User talk:Makumbe/sandbox
ndbox}}
| Arabian wolf | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Carnivora |
| Family: | Canidae |
| Genus: | Canis |
| Species: | |
| Subspecies: | C. l. arabs
|
| Trinomial name | |
| Canis lupus arabs | |
| |
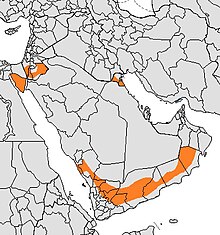
| Arabian wolf range | |
The Arabian wolf (Canis lupus arabs) is a subspecies of gray wolf which lives on the Arabian peninsula. It is a small, desert adapted wolf that normally lives in small groups and is omnivorous; eating carrion and garbage as well as small to medium-sized prey.[3]
Taxonomy[edit]
The Arabian wolf is designated Canis lupus arabs by the British zoologist Reginald Innes Pocock.[4] Once thought to possibly be C.L. Pallipes (the Indian wolf) the Arabian wolf is now thought to be its own sub-species- C.l. arabs as designated by Pocock in 1934. Pocock noted its smaller skull and smaller size.[5] A new study suggests that genetically the Arabian wolf is closer to C.l. lupus than it is to pallipes. This 2014 study posits that at this point the C.l. arabs subspecies designation should be used.[6] There is admixture with domestic dogs but it is unclear whether this is why it is closer genetically to C.l. lupus.[7] This raises a concern of extinction by hybridization as Arabian wolves are more adapted to desert life than wolf/dog hybrids.[8]
Description[edit]
The Arabian wolf is small for Canis lupus and stands on average 26 inches (66 cm) at shoulder height and weighs an average of 40 pounds (18.14 kg). Along with the Indian wolf, it is probably smaller than other wolves to help it adapt to life in a hot, dry climate. [9] This is an example of Bergmann's rule, where mammal size varies by the warmth of their environment. Its ears are proportionally larger in relation to its body size when compared to other sub-species of Canis lupus, an adaptation probably developed to help disperse body heat.[10] Arabian wolves do not usually live in large packs, and instead hunt in pairs or in groups of about three or four animals.[11] [12]They have a short thin coat which is usually a grayish beige color.[13] "...a mixture of black and slightly buffy grey," according to Pocock in his 1935 description.[14]Like other canines, the Arabian Wolf has no sweat glands - it controls body temperature by rapid panting which causes evaporation from the lungs.[15] It is distinguished from the Indian wolf by its smaller skull and smaller size and thinner coat.[16]

Diet[edit]

Arabian wolves are omnivorous and in some areas largely dependent on human excess products and waste.[17] They also feed on hares, rodents, small ungulates, and carrion. Opportunistically almost any small animal including fish, snails, baby baboons can be part of their diet; they also eat garbage.[18] Arabian wolves hunt small to medium-sized animals such as cape hares, Dorcas gazelles, and ibexes, though they feed on carrion and livestock when in the vicinity of human settlements.[19] Because Arabian wolves can attack and eat any domestic animals up to the size of a goat, Bedouins and farmers will not hesitate to shoot, poison, or trap them.[20]
Range and conservation[edit]
The Arabian wolf was once found throughout the Arabian Peninsula, but now lives only in small pockets in southern Israel,[21] southern and western Iraq, Oman, Yemen, Jordan,[22] Saudi Arabia,[23] and some parts of the Sinai Peninsula in Egypt.[24]
The Arabian wolf is rare throughout most of its range because of human persecution.[25] In Oman wolf populations have increased because of a ban on hunting, and they may naturally re-establish themselves in certain places within the region in the relatively near term.[26] In Israel, between 100 and 150 Arabian wolves are found across the Negev and the Arava. The U.A.E. has a captive breeding program and the wolf is protected in Oman and Israel; but elsewhere its future is uncertain.[27] In Saudi Arabia the wolf is protected in places and still exists in places with sparse human activity.[28]
References[edit]
- ^ a b {{IUCN |assessors=Mech, L.D., Boitani, L. (IUCN SSC Wolf Specialist Group) |year=2010 |id=3746 |title=Canis lupus|version=2011.2}}
- ^ a b Pocock, R.I. (1934). "LXVI.—Preliminary diagnoses of some new races of South Arabian mammals". Journal of Natural History Series 10. 14 (84): 635–636. doi:10.1080/00222933408654939.
- ^ http://www.jstor.org/stable/1383305?&seq=1#page_scan_tab_contents%7CDOI: 10.2307/1383305
- ^ Pocock, R.I. (1934). "LXVI.—Preliminary diagnoses of some new races of South Arabian mammals". Annals and Magazine of Natural History. 14 (84): 635–636. doi:10.1080/00222933408654939.
- ^ Pocock, R.I. (1935). "XLII.—The mammals collected in S.E. Arabia by Mr. Bertram Thomas and Mr. H. St. J. Philby". Annals and Magazine of Natural History. 15 (88): 441–467. doi:10.1080/00222933508654985.
- ^ http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1616504714000603?via%3Dihub
- ^ http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1616504714000603?via%3Dihub
- ^ http://canids.org/CBC/20/Arabian_wolf_and_domestic_dog_in_saudi_arabia.pdf
- ^ https://books.google.com/books/about/Wolves_of_the_World.html?id=M_q5FP2olaEC PG. 21
- ^ Mills, Clarence A. (1945). "Influence of Environmental Temperatures on Warm-Blooded Animals". Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 46: 97–105. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.1945.tb36162.x. S2CID 84266753.
- ^ https://books.google.com/books?id=6PTl3wUEJtgC&pg=PA219&lpg=PA219&dq=arabian+wolf+oman&source=bl&ots=iOuJXNjy_v&sig=buo7bp-NlFItWbglBByWj--C3l0&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwioub_y6N7VAhWjjVQKHSB7DTIQ6AEIXzAL#v=onepage&q=arabian&f=false pg 219
- ^ Hefner, Reuven; Geffen, Eli (1999). "Group Size and Home Range of the Arabian Wolf (Canis lupus) in Southern Israel". Journal of Mammalogy. 80 (2): 611–619. doi:10.2307/1383305. JSTOR 1383305.
- ^ http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1096-3642.1935.tb01687.x/abstract PG. 672-673
- ^ Hefner, Reuven; Geffen, Eli (1999). "Group Size and Home Range of the Arabian Wolf (Canis lupus) in Southern Israel". Journal of Mammalogy. 80 (2): 611–619. doi:10.2307/1383305. JSTOR 1383305.
- ^ Harrington & Paquet 1983.
- ^ http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1096-3642.1935.tb01687.x/abstract PG. 672-673
- ^ Hefner, Reuven; Geffen, Eli (1999). "Group Size and Home Range of the Arabian Wolf (Canis lupus) in Southern Israel". Journal of Mammalogy. 80 (2): 611–619. doi:10.2307/1383305. JSTOR 1383305.
- ^ http://nwrc.gov.sa/NWRC_ARB/mzyd_files/1-1994-005.pdf
- ^ Hefner & Geffen 1999. sfn error: multiple targets (4×): CITEREFHefnerGeffen1999 (help)
- ^ http://www.canids.org/canidnews/13/Arabian_wolf_in_Saudi_Arabia.pdf
- ^ http://www.tau.ac.il/~geffene/PDFs/89-Oryx_2013.pdf
- ^ http://journals.tubitak.gov.tr/zoology/issues/zoo-01-25-1/zoo-25-1-3-9909-8.pdf
- ^ http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1616504714000603?via%3Dihub
- ^ http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0140196317300174
- ^ https://academic.oup.com/jmammal/article/80/2/611/899899/Group-Size-and-Home-Range-of-the-Arabian-Wolf
- ^ Natural Emirates: Wildlife and Environment of the United Arab Emirates. 1996. ISBN 9781900724029.
- ^ http://www.middleeasteye.net/in-depth/features/conservation-conflict-isis-advancement-and-arabian-wolf-811485183
- ^ http://www.canids.org/canidnews/13/Arabian_wolf_in_Saudi_Arabia.pdf
Citation generator[edit]
- Journal [2]
- Web [3]
- Book [4]
- Google book app http://reftag.appspot.com/
| Arabian wolf | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Carnivora |
| Family: | Canidae |
| Genus: | Canis |
| Species: | |
| Subspecies: | C. l. arabs
|
| Trinomial name | |
| Canis lupus arabs | |

| |
| Arabian wolf range | |
The Arabian wolf (Canis lupus arabs) is a subspecies of gray wolf which lives on the Arabian peninsula. It is the smallest sized wolf known. It is a desert-adapted wolf that normally lives in small groups and is omnivorous, eating carrion and garbage as well as small to medium-sized prey.[7]
Taxonomy[edit]
Once thought to possibly be C. l. pallipes (the Indian wolf), the Arabian wolf was designated Canis lupus arabs by the British zoologist Reginald Innes Pocock in 1934.[8] Pocock noted its smaller skull and smaller size.[9] In the third edition of Mammal Species of the World published in 2005, the mammalogist W. Christopher Wozencraft listed under the wolf Canis lupus the subspecies Canis lupus arabs.[10] A 2014 study suggests that genetically the Arabian wolf is closer to C. l. lupus than it is to C. l. pallipes and supports the subspecies designation C. l. arabs. [11] There has been admixture with domestic dogs but it is unclear whether this is why this wolf is genetically closer to C. l. lupus.[11] This raises a concern of extinction by hybridization as Arabian wolves are more adapted to desert life than wolf/dog hybrids.[12]
Description[edit]
The Arabian wolf is small for Canis lupus and stands on average 26 inches (66 cm) at shoulder height and weighs an average of 40 pounds (18.14 kg). The cranial length of the adult Arab wolf (Canis lupus arabs) measures on average 200.8 mm, which is smaller than most wolves.[13] Along with the Indian wolf, it is probably smaller than other wolves to help it adapt to life in a hot, dry climate.[14] This is an example of Bergmann's rule, where mammal size varies by the warmth of their environment. Its ears are proportionally larger in relation to its body size when compared to other sub-species of Canis lupus, an adaptation probably developed to help disperse body heat.[15] Arabian wolves do not usually live in large packs, and instead hunt in pairs or in groups of about three or four animals.[16] [17] They have a short thin coat which is usually a grayish beige color.[9] "...a mixture of black and slightly buffy grey," according to Pocock.[9] Similar to other canines, the Arabian wolf does not have sweat glands and so it must control its body temperature by rapid panting, which causes evaporation from the lungs.[18] It is distinguished from the Indian wolf by its smaller skull and smaller size and thinner coat.[9]

Diet[edit]

Arabian wolves are omnivorous and in some areas largely dependent on human excess products and waste.[19] They also feed on hares, rodents, small ungulates, and carrion. Opportunistically almost any small animal including fish, snails, baby baboons can be part of their diet; they also eat garbage.[20] Arabian wolves hunt small to medium-sized animals such as cape hares, Dorcas gazelles, and ibexes, though they feed on carrion and livestock when in the vicinity of human settlements.[21] Because Arabian wolves can attack and eat any domestic animals up to the size of a goat, Bedouins and farmers will not hesitate to shoot, poison, or trap them.[22]
Range and conservation[edit]
The Arabian wolf was once found throughout the Arabian Peninsula but now lives only in small pockets in southern Israel,[23] southern and western Iraq, Oman, Yemen, Jordan,[24] Saudi Arabia,[25] and some parts of the Sinai Peninsula in Egypt.[26] It is rare throughout most of its range because of human persecution.[27] In Oman wolf populations have increased because of a ban on hunting, and they may naturally re-establish themselves in certain places within the region in the relatively near term.[28] In Israel, between 100 and 150 Arabian wolves are found across the Negev and the Arava. The United Arab Emirates and Egypt both have a captive breeding program and the wolf is protected in Oman and Israel but elsewhere its future is uncertain.[29] In Saudi Arabia the wolf is protected in places and still exists in places with sparse human activity.[30]
References[edit]
- ^ Cohen, Orly; Barocas, Adi; Geffen, Eli (2013). "Conflicting management policies for the Arabian wolf Canis lupus arabsin the Negev Desert: Is this justified?". Oryx. 47 (2): 228–236. doi:10.1017/S0030605311001797. S2CID 30686630.
- ^
{{cite journal}}: Empty citation (help) - ^
{{cite web}}: Empty citation (help) - ^ https://books.google.com/books?id=.
{{cite book}}: Missing or empty|title=(help) - ^ {{IUCN |assessors=Mech, L.D., Boitani, L. (IUCN SSC Wolf Specialist Group) |year=2010 |id=3746 |title=Canis lupus|version=2011.2}}
- ^ Pocock, R.I. (1934). "LXVI.—Preliminary diagnoses of some new races of South Arabian mammals". Journal of Natural History Series 10. 14 (84): 635–636. doi:10.1080/00222933408654939.
- ^ Hefner, R.; Geffen, E. (1999). "Group Size and Home Range of the Arabian Wolf (Canis lupus) in Southern Israel". Journal of Mammalogy. 80 (2): 611–619. doi:10.2307/1383305. ISSN 1545-1542. JSTOR 1383305.
- ^ Pocock, R.I. (1934). "LXVI.—Preliminary diagnoses of some new races of South Arabian mammals". Journal of Natural History Series 10. 14 (84): 635. doi:10.1080/00222933408654939.
- ^ a b c d Pocock, R.I. (1935). "XLII.—The mammals collected in S.E. Arabia by Mr. Bertram Thomas and Mr. H. St. J. Philby". Journal of Natural History Series 10. 15 (88): 441–467. doi:10.1080/00222933508654985. ISSN 0374-5481. Cite error: The named reference "Pocock1935" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- ^ Wozencraft, W. C. (2005). "Order Carnivora". In Wilson, D. E.; Reeder, D. M. (eds.). Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. pp. 575–577. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0. OCLC 62265494. url=https://books.google.com.au/books?id=JgAMbNSt8ikC&pg=PA576
- ^ a b Bray, Timothy C.; Mohammed, Osama Badri; Butynski, Thomas M.; Wronski, Torsten; Sandouka, Mohamed Abdelkader; Alagaili, Abdulaziz Nasser (2014). "Genetic variation and subspecific status of the grey wolf (Canis lupus) in Saudi Arabia". Mammalian Biology - Zeitschrift für Säugetierkunde. 79 (6): 409–413. doi:10.1016/j.mambio.2014.06.005. ISSN 1616-5047.
- ^ http://canids.org/CBC/20/Arabian_wolf_and_domestic_dog_in_saudi_arabia.pdf
- ^ Walker, Brett (2008). The Lost Wolves of Japan. University of Washington Press, Seattle. p. 53. ISBN 9780295988146.
- ^ T. K. Fuller (2004). Wolves of the World. Voyageur Press. ISBN 978-0-89658-640-6.
- ^ Mills, Clarence A. (1945). "Influence of Environmental Temperatures on Warm-Blooded Animals". Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 46 (1 Animal Colony): 97–105. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.1945.tb36162.x. ISSN 0077-8923. S2CID 84266753.
- ^ Natural Emirates: Wildlife and Environment of the United Arab Emirates. Trident Press Ltd. 1996. pp. 219–. ISBN 978-1-900724-02-9.
- ^ Hefner, R.; Geffen, E. (1999). "Group Size and Home Range of the Arabian Wolf (Canis lupus) in Southern Israel". Journal of Mammalogy. 80 (2): 611–619. ISSN 1545-1542. doi:10.2307/1383305.
- ^ Harrington & Paquet 1983.
- ^ Hefner, R.; Geffen, E. (1999). "Group Size and Home Range of the Arabian Wolf (Canis lupus) in Southern Israel". Journal of Mammalogy. 80 (2): 611–619. ISSN 1545-1542. doi:10.2307/1383305.
- ^ http://nwrc.gov.sa/NWRC_ARB/mzyd_files/1-1994-005.pdf Biquand, S., V. Urios, A. Baoug, C. Vila, J. Castroviejo, and I. Nader. 1994. Fishes as diet of a wolf (Canis lupus arabs) in Saudi Arabia. Mammalia 58 (3):492–494.
- ^ Hefner, R.; Geffen, E. (1999). "Group Size and Home Range of the Arabian Wolf (Canis lupus) in Southern Israel". Journal of Mammalogy. 80 (2): 611–619. ISSN 1545-1542. doi:10.2307/1383305.
- ^ http://www.canids.org/canidnews/13/Arabian_wolf_in_Saudi_Arabia.pdf
- ^ Cohen, Orly; Barocas, Adi; Geffen, Eli (2013). "Conflicting management policies for the Arabian wolf Canis lupus arabs in the Negev Desert: is this justified?". Oryx. 47 (2): 228–236. doi:10.1017/S0030605311001797. ISSN 0030-6053. S2CID 30686630.
- ^ http://journals.tubitak.gov.tr/zoology/issues/zoo-01-25-1/zoo-25-1-3-9909-8.pdf
- ^ Bray, Timothy C.; Mohammed, Osama Badri; Butynski, Thomas M.; Wronski, Torsten; Sandouka, Mohamed Abdelkader; Alagaili, Abdulaziz Nasser (2014). "Genetic variation and subspecific status of the grey wolf (Canis lupus) in Saudi Arabia". Mammalian Biology - Zeitschrift für Säugetierkunde. 79 (6): 409–413. ISSN 1616-5047. doi:10.1016/j.mambio.2014.06.005.
- ^ Gecchele, Lisa V.; Bremner-Harrison, Samantha; Gilbert, Francis; Soultan, Alaaeldin; Davison, Angus; Durrant, Kate L. (2017). "A pilot study to survey the carnivore community in the hyper-arid environment of South Sinai mountains". Journal of Arid Environments. 141: 16–24. doi:10.1016/j.jaridenv.2017.01.009. ISSN 0140-1963.
- ^ Hefner, R.; Geffen, E. (1999). "Group Size and Home Range of the Arabian Wolf (Canis lupus) in Southern Israel". Journal of Mammalogy. 80 (2): 611–619. ISSN 1545-1542. doi:10.2307/1383305.
- ^ Natural Emirates: Wildlife and Environment of the United Arab Emirates. Trident Press Ltd. 1996. pp. 219–. ISBN 978-1-900724-02-9.
- ^ http://www.middleeasteye.net/in-depth/features/conservation-conflict-isis-advancement-and-arabian-wolf-811485183
- ^ http://www.canids.org/canidnews/13/Arabian_wolf_in_Saudi_Arabia.pdf
Citation generator[edit]
- Journal [2]
- Web [3]
- Book [4]
- Google book app http://reftag.appspot.com/
- ^ . 1945. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.tb36162.x (inactive 2022-06-26).
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help); Missing or empty|title=(help)CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of June 2022 (link) - ^
{{cite journal}}: Empty citation (help) - ^ http://www.middleeasteye.net/in-depth/features/conservation-conflict-isis-advancement-and-arabian-wolf-811485183=.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|title=(help) - ^ https://books.google.com/books?id=.
{{cite book}}: Missing or empty|title=(help)

