User:The High Fin Sperm Whale/Fact of the day/Archive
June[edit]
June 17[edit]

|
Chromium is a chemical element with the symbol Cr and the atomic number 24. It is a grey, lustrous, hard metal which has a high melting point. Chromium is resistant to corrosion. |
June 16[edit]

|
Anak Krakatau is a currently erupting stratovolcano, formed on the same vent as Krakatau. Anak Krakatau was previously a submarine volcano, until it broke the surface on August 1927. |
June 15[edit]

|
Gigantopithecus is an extinct genus of ape, native to Southeast Asia. Fossils indicate that it was one of the largest apes ever, growing up to 9.8 feet (3.0 m) in height. There are three known species, Gigantopithecus blacki, Gigantopithecus bilaspurensis, and Gigantopithecus giganteus. |
June 14[edit]
A Fossil is the preserved remains of an organism. Fossils are usually found in sedimentary rock. They are usually formed as organisms or parts of organisms are buried in sediment. The sediment is then crushed and turns into rock, preserving the organism. |
June 13[edit]

|
A Microburst is a small column of rapidly sinking air, causing damaging straight-line winds. Microbursts come under two categories, wet and dry. Microbursts spread out upon impact to the ground, causing powerful side winds. Microbursts pose a great danger to aircraft, and several airplane crashes have been attributed to this phenomenon. Microbursts typically last several seconds. |
June 12[edit]
The Smalltooth sawfish (Pristis pectinata) is a Critically Endangered species of sawfish, native to tropical and subtropical waters in the Coastal Atlantic and the Mediterranean. They can reach a length of up to 25 feet (7.6 m) in length. |
June 11[edit]

|
Mira is a red giant star in the constellation Cetus. Mira is a binary star, consisting of the red giant Mira A and Mira B. |
June 10[edit]

|
Bryce Canyon National Park is a national park in southwestern Utah. The main feature of the park is Bryce Canyon, distinctive because of the many geological structures known as hoodoos. Bryce Canyon is technically not a canyon, but a large natural amphitheatre. |
June 9[edit]

|
Giglioli’s Whale (Amphiptera pacifica) is a species of rorqual reportedly observed by Enrico Hillyer Giglioli on the Magenta about 1,200 miles off the coast of Chile on September 4, 1867. Giglioli was able to make very detailed observations, as it was very close to the ship for about 15 minutes. It was about 60 feet (18 m) in length with two dorsal fins 6.5 feet (2.0 m) apart. Another sighting was recorded later in the year on the Lily. In 1983, Jacques Maigret sighted a similar creature between Corsica and the French mainland. |
June 8[edit]

|
Copper(II) sulfate (CuSO4) is a sulfate of copper that is pale green when pure and deep blue when hydrated. CuSO4 can be an irritant. |
June 7[edit]

|
Pacaya is a currently erupting complex volcano in Guatemala. Due to the high volcanic activity, it is a popular tourist attraction. Most of the activity is Strombolian, although it does have some Plinian. |
June 6[edit]
The West Indian Ocean coelacanth (Latimeria chalumnae) is a species of coelacanth, easily recognizable by its vivid blue pigment. It is one of only two living coelacanth species. The West Indian Ocean coelacanth can reach 80 kilograms (180 lb) in weight and 2 metres (6.6 ft) long. They are found on the western rim of the Indian Ocean. |
June 5[edit]

|
In mineralogy, Streak is the colour of a mineral when dragged against a rough surface, such as unglazed porcelain. The streak of a mineral is always the same colour and smell, regardless of the colour of the mineral. |
June 3[edit]

|
A Thunderstorm, electrical storm, lightning storm, or thundershower is a large, rising low-pressure-cell, usually accompanied by strong winds, lightning, and heavy rain, snow, or hail. Thunderstorms sometimes line up to form a squall line. Very strong thunderstorms can rotate, creating supercells. Cells are formed as warm air rises. It rises until it reaches more warm air, and then it can rise no further. It often stops in the tropopause. The air is forced to spread out, causing the anvil shape. |
June 2[edit]

|
Balaenoptera brydei is a species of rorqual. It is the most elusive and strangest whales. They are relatively small compared to other rorquals, usually growing no more than 37 feet (11 m) in length. They usually prefer tropical or temperate water. Despite having plates of baleen, they eat almost nothing but fish such as anchovy, sardines, and herring. |
June 1[edit]

|
Cygnus X-1 is a galactic X-ray source X-ray astronomy in the constellation Cygnus. It is one of the strongest X-ray sources visible from Earth. Cygnus X-1 is thought to be a black hole with 8.7 solar masses, with an event horizon 52 km in diameter. It is believed that it has a compact star or blue supergiant that orbits it every five days. |
May[edit]
May 31[edit]

|
Speleothems, also known as a cave formation, are mineral deposits formed in caves. Speleothems are usually formed in solutional caves. Water seeping through cracks in the rock dissolve small amounts of limestone, aragonite, or gypsum. When the water drips from the roofs, it leaves small amounts of minerals behind, forming stalagtites. It then drips onto the cave floor, forming stalagmites. Other types include soda straws, helictites, flowstones, rimstones, dogtooth spar, frostwork, moonmilk, anthodites, cave popcorn, and cave pearls. |
May 30[edit]

|
The Canvey Island Monster was the name of an unusual creature that washed up on a beach on Canvey Island, England, in November of 1954. A second carcass was found on August of 1955. The specimen from 1954 was 76 centimetres (30 in) in length, had thick, reddish brown skin, bulging eyes, and gills. It had hind legs with five-toed horseshoe-shaped feet with concave arches, which appeared to be suited for bipedal locomotion and no forelimbs. The second specimen was similar to the first, although it was fresher and much larger, around 1.2 metres (3.9 ft) long and 11.3 kilograms (25 lb) in weight. No explanation has been given. |
May 29[edit]

|
In chemistry, pH of how acidic or basic a solution is. A low pH has a high concentration of hydronium ions (H3O+) (acidic), while a high pH has a low concentration of hydronium (basic). The pH scale is a logarithm, so a pH of 10 is 10 times more basic than a pH of nine. |
May 28[edit]

|
Cleveland Volcano, called Cleveland by the Alaska Volcano Observatory, also called Mount Cleveland, is an currently erupting stratovolcano, as of October 3, 2009, in the western half of Chuginadak Island in the central Aleutian Islands. |
May 27[edit]

|
Mixopterus was a genus of eurypterid. Like Megalograptus, Mixopterus had long, sharp spines on the first two legs, probably used to grasp prey. |
May 25[edit]

|
In mineralogy, Lustre is the way oncoming light reacts with the surface of the mineral. Adamantine lustre minerals are reflective and translucent or transparent, such as diamond. Minerals with a dull (or earthy), such as chalk, have little or no lustre. Minerals with a Greasy lustre, such as opal, resemble fat or oil. Metallic (or splendent) minerals resemble polished metal. Examples include galena, pyrite, and magnetite. ASubmetallic lustre, such as in cinnabar, are similar to metallic lustre, but duller. Pearly minerals resemble pearls. Examples include muscovite and stilbite. A Resinous lustre looks like resin or chewing gum, the most common example being amber. Silky minerals have a parallel arrangement of very fine fibres, causing them to resemble silk, the most common example of which is asbestos. Minerals with a Vitreous lustre, such as quartz, look like glass. Waxy minerals, such as jade and chalcedony have the appearance of wax. |
May 24[edit]

|
A Tropical cyclone is a storm system formed when air swirls into low-pressure centre over warm water. Tropical cyclones feed on heat from the moist air rising from the warm water below, causing thunderstorms that produce heavy precipitation and strong winds, as well as high waves and large storm surges. At the centre of is sinking mass of air called the eye. The eye is roughly circular and is perfectly clear and calm. The eye is surrounded by the eyewall, a region of very intense thunderstorms. The eye has the lowest atmospheric pressure of anywhere in the storm. |
May 23[edit]

|
The Giant California sea cucumber (Parastichopus californicus) is a sea cucumber that is found from the Gulf of Alaska to Southern California. Giant California sea cucumbers are found in the low intertidal zone, usually at a depth of about 250 metres (820 ft). It is the largest sea cucumber in the world, growing to lengths of up to 50 centimetres (20 in) and with a width of 5 centimetres (2.0 in). The mouth is surrounded by twenty tentacles, used to gather up food. Giant California sea cucumbers feed on plankton and organic matter. When attacked, they can expel sticky filaments to confuse and tangle up predators. |
May 22[edit]

|
Phoebe is an irregular moon of Saturn. Phoebe is roughly spherical and has a diameter of roughly 220 kilometres (140 miles), about one-fifteenth of Earth's moon. Phoebe rotates on its axis every nine hours and takes 19 months to orbit Saturn. Phoebe is most likely a captured asteroid. |
May 21[edit]

|
Giant's Causeway is an area by the ocean in Northern Ireland of 40,000 interlocking basalt columns as the result of a volcanic eruption. Most of the columns are hexagonal, although there are also some with four, five, seven and eight sides. The tallest are about 12 metres (39 ft) high, and the solidified lava in the cliffs is 28 metres (92 ft) thick in places. |
May 20[edit]

|
Sulfuric acid (sulphuric acid in British English) (H2SO4) is an strong mineral acid which is soluble in water. It is th emost widely produced chemical in the United States. Its lead uses are in lead–acid batteries, ore processing, fertilizer manufacturing, oil refining, wastewater processing, and chemical synthesis. It is produced by synthesis of SO3 and H2O. H2SO4 is common in space, such as in the atmosphere of Venus. |
May 19[edit]

|
Angel falls is a waterfall in Venezuela, and the tallest in the world at 3,212 feet (979 m) high. The waterfall is so tall that the water is either evaporated or carried away as mist before it reaches the bottom. The total height is 3,212 feet (979 m), however, 565 feet (172 m) of this is cascades and rapids. The tallest single drop is 2,647 feet (807 m). |
May 18[edit]

|
Anomalocaris is an extinct genus of anomalocaridid, found in the Burgess Shale in British Columbia. Anomalocaris is the largest Burgess Shale animal, measuring up to 3.3 feet (1.0 m) in length. It is thought to have been a predator, moving swiftly through the water by undulating the 11 flexible lobes on its sides, as well as a large fan-shaped tail. Anomalocaris had a large head, a pair of large compound eyes, and an unusual, disk-like mouth shaped liked a pineapple ring, made 32 overlapping plates, four large ones and 28 small ones. Two flexible 'arms', roughly 7 inches (18 cm) in length, with barbs pointing towards the mouth. |
May 17[edit]

|
Flint (or flintstone) is a hard, sedimentary cryptocrystalline form of chert, a type of quartz. It is often found in nodules in layers of other sedimentary rocks, such as chalk and limestone. Flint can be dark grey, black, green, white, or brown, and usually has a glassy or waxy appearance. Flint is useful for making stone tools, as it splits into thin, sharp splices called either flakes or blades, depending on the shape, when struck by a hard object such as a hammerstone made of another, harder material). This process is called to as knapping. Flint is also useful, because when struck against steel, it rubs off tiny particles of the steel, which the friction causes to ignite, producing sparks.(This statement is incorrect! If you strike two pieces of flint together, they will produce sparks! No steel involved!) Flint is often heat-treated before knapping, which causes it to split into sharper edges. However, it must be heated very slowly, otherwise some parts will expand faster than others, causing it to fracture and producing very sharp chips which fly of a high speeds. |
May 16[edit]

|
A Sun dog or sundog is an atmospheric phenomenon that causes to bright spots, or mock suns to appear on opposite sides of the real sun, often situated on a halo. Sundogs are most brilliant when the sun is low. Sundogs are formed by flat hexagonal ice crystals in very high cirrus clouds refract light rays passing through them by 22°. |
May 15[edit]

|
The Colossal Squid (Mesonychoteuthis hamiltoni), sometimes called the Antarctic or Giant Cranch Squid, is a species of squid thought to be the largest known invertebrate. The Colossal Squid is estimated to have a maximum size of 12–14 metres (39–46 feet). Unlike the giant squid, the Colossal Squid's tentacles are lined with small teeth.The Colossal Squid's range covers most pf the Southern Ocean. The largest known specimen, caught off the coast of New Zealand, measured 10 metres (33 ft) in length. |
May 14[edit]

|
A Quasi-stellar radio source (quasar) is very energetic, young, and distant galaxy with an active galactic nucleus (AGN). The quasar itself is a compact region in the middle of a huge galaxy around the central supermassive black hole. It is 10–10,000 times the Schwarzschild radius of the black hole in size. The quasar is powered by an accretion disc around the black hole. |
May 13[edit]
Lava Beds National Monument is a National Monument in Siskiyou and Modoc, California. It holds the highest concentration of lava tubes anywhere in the world. The monument is on the northeastern side of the Medicine Lake Volcano. The monument is rich in evidence of past volcanic activity, such as lava tube caves, fumaroles, cinder cones, spatter cones, maars, and lava flows. About ninety percent of the lava in the monument is basaltic. |
May 12[edit]

|
Slow Down is the name of an unidentified sound underwater sound detected by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) in the Equatorial Pacific on May 19, 1997. The sound was detected at 15°S 115°W / 15°S 115°W / -15; -115. The sound has been picked up several times each year since 1997. Five other unidentified sounds have been named by NOAA: Julia, Train, Bloop, Whistle, and Upsweep. |
May 11[edit]

|
A toxin is a poisonous substance produced by living cells or organisms. Blood agents affects the body by being absorbed into the blood. They are fast-acting, potentially lethal poisons that typically manifest at room temperature as volatile colorless gases with a faint odor. Blood agents are usually cyanide- or arsenic-based. These include cyanogen chloride and hydrogen cyanide. A Pulmonary agent is a poison designed to stop breathing, causing asphyxia. They include chlorine and phosgene. Nerve agents are a type of chemical which disrupt the mechanism by which nerves carry information. They include Tabun, Sarin, and Soman. |
May 10[edit]

|
Sakurajima is an active stratovolcano on the Osumi Peninsula. The lava flows from the 1914 eruption caused the formerly island to connect with the Peninsula. The volcano is currently erupting, dropping volcanic ash on the surroundings. Sakurajima is split into three peaks: Kitadake (the northern peak), Nakadake (middle peak) and Minamidake (southern peak), which is currently erupting. The northern peak, Kitadake, is the highest, rising 1,117 metres (3,665 ft) above sea level. |
May 9[edit]

|
Xiphactinus was large (15 to 20 feet) predatory bony fish that lived in what is now middle of North America. One 13 feet (4.0 m) fossil specimen was discovered by George F. Sternberg with an almost perfectly preserved 6 feet (1.8 m) long Gillicus arcuatus in its stomach. The Xiphactinus apparently died not long after swallowing its prey, probably because the smaller fish struggling and rupturing an organ as it was being eaten. The specimen is now at the Sternberg Museum of Natural History in Kansas. |
May 8[edit]

|
A Geode are rock formations which occur in sedimentary and certain igneous rocks. Geodes are rock cavities or vugs with crystal formations or concentric banding inside. The outside of most geodes are generally limestone or a related rock, while the inside usually contains quartz crystals or chalcedony. Some geodes are filled with crystals, such as agate, being solid all the way through. These are called nodules. |
May 7[edit]

|
A Lenticular cloud is stationary lens-shaped cloud that forms at high altitudes in the lee side of mountains. Pilots of powered aircraft often avoid flying around lenticular clouds due to the turbulence of the air systems that accompany them, but glider pilots actively can use them to their advantage due to the rising air masses. These can enable gilder pilots to soar to great altitudes. The location of the rising air mass is relatively easy to predict from the position of the clouds. |
May 6[edit]
The Goliath Bird-eater Spider, also called the Goliath Birdeater, (Theraphosa blondi) is an arachnid in the tarantula group, Theraphosidae, and is the second largest spider by leg-span in the world, after the Giant huntsman spider (Heteropoda maxima). The Goliath Birdeater is native to rainforest in northern South America. They can have a leg span of up to 11 inches (28 cm) and can weigh in excess of 6 ounces (170 g). Wild Goliath birdeaters live in burrows, and are commonly found in marshy or swampy areas, commonly living in burrows that they dig themselves or have been abandoned by other burrowing animals. |
May 5[edit]

|
The Vela Pulsar (PSR B0833-45 or PSR J0835-4510, sometimes called the Vega Pulsar) is a radio, optical, X-ray and gamma-emitting pulsar associated with Vela Supernova Remnant, in the constellation of Vela. |
May 4[edit]

|
A cenote is a sinkhole with exposed rocky edges containing groundwater. Cenotes are commonly found in the Yucatán Peninsula and some nearby Caribbean islands. Cenotes are caused when dissolution of rock creates a subsurface void, which is sometimes linked to an active cave system. Then, the rock ceiling above the void collapses, causing a deep pit, which fills with rainwater. |
May 3[edit]

|
The Bloop is the name of an ultra-low frequency and very powerful underwater sound detected by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) several times during 1997. The cause of the sound remains unknown. The sound was traced to near 50° S 100° W, an isolated point in the south Pacific Ocean west of the southern tip of South America. It was several times louder than the call of the blue whale, the loudest known biological sound. Five other unidentified sounds have been named by NOAA: Julia, Train, Slow Down, Whistle, and Upsweep. |
May 2[edit]

|
Combustion or burning is an exothermic chemical reaction between a fuel and an oxidant accompanied by the production of heat and, usually, light. The flame formed when carbon or carbon containing compounds in burned is caused by thousands of tiny glowing particles of carbon drifting upward. |
May 1[edit]
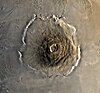
|
Olympus Mons is a large shield volcano on Mars. At a little under three times as tall as Mount Everest, and is the tallest known volcano and mountain in the Solar System. Olympus Mons is 550 kilometres (340 miles) in diameter, 21 kilometres (13 miles) in height, and has a caldera 85 kilometres (53 miles) long, 60 kilometres (37 miles) wide, and 3 kilometres (1.9 miles) deep in the middle. |
April 2010[edit]
April 30[edit]

|
Cameroceras was a genus of giant orthoconic cephalopod. It was the largest orthocone of all time, measuring nearly 30 feet (9 m) in total length. It was probably an apex predator that lived in deeper water, and probably fed on eurypterids such as Megalograptus, large trilobites, and smaller cephalopods. |
April 29[edit]

|
Tiger's Eye is a golden to red-brown chatoyant quartz mineral with a silky lustre. A very rare blue variant is called Hawk's eye. Tiger's Eyes are usually cut as cabochons to best display their chatoyancy. The main producer of Tiger's Eye is South Africa. Tiger's Eye is formed as asbestos in quartz dissolves away and is replaced by iron(III) oxide. |
April 28[edit]

|
Noctilucent clouds, or Polar mesospheric clouds are a type cloud in the upper atmosphere. They are visible in late twilight. They are made out of ice crystals. Noctilucent clouds are the highest clouds in the Earth's atmosphere, located in the mesosphere at altitudes of around 75,000 to 85,000 m (250,000 to 280,000 ft). |
April 27[edit]

|
Nomura's Jellyfish (Nemopilema nomurai) is a large species of jellyfish, growing up to 2 meters (6 feet 7 inches) in diameter and weighing up to 300 kilograms (660 pounds). Nomura's Jellyfish mostly reside in the Sea of Japan, the Yellow Sea and the East China Sea. |
April 26[edit]

|
Circinus X-1 is an X-ray binary star system (a star system in which a larger, denser object pulls material off a larger object) with a neutron star orbiting in the constellation circinus. |
April 25[edit]

|
The Cave of Swallows is a pit cave in San Luis Potosí, Mexico. The entrance of the cave is 160 by 205 feet (49 by 62 m), and it has a 1220 feet (372 m) freefall from the top to the bottom. This makes it the largest cave shaft in the world. |
April 24[edit]

|
A Globster, such as the St. Augustine Monster (left), is an unidentified organic mass washed up on a beach. Some globsters lack bones or recognizable structures, but others have bones, tentacles, or flippers. |
April 23[edit]
April 22[edit]

|
Eyjafjallajökull is a currently erupting subglacial volcano in Southern Iceland. The first signs of the oncoming eruption began in December 2009, when thousands of small earthquakes began going off. The fissure of the volcano is 500 metres (1,600 ft) long going in a north-east to south-west direction. The eruption has a VEI of 1. Some experts worry that another subglacial volcano 25 km west, Katla, will also begin erupting. |
April 21[edit]

|
Amphicoelias fragillimus is a species of sauropod dinosaur that may be the largest dinosaur yet discovered. A. fragillimus may have been the longest known vertebrate at 40–60 meters (131–196 ft) long, and may have wieghed up to 122 metric tons (135 short tons), coming close to the heaviest animal known, the Blue whale (Balaenoptera musculus). |
April 20[edit]
Birefringence, or double refraction, is when light is split into two rays when passing through minerals such as calcite and boron nitride. This causes the illusion of a 'ghost' object to the side of real objects. For this phenomenon to occur, the structure of the material must be anisotropic (directionally dependent). |
April 19[edit]
Upper-atmospheric lightning is a type of electrical discharge far above the levels of ordinary lighting. Sprites (left) are large flashes that occur much higher than cumulonimbus clouds, often related to large lightning strikes. They are usually red. Blue jets are electrical discharges that project from the top of cumulonimbus clouds into the lower Ionosphere. Blue jets are much rarer than spites, but are much brighter. Elves (Emissions of Light and Very Low Frequency Perturbations from Electromagnetic Pulse Sources) are seen as a dim, expanding glow, often 400 km (250 m) across. They typically last one millisecond. |
April 18[edit]

|
The Banded archerfish (Toxotes jaculatrix) is a species of archerfish (Toxotes sp.). Like all archerfish, its mouth is specially shaped to spit water to knock prey off into the water. Most banded archerfish can shoot a jet of water 150 centimetres (59.06 in), though some larger fish can shoot up to 3 metres (9.84 ft). Once the prey falls into the water, the archerfish can reach it within 100 ms. Banded archerfish are omnivorous, feeding on floating plant matter and crustaceans as well as insects. |
April 17[edit]

|
The Crab Nebula (otherwise known as M1, 1952 or NGC) is a supernova remnant in the constellation Taurus, roughly 6,500 light-years from Earth. It was formed after a bright supernova observed by Chinese and Arab in AD 1054. At the centre of the Crab Nebula is the Crab Pulsar, rotating at 30 times per second. |
April 16[edit]

|
Lechuguilla Cave is the fifth longest cave in the world, reaching 126.1 miles (203 km) from its entrance and 1,604 feet (489 m) deep. It is known for its unusual geology. It is located in Carlsbad Caverns National Park. Some of the unusual speleothems include 20 feet (6.1 m) gypsum chandeliers, 20 feet (6.1 m) gypsum hairs and beards, 15 feet (4.6 m) soda straws, hydromagnesite balloons, cave pearls, subaqueous helictites, and rusticles. The cave was formed when hydrogen sulphide (H2S) bubbled into the water, forming sulphuric acid (H2SO4). |
April 15[edit]
| File:Myakka skunk ape 2.png | The Skunk ape is a hominid cryptid from the Southeastern United States, especially the Florida Everglades. It is named after the colour of its fur and the bad smell. The Skunk ape was especially common in the 1960's and 70's. |
April 14[edit]

|
Chemiluminescence is the emission of light as the result of a chemical reaction. THis reaction generally produces little heat. The reaction of luminol and hydrogen peroxide one of the most common types of chemiluminescent reaction. |
April 13[edit]

|
Ol Doinyo Lengai is am active stratovolcano located in the Great Rift Valley in Eastern Tanzania. It is unique in that it has natrocarbonatite lava. Because of this, the lava melts at very low temperatures, often emerging from the volcano at 510 °C (950 °F), cool enough to pick up with a metal spoon. During the daytime hours, the molten lava appears black or gray, resembling mud. |
April 12[edit]

|
Parapuzosia seppenradensis was the largest species of ammonite, with an estimated shell diameter of 2.55 m. It is known from a single specimen found in Germany in 1895, measuring 1.95 m in diameter. |
April 11[edit]

|
Fluorescence is when a mineral emits light in the visible spectrum while absorbing a different wavelength. The most commons florescent mineral is fluorite. Some other minerals known to fluoresce are willemite, esperite, wollastonite, and clinohedrite. |
April 10[edit]
April 9[edit]

|
The Amazonian giant centipede (Scolopendra gigantea) is the largest species of centipede in the world, often reaching lengths of 10 inches, and on occasion growing to 12 inches. It lives in South America and Caribbean islands. The bites of theses centipedes are very painful, although very rarely fatal. They use their giant fangs to hunt lizards, frogs, birds, mice, bats, and, on occasion, tarantulas. |
April 8[edit]

|
VY Canis Majoris is a red hypergiant in the constellation Canis Major. It is the largest known star, at around 2,000 Solar radii. If the sun were replaced with VY Canis Majoris, it would extend past the orbit of Saturn. Despite its enormous size, it weighs only 30 to 40 M☉. |


