User:Mr. Ibrahem/Lefamulin
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Xenleta |
| Other names | Lefamulin acetate, BC-3781 |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| License data | |
| Routes of administration | Intravenous, by mouth |
| Drug class | Antibiotic (pleuromutilin)[1] |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| Chemical and physical data | |
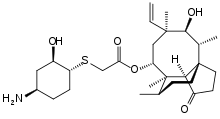
| Formula | C28H45NO5S |
| Molar mass | 507.73 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Lefamulin, sold under the brand name Xenleta, is an antibiotic used to treat community-acquired pneumonia.[1] It is used when other antibiotics are not appropriate.[1] It is effective against a number of bacteria including MRSA.[2] It is taken by mouth or by injection into a vein.[1]
Common side effects include diarrhea, nausea, pain at the site of injection, and liver inflammation.[2] Other side effects may include QT prolongation and Clostridioides difficile infection.[2] Use during pregnancy may harm the baby.[2] It is a pleuromutilin antibiotic and works by blocking the production of proteins from bacterial RNA.[1]
Lefamulin was approved for medical use in the United States in 2019 and Europe in 2020.[3][1] In the United States a 5 day course of treatment costs about 1450 USD as of 2021.[4] While it is approved in Europe, it is not commercially available there as of 2021.[5]
References[edit]
- ^ a b c d e f g h "Xenleta EPAR". European Medicines Agency. 26 May 2020. Archived from the original on 9 January 2021. Retrieved 24 September 2020.
- ^ a b c d e f "Xenleta- lefamulin acetate injection, solution citric buffered normal saline- anhydrous citric acid injection, solution Xenleta- lefamulin acetate tablet, coated". DailyMed. 12 February 2020. Archived from the original on 6 August 2020. Retrieved 24 September 2020.
- ^ "Lefamulin Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 24 January 2021. Retrieved 21 November 2021.
- ^ "Xenleta Prices, Coupons & Patient Assistance Programs". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 19 April 2021. Retrieved 21 November 2021.
- ^ "Lefamulin". SPS - Specialist Pharmacy Service. 14 January 2016. Archived from the original on 21 November 2021. Retrieved 21 November 2021.
