User:LuisGomez111/Spain
Kingdom of Spain Reino de España | |
|---|---|
| Motto: "Plus Ultra" (Latin) "Further Beyond" | |
| Anthem: ""Marcha Real" (Spanish) "Royal March" | |
![Location of LuisGomez111/Spain (dark green) – in Europe (light green & dark grey) – in the European Union (light green) – [Legend]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/2/21/EU-Spain.svg/250px-EU-Spain.svg.png) Location of LuisGomez111/Spain (dark green) – in Europe (light green & dark grey) | |
| Capital and largest city | Madrid 40°26′N 3°42′W / 40.433°N 3.700°W |
| Official languages | Spanish[2] |
| Recognised regional languages | Aranese, Basque, Catalan/Valencian and Galician |
| Ethnic groups | 89% Spanish, 11% minority groups |
| Demonym(s) | Spanish, Spaniard |
| Government | Parliamentary democracy and Constitutional monarchy |
• Monarch | King Juan Carlos I |
José L. Rodríguez Zapatero | |
| Formation 15th century | |
• Unification | 1469 |
• Dynastic union | 1516 |
• de facto | 1716 |
• de jure | 1812 |
| Area | |
• Total | 504,030 km2 (194,610 sq mi) (51st) |
• Water (%) | 1.04 |
| Population | |
• 2007 estimate | 45,200,737[1] (28th) |
• Density | [convert: invalid number] (106th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2007[2] estimate |
• Total | $1.310 trillion (11th) |
• Per capita | $33,700 (2007) (27th) |
| GDP (nominal) | 2007[3] estimate |
• Total | $1.439 trillion (8th) |
• Per capita | $31,471 (2007) (26th) |
| Gini (2005) | 32[4] Error: Invalid Gini value |
| HDI (2005) | 0.949 very high (13th) |
| Currency | Euro (€) ³ (EUR) |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET4) |
• Summer (DST) | UTC+2 (CEST) |
| Calling code | 34 |
| ISO 3166 code | ES |
| Internet TLD | .es, .cat5 |
| |
Spain (Spanish: ⓘ, IPA: [es'paɲa]) or the Kingdom of Spain (Spanish: Reino de España),[5] is a country located mostly in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula. The Spanish mainland is bordered to the south and east almost entirely by the Mediterranean Sea (except for a small land boundary with Gibraltar); to the north by France, Andorra, and the Bay of Biscay; and to the west by the Atlantic Ocean and Portugal. Spanish territory also includes the Balearic Islands in the Mediterranean, the Canary Islands in the Atlantic Ocean off the African coast, and two autonomous cities in North Africa, Ceuta and Melilla, that border Morocco. With an area of 504,030 km2, Spain is the second largest country in Western Europe (behind France) and with an average altitude of 650 m, the second highest country in Europe (behind Switzerland).
Spain is a constitutional monarchy organised as a parliamentary democracy and has been a member of the European Union since 1986. It is a developed country with the eighth largest economy in the world and fifth largest in the EU, based on nominal GDP.[6]
History[edit]
Summary[edit]
Spain is a key site when it comes to studying the human prehistory of Europe. After a long and hard conquest Hispania became one of the Roman Empire's most important regions. During the early Middle Ages it came under Germanic rule. Later it was conquered by Muslim invaders. Through a very long and fitful process, the Christian kingdoms in the north gradually rolled back Muslim rule, finally extinguishing its last remnant in Almería in 1492. The same year Columbus reached the New World, a global empire began. Spain became the strongest kingdom in Europe and leading world power during the 16th century and first half of the 17th century, but continued wars and other problems eventually led to a diminished status. A French invasion of Spain in the early 19th century led to chaos; triggering independence movements that tore apart most of the empire and left the country politically unstable. In the 20th century it suffered a devastating civil war and came under the rule of a dictatorship, leading to years of stagnation, but finishing in a strong economic revival. Democracy was restored in 1978 in the form of a constitutional monarchy. In 1986, Spain joined the European Union; experiencing a cultural renaissance and steady economic growth.
Prehistory and pre-Roman peoples in the Iberian Peninsula[edit]
Archeological research at Atapuerca indicates that the Iberian Peninsula was peopled more than a million years ago.[7] Modern humans in the form of Cro-Magnons began arriving in the Iberian Peninsula through the Pyrenees some 35,000 years ago. The best known artifacts of these prehistoric human settlements are the famous paintings in the Altamira cave of Cantabria in northern Spain, which were created about 15,000 BCE. Furthermore, archeological evidence in places like Los Millares in Almería and in El Argar in Murcia suggests that developed cultures existed in the eastern part of the Iberian Peninsula during the late Neolithic and the Bronze Age.
The two main historical peoples of the peninsula were the Iberians and the Celts, the former inhabiting the Mediterranean side from the northeast to the southwest, the latter inhabiting the Atlantic side, in the north and northwest part of the peninsula. In the inner part of the peninsula, where both groups were in contact, a mixed, distinctive culture—known as Celtiberian—was present. In addition, Basques occupied the western area of the Pyrenees mountains. Other ethnic groups existed along the southern coastal areas of present-day Andalusia. Among these southern groups there grew the earliest urban culture in the Iberian Peninsula, that of the semi-mythical southern city of Tartessos (perhaps pre-1100 BC) near the location of present-day Cádiz. The flourishing trade in gold and silver between the people of Tartessos and Phoenicians and Greeks is documented in the history of Strabo and in the biblical book of king Solomon. Between about 500 BC and 300 BC, the seafaring Phoenicians and Greeks founded trading colonies all along the Spanish Mediterranean coast. Carthaginians briefly took control of much of the Mediterranean coast in the course of the Punic Wars, until they were eventually defeated and replaced by the Romans.[8]
Roman Empire and Germanic invasions[edit]

During the Second Punic War, an expanding Roman Empire captured Carthaginian trading colonies along the Mediterranean coast (from roughly 210 BC to 205 BC), leading to eventual Roman control of nearly the entire Iberian Peninsula—a control which lasted over 500 years, bound together by law, language, and the Roman road.[9] The base Celt and Iberian population remained in various stages of Romanisation,[10] and local leaders were admitted into the Roman aristocratic class.[8]
The Romans improved existing cities, such as Tarragona (Tarraco), and established others like Zaragoza (Caesaraugusta), Mérida (Augusta Emerita), Valencia (Valentia), León ("Legio Septima"), Badajoz ("Pax Augusta"), and Palencia.[11] The peninsula's economy expanded under Roman tutelage. Hispania served as a granary for the Roman market, and its harbors exported gold, wool, olive oil, and wine. Agricultural production increased with the introduction of irrigation projects, some of which remain in use. Emperors Trajan, Theodosius I, and the philosopher Seneca were born in Hispania.[12] Christianity was introduced into Hispania in the 1st century CE and it became popular in the cities in the 2nd century CE.[8] Most of Spain's present languages and religion, and the basis of its laws, originate from this period.[9]
The first Germanic tribes to invade Hispania arrived in the 5th century, as the Roman Empire decayed.[9] The Visigoths, Suebi, Vandals and Alans arrived in Spain by crossing the Pyrenees mountain range.[13] The Romanized Visigoths entered Hispania in 415. After the conversion of their monarchy to Roman Catholicism, the Visigothic Kingdom eventually encompassed a great part of the Iberian Peninsula after conquering the disordered Suebic territories in the northwest and Byzantine territories in the southeast.[8]
Muslim Iberia[edit]
In the 8th century, nearly all of the Iberian Peninsula was conquered (711-718) by mainly Muslims (see Moors) from North Africa. These conquests were part of the expansion of the Umayyad Islamic Empire.[14] Only a number of areas in the mountains to the north of the Iberian Peninsula managed to cling to their independence, occupying the areas roughly corresponding to modern Asturias, Navarre and Aragon.

Under Islam, Christians and Jews were recognised as "peoples of the book", and were free to practice their religion, but faced a number of mandatory discriminations and penalties as dhimmis.[15][16][17] Conversion to Islam proceeded at a steadily increasing pace. Following the mass conversions in the 10th and 11th centuries it is believed that Muslims came to outnumber Christians in the remaining Muslim controlled areas.[18]
The Muslim community in the Iberian peninsula was itself diverse and beset by social tensions. The Berber people of North Africa, who had provided the bulk of the invading armies, clashed with the Arab leadership from the Middle East.[19] Over time, large Moorish populations became established, especially in the Guadalquivir River valley, the coastal plain of Valencia, and (towards the end of this period) in the mountainous region of Granada.[18]
Córdoba, the capital of the caliphate, was the largest, richest and most sophisticated city of medieval western Europe.[20] Mediterranean trade and cultural exchange flourished. Muslims imported a rich intellectual tradition from the Middle East and North Africa. Muslim and Jewish scholars played a great part in reviving and expanding classical Greek learning in Western Europe. The Romanized cultures of the Iberian peninsula interacted with Muslim and Jewish cultures in complex ways, thus giving the region a distinctive culture.[18] Outside the cities, where the vast majority lived, the land ownership system from Roman times remained largely intact as Muslim leaders rarely dispossessed landowners, and the introduction of new crops and techniques led to a remarkable expansion of agriculture.
However, by the 11th century, Muslim holdings had fractured into rival Taifa kingdoms, allowing the small Christian states the opportunity to greatly enlarge their territories and consolidate their positions.[18] The arrival of the North African Muslim ruling sects of the Almoravids and the Almohads restored unity upon Muslim holdings, with a stricter, less tolerant application of Islam, but ultimately, after some successes in invading the north, proved unable to resist the increasing military strength of the Christian states.[8]
Fall of Muslim rule and unification[edit]

The Reconquista ("Reconquest") is the centuries-long period of expansion of Spain's Christian kingdoms; the Reconquista is viewed as beginning after the battle of Covadonga in 722. The Christian army victory over the Muslim forces led to the creation of the Christian Kingdom of Asturias. Muslim armies had also moved north of the Pyrenees, but they were defeated at the Battle of Poitiers in France. Subsequently, they retreated to more secure positions south of the Pyrenees with a frontier marked by the Ebro and Duero rivers in Spain. As early as 739 Muslim forces were driven from Galicia, which was to host one of medieval Europe's holiest sites, Santiago de Compostela. A little later Frankish forces established Christian counties south of the Pyrenees; these areas were to grow into kingdoms, in the north-east and the western part of the Pyrenees. These territories included Navarre, Aragon and Catalonia.[21]
The breakup of Al-Andalus into the competing Taifa kingdoms helped the expanding Christian kingdoms. The capture of the central city of Toledo in 1085 largely completed the reconquest of the northern half of Spain.[22] After a Muslim resurgence in the 12th century,[23] the great Moorish strongholds in the south fell to Christian Spain in the 13th century—Córdoba in 1236 and Seville in 1248—leaving only the Muslim enclave of Granada as a tributary state in the south.[24] Marinid invasions from north Africa in the 13th and 14th centuries failed to re-establish Muslim rule. Also in the 13th century, the kingdom of Aragon, still ruled by the Catalan count of Barcelona, expanded its reach across the Mediterranean to Sicily.[25] Around this time the universities of Palencia (1212/1263) and Salamanca (1218/1254) were established; among the earliest in Europe. The Black Death of 1348 and 1349 devastated Spain.[26]
In 1469, the crowns of the Christian kingdoms of Castile and Aragon were united (even though both kingdoms kept a high degree of political and economical independence) by the marriage of Isabella and Ferdinand. In 1478 began the final stage of the conquest of Canary Islands and in 1492, these united kingdoms captured Granada, ending the last remnant of a 781-year presence of Islamic rule in the Iberian Peninsula.[27] The year 1492 also marked the arrival in the New World of Christopher Columbus, during a voyage funded by Isabella. That same year, Spain's Jews were ordered to convert to Catholicism or face expulsion from Spanish territories during the Spanish Inquisition.[28][29]
As Renaissance New Monarchs, Isabella and Ferdinand centralized royal power at the expense of local nobility, and the word España - whose root is the ancient name "Hispania" - began to be used to designate the whole of the two kingdoms.[29] With their wide-ranging political, legal, religious and military reforms, Spain emerged as the first world power.
Imperial Spain[edit]
The unification of the kingdoms of Aragon, Castile, León, and Navarre laid the basis for modern Spain and the Spanish Empire.[30] Spain became Europe's leading power throughout the 16th century and most of the 17th century, a position reinforced by trade and wealth from colonial possessions. Spain reached its apogee during the reigns of the first two Spanish Habsburgs, Charles I (1516–1556) and Philip II (1556–1598). Included in this period are the Italian Wars, the Dutch revolt, clashes with the Ottomans, the Anglo-Spanish war and war with France.[31]

The Spanish Empire expanded to include most part of South and Central America, Mexico, southern and western portions of today's United States, the Philippines, Guam and the Mariana Islands in Eastern Asia, the Iberian peninsula (including the Portuguese Empire (from 1580), southern Italy, Sicily, cities in Northern Africa, as well as parts of modern Germany, Belgium, Luxembourg, and the Netherlands. It was the first empire about which it was said that the sun did not set. This was an age of discovery, with daring explorations by sea and by land, the opening up of new trade routes across oceans, conquests and the beginnings of European colonialism. Along with the arrival of precious metals, spices, luxuries, and new agricultural plants, Spanish explorers and others brought back knowledge, playing a leading part in transforming the European understanding of the world.[32]
Of note was the cultural efflorescence now known as the Spanish Golden Age and the intellectual movement known as the School of Salamanca.
In the 16th and 17th centuries, Spain was confronted by unrelenting challenges from all sides. Barbary pirates under the aegis of the rapidly growing Ottoman empire, disrupted life in many coastal areas through their slave raids and renewed the threat of an Islamic invasion.[33] This at a time when Spain was often at war with France in Italy and elsewhere. Later the Protestant Reformation schism from the Catholic Church dragged the kingdom ever more deeply into the mire of religiously charged wars. The result was a country forced into ever expanding military efforts across Europe and in the Mediterranean.[34]
By the middle decades of a war and plague ridden 17th century Europe, the effects of the strain began to show. The Spanish Habsburgs had enmeshed the country in the continent wide religious-political conflicts. These conflicts drained it of resources and undermined the European economy generally. Spain managed to hold on to most of the scattered Habsburg empire, and help the imperial forces of the Holy Roman Empire reverse a large part of the advances made by Protestant forces, but it was finally forced to recognise the independence of Portugal—within its empire—and the Netherlands, and eventually surrendered Toulouse to France after the immensely destructive, Europe-wide Thirty Years War.[35]
During the latter half of the 17th century, Spain went into a gradual decline, however it maintained and enlarged its vast overseas empire, which remained intact until the 19th century.
The decline culminated in a controversy over succession to the throne which consumed the first years of the 18th century. The War of Spanish Succession (1701–1714), a wide-ranging international conflict combined with a civil war, cost Spain its European possessions and its position as one of the leading powers on the Continent.[36]
During this war, a new dynasty—the French Bourbons—was installed. Long united only by the Crown, a true Spanish state was established when the first Bourbon king Philip V of Spain united Castile and Aragon into a single state, abolishing many of the regional privileges (fueros).[37]
The 18th century saw a gradual recovery and an increase in prosperity through much of the empire. The new Bourbon monarchy drew on the French system of modernising the administration and the economy. Enlightenment ideas began to gain ground among some of the kingdom's elite and monarchy. Towards the end of the century trade finally began growing strongly. Military assistance for the rebellious British colonies in the American War of Independence improved Spain's international standing.[38]
Napoleonic rule and its consequences[edit]

In 1793, Spain went to war against the new French Republic, which had overthrown and executed its Bourbon king, Louis XVI. The war polarised the country in an apparent reaction against the gallicised elites. Defeated in the field, Spain made peace with France in 1795 and effectively became a client state of that country; the following year, it declared war against Britain and Portugal. A disastrous economic situation, along with other factors, led to the abdication of the Spanish king in favour of Napoleon's brother, Joseph Bonaparte.
This new foreign monarch was regarded with scorn. On May 2, 1808, the people of Madrid began a nationalist uprising against the French army, marking the beginning of what is known to the Spanish as the War of Independence, and to the English as the Peninsular War. Napoleon was forced to intervene personally, defeating several badly-coordinated Spanish armies and forcing a British Army to retreat to Corunna. However, further military action by Spanish guerrillas and Wellington's Anglo-Portuguese army, combined with Napoleon's disastrous invasion of Russia, led to the ousting of the French from Spain in 1814, and the return of King Ferdinand VII.
The French invasion proved disastrous for Spain's economy, and left a deeply divided country that was prone to political instability for more than a century. The power struggles of the early 19th century led to the loss of all of Spain's colonies in Latin America, with the exception of Cuba and Puerto Rico.
Spanish-American War[edit]
Amid the instability and economic crisis that afflicted Spain in the 19th century there arose nationalist movements in the Philippines and Cuba. Wars of independence ensued in those colonies and eventually the United States became involved. Despite the commitment and ability shown by some military units, they were so mismanaged by the highest levels of command that the Spanish–American War of 1898 was soon over. "El Desastre" (The Disaster), as the war became known in Spain, helped give impetus to the Generation of 98 who were already conducting much critical analysis concerning the country. It also weakened the stability that had been established during Alfonso XII's reign.
20th century[edit]
The 20th century brought little peace; Spain played a minor part in the scramble for Africa, with the colonisation of Western Sahara, Spanish Morocco and Equatorial Guinea. The heavy losses suffered during the Rif war in Morocco helped to undermine the monarchy. A period of authoritarian rule under General Miguel Primo de Rivera (1923-1931) ended with the establishment of the Second Spanish Republic. The Republic offered political autonomy to the Basque Country, Catalonia and Galicia and gave voting rights to women.

The bitterly fought Spanish Civil War (1936-39) ensued. Three years later the Nationalist forces, led by General Francisco Franco, emerged victorious with the support of Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy. The Republican side was supported by the Soviet Union and Mexico, but it was not supported by the Western powers due to the British-led policy of Non-Intervention. The Spanish Civil War has been called the first battle of the Second World War; under Franco, Spain was neutral in the Second World War though sympathetic to the Axis.[39]
The only legal party under Franco's regime was the Falange española tradicionalista y de las JONS, formed in 1937; the party emphasised anti-Communism, Catholicism and nationalism. Nonetheless, since Franco's anti-democratic ideology was opposed to the idea of political parties, the new party was renamed officially a National Movement (Movimiento Nacional) in 1949.
After World War II, Spain was politically and economically isolated, and was kept out of the United Nations until 1955, when due to the Cold War it became strategically important for the U.S. to foment a military presence on the Iberian peninsula, next to the Mediterranean Sea and the Strait of Gibraltar, in order to protect southern Europe. In the 1960s, Spain registered an unprecedented economic growth in what was called the Spanish miracle, which rapidly resumed the long interrupted transition towards a modern industrial economy with a thriving tourism sector and a high degree of human development.
Upon the death of General Franco in November 1975, Prince Juan Carlos assumed the position of king and head of state. With the approval of the new Spanish Constitution of 1978 and the arrival of democracy, the State devolved autonomy to the regions and created an internal organization based on autonomous communities. In the Basque Country, moderate Basque nationalism coexisted with a radical nationalism supportive of the terrorist group ETA.
On February 23 1981, rebel elements among the security forces seized the Cortes and tried to impose a military-backed government. However, the great majority of the military forces remained loyal to King Juan Carlos, who used his personal authority and addressed the usurpers via national TV as commander in chief to put down the bloodless coup attempt.
In 1982, the Spanish Socialist Workers Party (PSOE) came to power, which represented the return to power of a leftist party after 43 years. In 1986, Spain joined the European Community (which was to become the European Union). The PSOE was replaced in government by the Partido Popular (PP) after the latter won the 1996 General Elections; at that point the PSOE had served almost 14 consecutive years in office.
The Government of Spain has been involved in a long-running campaign against the terrorist organization ETA ("Basque Homeland and Freedom"), founded in 1959 in opposition to Franco and dedicated to promoting Basque independence through violent means. They consider themselves a guerrilla organization while they are listed as a terrorist organization by both the European Union and the United States on their respective watchlists. The current nationalist-led Basque Autonomous government does not endorse ETA's nationalist violence, which has caused over 800 deaths in the past 40 years.
21st century[edit]
On January 1, 2002, Spain terminated its historic peseta currency and replaced it with the euro, which has become its national currency shared with 15 other countries from the Eurozone. This culminated the first phase of a period of economic growth,[40] which has kept the Spanish economy growing well over the EU average, but concerns are growing that the extraordinary property boom and high foreign trade deficits of recent years may bring this to an end.[41]
On March 11, 2004, a series of bombs exploded in commuter trains in Madrid, Spain. The bombings were claimed by al Qaeda[42], whereas after a five months trial in 2007 it was concluded that the bombings were perpetrated by a local Islamist militant group inspired by al-Qaeda, but without direct links to that organisation[43]. The bombings killed 191 people and wounded more than 1800, and it has been claimed that the intention of the perpetrators was to influence the outcome of the Spanish general election, held three days later on March 14.[44] Although initial suspicions of responsibility for the bombings focused on the Basque group ETA, evidence soon emerged indicating possible Islamist involvement. Because of the proximity of the election, the issue of responsibility quickly became a source of political controversy, with the main competing parties PP and PSOE crossing accusations over the handling of the aftermath.[45] A couple of days later, at the March 14 elections, PSOE, led by José Luis Rodríguez Zapatero, obtained a relative majority, enough to form the new cabinet with Rodríguez Zapatero as the new Presidente del Gobierno or prime minister of Spain, thus succeeding the former PP administration.[46]
Politics[edit]
Spanish Government[edit]

Spain is a constitutional monarchy, with a hereditary monarch and a bicameral parliament, the Cortes Generales. The executive branch consists of a Council of Ministers presided over by the President of Government (comparable to a prime minister), proposed by the monarch and elected by the National Assembly following legislative elections.
The legislative branch is made up of the Congress of Deputies (Congreso de los Diputados) with 350 members, elected by popular vote on block lists by proportional representation to serve four-year terms, and a Senate (Senado) with 259 seats of which 208 are directly elected by popular vote and the other 51 appointed by the regional legislatures to also serve four-year terms.
- Chief of State
- King Juan Carlos I, since November 22 1975
- Head of Government
- Cabinet
- Council of Ministers (Spanish Consejo de Ministros) designated by the president.
The Spanish nation is organizationally composed in the form of called Estado de las Autonomías ("State of Autonomies"); it is one of the most decentralized countries in Europe, along with Switzerland, Germany and Belgium;[47][48][49][50] for example, all Autonomous Communities have their own elected parliaments, governments, public administrations, budgets, and resources; therefore, health and education systems among others are managed regionally, besides, the Basque Country and Navarre also manage their own public finances based on foral provisions. In Catalonia and the Basque Country, a full-fledged autonomous police corps replaces some of the State police functions (see Mossos d'Esquadra and Ertzaintza).
Spanish Constitution[edit]
The Spanish Constitution of 1978 is the culmination of the Spanish transition to democracy.
The constitutional history of Spain dates back to the constitution of 1812. After the death of Francisco Franco in 1975, a general election in 1977 convened the Constituent Cortes (the Spanish Parliament, in its capacity as a constitutional assembly) for the purpose of drafting and approving the constitution of 1978.
As a result, Spain is now composed of 17 autonomous communities and two autonomous cities with varying degrees of autonomy thanks to its Constitution, which nevertheless explicitly states the indivisible unity of the Spanish nation as well as that Spain has today no official religion but all are free to practice and believe as they wish.[51]
Foreign relations of Spain[edit]
After the return of democracy following the death of Franco in 1975, Spain's foreign policy priorities were to break out of the diplomatic isolation of the Franco years and expand diplomatic relations, enter the European Community, and define security relations with the West.
As a member of NATO since 1982, Spain has established itself as a major participant in multilateral international security activities. Spain's EU membership represents an important part of its foreign policy. Even on many international issues beyond western Europe, Spain prefers to coordinate its efforts with its EU partners through the European political cooperation mechanisms.
With the normalization of diplomatic relations with North Korea in 2001, Spain completed the process of universalizing its diplomatic relations.
Spain has maintained its special identification with Latin America. Its policy emphasizes the concept of an Iberoamerican community, essentially the renewal of the historically liberal concept of hispanoamericanismo (or hispanism as it is often referred to in English), which has sought to link the Iberian peninsula with Latin America through language, commerce, history and culture. Spain has been an effective example of transition from dictatorship to democracy for formerly non-democratic South American states, as shown in the many trips that Spain's King and Prime Ministers have made to the region.
Territorial disputes[edit]
Territory claimed by Spain[edit]
There is a territorial dispute with the United Kingdom over Gibraltar, a 6 square km Overseas Territory of the United Kingdom in the southernmost part of the Iberian Peninsula which was conquered by Britain from Spain in 1704 during the War of the Spanish Succession, along with the Spanish island of Minorca (which had also been invaded but was reconquered in 1782 and finally ceded back to Spain in 1802 by the Treaty of Amiens).
The legal situation concerning Gibraltar was settled in 1713 by the Treaty of Utrecht, in which Spain ceded the territory in perpetuity to the British Crown[52] stating that, should the British abandon this post, it would return to Spanish sovereignty.
Ever since the 1940s Spain has called for the return of Gibraltar. The overwhelming majority of Gibraltarians strongly oppose this, along with any proposal of shared sovereignty.[53] UN resolutions call on the United Kingdom and Spain, both EU members, to reach an agreement over the status of Gibraltar.[54]
Spanish territories claimed by other countries[edit]
Morocco claims the Spanish cities of Ceuta and Melilla and the plazas de soberanía islets off the northern coast of Africa. Portugal does not recognise Spain's sovereignty over the territory of Olivenza.
Administrative divisions[edit]
Spain is politically organized into 17 Autonomous Communities (comunidades autónomas) and 2 autonomous cities (ciudades autónomas) - Ceuta and Melilla.
Administratively Spain also comprises fifty provinces. Seven autonomous communities are composed of only one province: Asturias, Balearic Islands, Cantabria, La Rioja, Madrid, Murcia, and Navarre.
Historically, some provinces are also divided into comarcas (roughly equivalent to a US "county" or an English district). The lowest administrative division of Spain is the municipality (municipio).
Geography[edit]
At 194,884 mi2 (504,782 km2), Spain is the world's 51st-largest country. It is some 47,000 km2 smaller than France and 81,000 km2 larger than the U.S. state of California.
On the west, Spain borders Portugal, on the south, it borders Gibraltar (a British overseas territory) and Morocco, through its cities in North Africa (Ceuta and Melilla). On the northeast, along the Pyrenees mountain range, it borders France and the tiny principality of Andorra. Spain also includes the Balearic Islands in the Mediterranean Sea, the Canary Islands in the Atlantic Ocean and a number of uninhabited islands on the Mediterranean side of the strait of Gibraltar, known as [Plazas de soberanía] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help), such as the Chafarine islands, the isle of Alborán, the "rocks" ([peñones] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help)) of Vélez and Alhucemas, and the tiny Isla Perejil. Along the Pyrenees in Catalonia, a small exclave town called Llívia is surrounded by France.
Mainland Spain is dominated by high plateaus and mountain ranges, such as the Sierra Nevada. Running from these heights are several major rivers such as the Tagus, the Ebro, the Duero, the Guadiana and the Guadalquivir. Alluvial plains are found along the coast, the largest of which is that of the Guadalquivir in Andalusia.
Climate[edit]
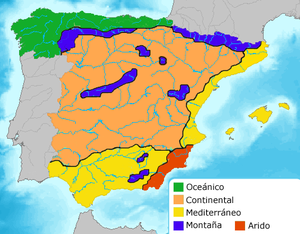
Due to Spain's geographical situation and orographic conditions, the climate is extremely diverse; it can be roughly divided into three areas:
- A Continental Mediterranean climate in the inland areas of the Peninsula (largest city, Madrid).
- A Mediterranean climate region extends from the Andalusian plain along the southern and eastern coasts up to the Pyrenees, on the seaward side of the mountain ranges that run near the coast (largest city, Barcelona).
- An Oceanic climate in Galicia and the coastal strip near the Bay of Biscay (largest city, Bilbao). This area is often called Green Spain.
Military of Spain[edit]
The armed forces of Spain are known as the Spanish Armed Forces (Spanish: Fuerzas Armadas Españolas). Their Commander-in-Chief is the King of Spain, Juan Carlos I.
The Spanish Armed Forces are divided into four branches:
- Army (Ejército de Tierra)
- Navy (Armada)
- Air Force (Ejército del Aire)
- Guardia Civil (Military police) which serves for the most part as a rural and general purpose police force.
Economy[edit]
According to the World Bank, Spain's economy is the eighth largest worldwide and the fifth largest in Europe. As of 2007, absolute GDP was valued at $1.362 trillion according to the CIA Factbook, (see List of countries by GDP (nominal)). The per capita PPP is estimated at $33,700 (2007), ahead of G7 countries like Italy and placing Spain at a similar per capita basis as France or Japan (both with an 2007 estimated at $33,800). The Spanish economy grew 3.8% in 2007 outpacing all G7 members and all the big EU economies for the 3rd consecutive year.
The centre-right government of former prime minister José María Aznar worked successfully to gain admission to the group of countries launching the euro in 1999. Unemployment stood at 7.6% in October 2006, a rate that compares favorably to many other European countries, and which is a marked improvement over rates that exceeded 20% in the early 1990s. Perennial weak points of Spain's economy include high inflation,[55] a large underground economy,[56] and an education system which OECD reports place among the poorest for developed countries, together with the United States and UK.[57] Nevertheless, it is expected that the Spanish economy will continue growing above the EU average based on the strengthening of industry, the growth of the global economy and increasing trade with Latin America and Asia.
The Spanish economy is credited for having avoided the virtual zero growth rate of some of its largest partners in the EU.[58] In fact, the country's economy has created more than half of all the new jobs in the European Union over the five years ending 2005.[59] The Spanish economy has thus been regarded lately as one of the most dynamic within the EU, attracting significant amounts of foreign investment.[60] During the last four decades the Spanish tourism industry has grown to become the second biggest in the world,[61] worth approximately 40 billion Euros (approx. 5% of GDP) in 2006[62] More recently, the Spanish economy has benefited greatly from the global real estate boom, with construction representing 16% of GDP and 12% of employment.[61] According to calculations by the German newspaper Die Welt, Spain is on pace to overtake countries like Germany in per capita income by 2011.[63] However, the downside of the real estate boom has been a corresponding rise in the levels of personal debt; as prospective homeowners struggle to meet asking prices, the average level of household debt has tripled in less than a decade. Among lower income groups, the median ratio of indebtedness to income was 125% in 2005.[64]
Demographics[edit]

In 2008 Spain officially reached 46.06 million people[65] registered at the Padrón municipal, an official record analogous to the British Register office. Spain's population density, at 89.6/km2 (231/sq. mile), is lower than that of most Western European countries and its distribution along the country is very unequal. With the exception of the region surrounding the capital, Madrid, the most populated areas lie around the coast.
The population of Spain doubled during the 20th century, due to the spectacular demographic boom by the 1960s and early 1970s. The pattern of growth was extremely uneven due to large-scale internal migration from the rural interior to the industrial cities during the 60s and 70s. No fewer than eleven of Spain's fifty provinces saw an absolute decline in population over the century. Then, after the birth rate plunged in the 80s and Spain's population became stalled, a new population increase started based initially in the return of many Spanish who emigrated to other European countries during the 70s and, more recently, it has been boosted by the large figures of foreign immigrants, mostly from Latin America (38.75%), Eastern Europe (16.33%), North Africa (14.99%) and Sub-Saharan Africa (4.08%).[66] In 2005, Spain instituted a 3-month amnesty program through which certain hitherto undocumented aliens were granted legal residency. Also some important pockets of population coming from other countries in the European Union are found (20.77% of the foreign residents), specially along the Mediterranean costas and Balearic islands, where many choose to live their retirement or even telework. These are mostly English, French, German, and Dutch from fellow EU countries and, from outside the EU, Norwegian.
Immigration in Spain[edit]
According to the Spanish government there were 4.5 million foreign residents in Spain in 2007; independent estimates put the figure at 4.8 million people, or 11% of the total population (Red Cross, World Disasters Report 2006). According to residence permit data for 2005, about 500,000 were Moroccan, another 500,000 were Ecuadorian, more than 200,000 were Romanian, and 260,000 were Colombian. Other important foreign communities are British (8.09%), French (8.03%), Argentine (6.10%), German (5.58%) and Bolivian (2.63%). In 2005, a regularisation programme increased the legal immigrant population by 700,000 people. Since 2000, Spain has experienced high population growth as a result of immigration flows, despite a birth rate that is only half the replacement level. This sudden and ongoing inflow of immigrants, particularly those arriving clandestinely by sea, has caused noticeable social tension.[67][68][69][70][71]
Based on 2004 figures,[72] within the EU Spain has the second highest immigration rate in percentage terms (after Cyprus), but by a great margin the highest in actual numbers of immigrants.
There are a number of reasons to explain the high level of immigration, including Spain's cultural ties with Latin America, its geographical position, the porosity of its borders, the large size of its underground economy and the strength of the agricultural and construction sectors which demand more low cost labour than can be offered by the national workforce. Another statistically significant factor is the large number of residents of the EU origin typically retiring to Spain's Mediterranean coast. In fact, Spain has been Europe's largest absorber of migrants for the past six years, with its immigrant population increasing fourfold as 2.8 million people have arrived. According to the Financial Times, Spain is the most favoured destination for West Europeans considering a move from their own country and seeking jobs elsewhere in the EU. [3] (see Immigration to Spain).
Minority groups[edit]
Spain has a number of descendants of populations from former colonies (especially Equatorial Guinea) and immigrants from several Sub-Saharan and Caribbean countries have been recently settling in Spain. There are also sizeable numbers of Asian immigrants, most of whom are of Chinese, Filipino, Middle Eastern, Pakistani and Indian origins; the population of Spaniards of Latin American descent is sizeable as well and a fast growing segment. Other growing groups are Britons (761,000 in 2006), Germans and other immigrants from western and Eastern Europe.[73]
Jewish emigration to Spain is primarily the result of three events: after the 19th century, some Jews established themselves in Spain as a result of migration from what was formerly Spanish Morocco, the flight of Jews escaping from Nazi repression, and immigration from Argentina. Spanish law allows Sephardi Jews to claim Spanish citizenship.
The arrival of the Gitanos (Gypsies), a Roma people group, began in the 16th century.
Most populous urban regions[edit]
- Madrid 5,943,041
- Barcelona 5,327,872
- Valencia 1,623,724
- Seville 1,317,098
- Málaga 1,074,074
- Bilbao 946,829
Identities[edit]
Peoples[edit]
The Spanish Constitution of 1978, in its second article, recognises historic entities ("nationalities", a carefully chosen word in order to avoid the more politically charged "nations") and regions, within the context of the Spanish nation. For some people, Spain's identity consists more of an overlap of different regional identities than of a sole Spanish identity. Indeed, some of the regional identities may even conflict with the Spanish one. Distinct ethnic groups within Spain include the Basques, Catalans, and Galicians.[74]
It is this last feature of "shared identity" between the more local level or Autonomous Community and the Spanish level which makes the identity question in Spain complex and far from univocal.
Languages[edit]

| Catalan (17%), co-official, except in La Franja and Carxe Basque (2%), co-official, in Basque Country and Navarre Galician (7%), co-official, except in Asturias and Castile and Leon | Extremaduran, unofficial Aragonese, unofficial |
Spanish ([español] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) or [castellano] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help)), also known as Castilian, is the only language with official status nationwide. Other languages have been declared co-official, along with Spanish, in (some of) their constituent communities where they are spoken:
- Aranese ([aranés] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help)) (a variant of Occitan), in Catalonia;
- Basque ([euskera] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help)) in the Basque Country and Navarre;
- Catalan ([català] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help)) in Catalonia, the Balearic Islands and in the Valencian Community, known in the latter officially as Valencian;
- Galician ([galego] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help)) in Galicia.
There are also some other surviving Romance minority languages such as Astur-Leonese (which includes Asturian, Leonese, Extremaduran and Cantabrian) and Aragonese. Asturian ([asturianu] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help)) is "protected" in Asturias[77] and Aragonese is vaguely recognized in Aragon. But unlike Aranese, Basque, Catalan/Valencian and Galician, they do not have any official status. This might be due to their very small number of speakers, a less significant written tradition (in comparison to Catalan or Galician) and lower self-awareness of their speakers which traditionally meant lack of strong popular demand for their recognition in the regions in which they are spoken.[78] In the North African Spanish city of Melilla, Tarifit is spoken by an important part of the population.
In the tourist areas of the Mediterranean coast and the islands, English and German are widely spoken by tourists, foreign residents, and tourism workers.
Religion[edit]
Although Chapter 2 of the Constitution states that no religion shall have a state character, Roman Catholicism is the main religion in the country. About 76% of Spaniards identify themselves as Catholics, about 2% identify with another religious faith, and about 19% identify themselves as non-religious. A study conducted in October 2006 by the Spanish Centre of Sociological Investigations[79] shows that of the 76% of Spaniards who identify themselves as Catholics or with another religious faith, 54% hardly ever or never go to church, 15% go to church a few times per year, 10% a few times per month and 19% attend church every Sunday or multiple times per week. About 22% of the entire Spanish population attends religious services at least once per month.

Evidence of the secular nature of contemporary Spain can be seen in the widespread support for the legalisation of same-sex marriage in Spain — over 66% of Spaniards support gay marriage according to a 2004 study by the Centre of Sociological Investigations.[80] Indeed, in June 2005 a bill was passed by 187 votes to 147 to allow gay marriage, making Spain the third country in the European Union to allow same-sex couples to marry after Belgium and the Netherlands.
Protestant denominations are also present, all of them with less than 50,000 members. Evangelism has been better received among Gypsies than among the general population; pastors have integrated flamenco music in their liturgy. Taken together, all self-described "Evangelicals" slightly surpass Jehovah's Witnesses (105,000) in number. While not Protestants, about 35,000 residents of Spain are members of the The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (Mormons).
The recent waves of immigration have led to an increasing number of Muslims, who have about 1 million members. Muslims had not lived in Spain for centuries; however, colonial expansion in Northern and Western Africa gave some number of residents in the Spanish Morocco and the Western Sahara full citizenship. Presently, Islam is the second largest religion in Spain, accounting for approximately 2.5% of the total population.
Along with these waves of immigration, a significant number of Latin American people, who tend to be strong Catholic practitioners, have helped the Catholic Church to recover.
Judaism was practically non-existent until the 19th century, when Jews were again permitted to enter the country. Currently there are around 62,000 Jews in Spain, most arrivals in the past century and some descendants of Spanish Jews and accounting for less than 1% of the total number of inhabitants. Spain is believed to have been about 8% Jewish on the eve of the Spanish Inquisition.[citation needed]
Culture[edit]

Spain is known for its culturally diverse heritage, having been influenced by many nations and peoples throughout its history. Spanish culture has its origins in the Iberian, Celtiberian, Latin, Visigothic, Roman Catholic, and Islamic cultures. The definition of a national Spanish culture has been characterized by tension between the centralized state (dominated in recent centuries by Castile) and numerous regions and minority peoples. In addition, the history of the nation and its Mediterranean and Atlantic environment have played strong roles in shaping its culture.
After Italy, Spain is the country with the second highest number of UNESCO World Heritage Sites in the world, with a total of 40.
Education in Spain[edit]
State Education in Spain is free and compulsory from the age of 6 to 16. The current education system is called LOGSE (Ley de Ordenación General del Sistema Educativo).
Spanish Academy[edit]
The Real Academia Española (Spanish for "Royal Spanish Academy"; RAE) is the institution responsible for regulating the Spanish language. It is based in Madrid, but is affiliated with national language academies in 21 Spanish-speaking nations through the Association of Spanish Language Academies. Its emblem is a fiery crucible, and its motto is Limpia, fija y da esplendor ("It cleans, sets, and gives splendor").
Spanish art[edit]

Spanish art is an important and influential type of art in Europe. Spanish art is the name given to the artistic disciplines and works developed in Spain throughout time, and those by Spanish authors world-wide. Due to historical, geographical and generational diversity, Spanish art has known a great number of influences. The Moorish heritage in Spain, especially in Andalusia, is still evident today in cities like Córdoba, Seville, and Granada. European influences include Italy, Germany and France, especially during the Baroque and Neoclassical periods.
Spanish literature[edit]

Spanish literature is the name given to the literary works written in Spain throughout time, and those by Spanish authors world-wide. Due to historic, geographic and generational diversity, Spanish literature has known a great number of influences and it is very diverse. Some major movements can be identified within it.
Spanish architecture[edit]

Spanish architecture refers to architecture carried out during any era in what is now modern-day Spain, and by Spanish architects worldwide. The term includes buildings within the current geographical limits of Spain before this name was given to those territories (whether they were called Hispania, Al-Andalus, or were formed of several Christian kingdoms). Due to its historical and geographical diversity, Spanish architecture has drawn from a host of influences.
For example, Córdoba was established as the cultural Capital of its time under the Umayyad dynasty. Simultaneously, the Christian kingdoms gradually emerged and developed their own styles, at first mostly isolated from European architectural influences, and later integrated into Romanesque and Gothic streams, they reached an extraordinary peak with numerous samples along the whole territory. The Mudéjar style, from the 12th to 17th centuries, was characterised by the blending of cultural European and Arabic influences.
The arrival of Modernism in the academic arena produced figures such as Gaudí and much of the architecture of the 20th century. The International style was led by groups like GATEPAC. Spain is currently experiencing a revolution in contemporary architecture and Spanish architects like Rafael Moneo, Santiago Calatrava, Ricardo Bofill as well as many others have gained worldwide renown.
Music of Spain[edit]
Spanish music is often considered abroad to be synonymous with flamenco, an Andalusian musical genre, which, contrary to popular belief, is not widespread outside that region. Various regional styles of folk music abound in Aragon, Catalonia, Valencia, Castile, the Basque Country, Galicia and Asturias. Pop, rock, hip hop and heavy metal are also popular.
Cinema of Spain[edit]
In recent years, Spanish cinema has achieved high marks of recognition as a result of its creative and technical excellence. In the long history of Spanish cinema, the great filmmaker Luis Buñuel was the first to achieve universal recognition, followed by Pedro Almodóvar in the 1980s. Spanish cinema has also seen international success over the years with films by directors like Segundo de Chomón, Florián Rey, Luis García Berlanga, Carlos Saura, Julio Medem and Alejandro Amenábar.

Spanish cuisine[edit]
Spanish cuisine consists of a great variety of dishes which stem from differences in geography, culture and climate. It is heavily influenced by seafood available from the waters that surround the country, and reflects the country's deep Mediterranean roots. Spain's extensive history with many cultural influences has led to a unique cuisine.
Sports in Spain[edit]
Sport in Spain has been dominated by football since the early 20th century. Basketball, tennis, cycling, handball, motorcycling and, lately, Formula 1 are also important due to presence of Spanish champions in all these disciplines. Today, Spain is a major world sports power, especially since the 1992 Summer Olympics that were hosted in Barcelona and promoted a great variety of sports in the country. The tourism industry has led to an improvement in sports infrastructure, especially for water sports, golf and skiing.
Public holidays in Spain[edit]
Public holidays celebrated in Spain include a mix of religious (Roman Catholic), national and regional observances. Each municipality is allowed to declare a maximum of 14 public holidays per year; up to nine of these are chosen by the national government and at least two are chosen locally.
International rankings[edit]
- Reporters Without Borders world-wide press freedom index 2007: Rank 33 out of 169 countries.[81]
- The Economist Intelligence Units: Rank 10 out of 111 countries (ahead of countries like the United States of America, the United Kingdom, and France)[82]
- Nation Master's list by economic importance: Rank 9 of 25 countries, only surpassed by G-8 members.[83]
- Nation Master's list by technological achievement: Rank 18 of 68 countries.[84]
- Gallery of Images
-
The Sagrada Família by night, Barcelona
-
The Sanctuary of Santa María Magdalena in Novelda
-
The Pyrenees
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^ Instituto Nacional de Estadística de España. "Official Population Figures of Spain. Population on the 1st January 2007". Retrieved 2008-02-05.
- ^ IMF (2008 Data base)
- ^ International Monetary Fund "IMF (2007)". World Economic Outlook Database, April 2008.
{{cite web}}: Check|url=value (help); Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ CIA World Factbook
- ^ The Spanish constitution does not establish any official denomination of the country, even though España (Spain), Estado español (Spanish State) and Nación española (Spanish Nation) are used interchangeably. The Ministry of Foreign Affairs, in an Ordinance published in 1984, declared that "[...] denominations "Spain" and "Kingdom of Spain" are equally valid to designate the Spanish State in international treaties..."[1]
- ^ Rank by nominal GDP: 8 (2007) ; List of countries by GDP (PPP) per capita: 28 (2007) ; Economy of the European Union: 13 (2006).
- ^ "'First west Europe tooth' found". BBC News. 30 June 2007. Retrieved 2007-10-10.
- ^ a b c d e Rinehart, Robert (1998). "A Country Study: Spain - Hispania". Library of Congress Country Series. Retrieved 2007-03-08.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c Payne, Stanley G. (1973). "A History of Spain and Portugal; Ch. 1 Ancient Hispania". The Library of Iberian Resources Online. Retrieved 2007-03-08.
- ^ The latifundia (sing., latifundium), large estates controlled by the aristocracy, were superimposed on the existing Iberian landholding system.
- ^ The Roman provinces of Hispania included Provincia Hispania Ulterior Baetica (Hispania Baetica), whose capital was Corduba, presently Córdoba, Provincia Hispania Ulterior Lusitania (Hispania Lusitania), whose capital was Emerita Augusta (now Mérida), Provincia Hispania Citerior, whose capital was Tarraco (Tarragona), Provincia Hispania Nova, whose capital was Tingis (Tánger in present Morocco), Provincia Hispania Nova Citerior and Asturiae-Calleciae (these latter two provinces were created and then dissolved in the 3rd century CE).
- ^ The poets Martial, Quintilian and Lucan were also born in Hispania.
- ^ This led to the establishment of the Suebi Kingdom in Gallaecia, in the northwest, the Vandal Kingdom of Vandalusia (Andalusia) and the Visigothic Kingdom in Toledo.
- ^ The Moorish armies continued northwards until they were defeated in central France at the Battle of Tours in 732.
- ^ The Treatment of Jews in Arab/Islamic Countries
- ^ The Forgotten Refugees
- ^ The Almohads
- ^ a b c d Payne, Stanley G. (1973). "A History of Spain and Portugal; Ch. 2 Al-Andalus". The Library of Iberian Resources Online. Retrieved 2007-03-09.
- ^ The Berbers soon gave up attempting to settle the harsh lands in the north of the Meseta Central handed to them by the Arab rulers.
- ^ It was not until the 12th century that western medieval Christendom began reaching comparable levels of sophistication, and this was due in to a great extent to the stimulus coming from Muslim Al-Andalus.
- ^ Rinehart, Robert (1998). "A Country Study: Spain - Castile and Aragon". Library of Congress Country Series. Retrieved 2007-03-11.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Initially, as the Reconquista advanced south, different religions were respected and several Castilian kings in subsequent years (Ferdinand III, Alfonso X, Peter I) named themselves 'king of the three peoples' or 'king of the three religions'. Only rarely mosques and synagogues were converted into churches before 1492, and some areas of Christian Spain had large Muslim and Jewish populations that were a substantial component in the economic activity. Indeed they brought many of the Moorish influences in art, architecture and food with them.
- ^ Ransoming Captives in Crusader Spain: The Order of Merced on the Christian-Islamic Frontier
- ^ Payne, Stanley G. (1973). "A History of Spain and Portugal; Ch. 4 Castile-León in the Era of the Great Reconquest". The Library of Iberian Resources Online. Retrieved 2007-03-11.
- ^ Payne, Stanley G. (1973). "A History of Spain and Portugal; Ch. 5 The Rise of Aragón-Catalonia". The Library of Iberian Resources Online. Retrieved 2007-03-11.
- ^ Channel 4 - History - The Black Death
- ^ The Treaty of Granada (see The Treaty of Granada, 1492) guaranteed religious tolerance toward Muslims.
- ^ Muslims were expelled in a lengthier process beginning in 1502, and ending as late as 1609-1614.
- ^ a b Rinehart, Robert (1998). "A Country Study: Spain - The Golden Age". Library of Congress Country Series. Retrieved 2007-03-11.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ European Voyages of Exploration: Imperial Spain
- ^ Payne, Stanley G. (1973). "A History of Spain and Portugal; Ch. 13 The [[Spanish Empire]]". The Library of Iberian Resources Online. Retrieved 2007-03-12.
{{cite web}}: URL–wikilink conflict (help) - ^ Thomas, Hugh (2003). Rivers of gold: the rise of the Spanish Empire. London: George Weidenfeld & Nicholson. pp. passim.
- ^ The coastal villages and towns of Spain and Mediterranean islands were frequently attacked by Barbary pirates from North Africa, who were under the aegis of the Ottoman empire. The Formentera was even temporarily left by its population and long stretches of the Spanish and Italian coasts were almost completely abandoned by their inhabitants. In 1514, 1515 and 1521 coasts of the Balearic Islands and the Spanish mainland were raided by the Turkish privateer and Ottoman admiral Hayreddin Barbarossa. According to Robert Davis between 1 million and 1.25 million Europeans were captured by North African pirates and sold as slaves during the 16th and 17th centuries. These slaves were captured mainly from seaside villages in Spain, Italy and Portugal.
- ^ The Seventeenth-Century Decline
- ^ Payne, Stanley G. (1973). "A History of Spain and Portugal; Ch. 14 Spanish Society and Economics in the Imperial Age". The Library of Iberian Resources Online. Retrieved 2007-03-12.
- ^ Rinehart, Robert (1998). "A Country Study: Spain - Spain in Decline". Library of Congress Country Series. Retrieved 2007-03-12.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Rinehart, Robert (1998). "A Country Study: Spain - Bourbon Spain". Library of Congress Country Series. Retrieved 2007-03-12.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Gascoigne, Bamber (1998). "History of Spain: Bourbon dynasty: from AD 1700". Library of Congress Country Series. Retrieved 2007-03-12.
- ^ Over a hundred thousand highly motivated Spanish Civil War veterans were to give both sides the benefit of their experience throughout the Second World War in Europe, the Eastern Front and North Africa. Many in the French Resistance and French Foreign Legion were Spanish as was the 9th Armoured Company that spearheaded Général Leclerc's 2nd Armoured Division's liberation of Paris. On the other side, some 47,000 Spaniards fought against the Soviet Union in the Wehrmacht's Blue Division (División Azul).
- ^ Pfanner, Eric (July 11, 2002). "Economy reaps benefits of entry to the 'club' : Spain's euro bonanza". International Herald Tribune. Retrieved 2007-10-10.
- ^ "Spain's economy / Plain sailing no longer / Economist.com". May 3, 2007. Retrieved 2007-10-10.
- ^ BBC NEWS World | Europe | Al-Qaeda 'claims Madrid bombings'
- ^ BBC NEWS World | Europe | Madrid bombers get long sentences
- ^ Del 11-M al 14-M: estrategia yihadista, elecciones generales y opinión pública
- ^ BBC NEWS World | Europe | Spain votes under a shadow
- ^ BBC NEWS World | Europe | Spain awakes to socialist reality
- ^ CNN.com - Catalonians vote for more autonomy - Jun 18, 2006
- ^ "Economic Survey: Spain 2005". Organisation for Economic Co-Operation and Development. Retrieved 2007-10-10.
- ^ "Economist.com / Country Briefings: Spain". Retrieved 2007-10-10.
- ^ The World Bank: Swiss Experience With Decentralized Government
- ^ Spanish Constitution
- ^ Tratado de Utretch - Gibraltar (Spanish)
- ^ Gibraltar rejects Spain
- ^ UN Consensus Resolution
- ^ "Spain's Economy: Closing the Gap," in the OECD Observer, May 2005. Retrieved July 8, 2007.
- ^ Going Underground: America's Shadow Economy, FrontPage magazine, January 2005
- ^ OECD report for 2006
- ^ OECD figures
- ^ Economic statistics
- ^ Official report on Spanish recent Macroeconomics, including tables and graphics
- ^ a b "Global Guru" analysis
- ^ Bank of Spain economic report.
- ^ http://www.europeanfoundation.org/docs/id210.pdf
- ^ Bank of Spain Economic Bulletin 07/2005
- ^ http://www.ine.es/jaxi/menu.do?type=pcaxis&path=%2Ft20/e260&file=inebase&L=1
- ^ Instituto Nacional de Estadística
- ^ Instituto Nacional de Estadística: Avance del Padrón Municipal a 1 de enero de 2006. Datos provisionales
- ^ Immigration Shift: Many Latin Americans Choosing Spain Over U.S.
- ^ Spain: Immigrants Welcome
- ^ Immigrants Fuel Europe's Civilization Clash
- ^ Spanish youth clash with immigrant gangs
- ^ Eurostat - Population in Europe in 2005
- ^ Immigration statistics.
- ^ Kingdom of Spain: People
- ^ Spain: People, CIA World Factbook.
- ^ BOPA N° 229 - Martes, 3 de octubre de 2006
- ^ Junta General del Principado de Asturias
- ^ Ethnologue report of Spain and map from Proel.org
- ^ Centre of Sociological Investigations, questions 32 and 32a
- ^ Centre of Sociological Investigations
- ^ Annual Worldwide Press Freedom Index, 2007
- ^ Worldwide Quality-of-Life Index, 2005 The Economist.
- ^ Nation Master's country ranking by economic importance.
- ^ Nation Master's country ranking by technological achievement.
Further reading[edit]
- Thomas, Hugh (2003). Rivers of gold: the rise of the Spanish Empire. London: George Weidenfeld & Nicholson. ISBN 978-0297645634.
- John Hickman and Chris Little, "Seat/Vote Proportionality in Romanian and Spanish Parliamentary Elections", Journal of Southern Europe and the Balkans Volume 2, Number 2, November 2000.
- Harold Raley, "The Spirit of Spain", Houston: Halcyon Press 2001. (ISBN 0-9706054-9-8)
- George Orwell's Homage to Catalonia.
External links[edit]
Overviews[edit]
|















