of 4,000 years in the treatment of some ninety illnesses has been uncovered. Saffron slowly spread throughout much of Eurasia, later reaching parts of North Africa, North America, and Oceania. (more...)
Recently featured: Hasekura Tsunenaga – United States Bill of Rights – Battle of Cannae
January 27
Alain Prost is a retired French racing driver and four-time Formula One World Champion. In terms of World Drivers' Championship titles, only Juan Manuel Fangio and Michael Schumacher have been more successful in the sport's history. He held the record for most Grand Prix victories from 1987 to 2001, when it was broken by Schumacher. Prost discovered karting at the age of 14 during a family holiday. He won the French and European F3 championships before joining McLaren in 1980 at the age of 25. He finished in the points on his Formula One debut and took his first of 51 race victories at his home Grand Prix in France a year later, while he was driving for the Renault Factory team. Prost employed a smooth, relaxed style behind the wheel, deliberately modeling himself on personal heroes like Jackie Stewart and Jim Clark. In 1997 Prost took over the French Ligier team, running it as Prost Grand Prix until it went bankrupt in 2001. In 2006, Prost started his fourth year in the Andros Trophy, which is an Ice Racing competition. Denis Jenkinson, a well respected journalist, describes Prost as "a very warm and uncomplicated man who doesn't rely on passion or inspiration. Nor does he indulge in showmanship or bullshit. He is capable of a level of mental discipline beyond the comprehension of most people." (more...)
Recently featured: History of saffron – Hasekura Tsunenaga – United States Bill of Rights
January 28
The Space Shuttle Challenger disaster was a space disaster that occurred at 11:39 a.m. EST on January 28, 1986, when the NASA Space Shuttle Challenger disintegrated 73 seconds into its flight after an O-ring seal in its right solid rocket booster (SRB) failed. The seal failure caused a flame leak from the solid rocket booster that impinged upon the adjacent external propellant tank. Within seconds, the flame caused structural failure of the external tank, and the orbiter broke up abruptly due to aerodynamic forces. The shuttle was destroyed and all seven crew members were killed. The disaster resulted in a 32-month hiatus in the shuttle program and the formation of the Rogers Commission, a special commission appointed by President Ronald Reagan to investigate the accident. The Rogers Commission found that NASA's organizational culture and decision-making processes had been a key contributing factor to the accident. The Challenger disaster has been used as a case study in many discussions of engineering safety and workplace ethics and has inspired both a television movie, Challenger, which was made in 1990, and a theatrical movie of the same name, scheduled for release in 2008. (more...)
Recently featured: Alain Prost – Hasekura Tsunenaga – History of saffron
January 29
Hurricane Juan was a significant hurricane that struck much of Atlantic Canada in late September 2003. It was the tenth named storm and the sixth hurricane of the 2003 Atlantic hurricane season. Juan formed southeast of Bermuda on September 24 and peaked at 105 mph (165 km/h) as it rapidly approached the coast of Nova Scotia, losing little intensity over the cooler waters. Juan made landfall near Halifax, Nova Scotia early on September 29 while still a Category 2 hurricane, and remained a hurricane across Nova Scotia and onto Prince Edward Island, weakening to a tropical storm over the island. It was absorbed by another extratropical low later on September 29 near Anticosti Island in the Gulf of St. Lawrence. The storm left extensive damage across central Nova Scotia and into Prince Edward Island, with lesser damage east and west of the storm center. Most of the damage was as a result of the high winds that whipped across the region. Juan resulted in eight fatalities and over $200 million (in 2003 USD) in damage. It was described as the worst storm to hit Halifax since 1893. (more...)
Recently featured: Space Shuttle Challenger disaster – Alain Prost – History of saffron
January 30
The New Radicals were an American rock band in the late 1990s, centered on front man Gregg Alexander, who wrote and produced all of their songs and was the sole constant member. They released only one album, 1998's Maybe You've Been Brainwashed Too, a pop rock album heavily influenced by the funk, rock and soul of the 1970s, containing—amongst radio-friendly modern rock tracks and love songs—strong criticism of Corporate America. The band is best known for their debut single "You Get What You Give", which became a top 5 hit in the United Kingdom and whose celebrity-dissing lyrics at the end of the song provided a minor media spectacle. Tired of touring and promotional interviews, Alexander disbanded the group in mid 1999 before the release of their second single, "Someday We'll Know", to focus on writing and producing songs for other artists. As a result, "Someday We'll Know" received little attention in most countries and the band is widely considered a one-hit wonder. (more...)
Recently featured: Hurricane Juan – Space Shuttle Challenger disaster – Alain Prost
January 31
Regulamentul Organic was a quasi-constitutional organic law enforced in 1831-1832 by the Imperial Russian authorities in Moldavia and Wallachia (the two Danubian Principalities that were to become the basis of the modern Romanian state). The official onset of a common Russian protectorate lasting until 1854, and itself officially in place until 1858, the document signified a partial confirmation of traditional government (including rule by the hospodars). Conservative in its scope, it also engendered a period of unprecedented reforms which provided a setting for the Westernization of local society. The Regulament offered the two Principalities their first common system of government. (more...)
Recently featured: New Radicals – Hurricane Juan – Space Shuttle Challenger disaster