User:JaeHyung Choi/Vision Rehabilitation
| This article was the subject of an educational assignment in 2013 Q3. Further details were available on the "Education Program:Georgia Institute of Technology/Introduction to Neuroscience (Fall 2013)" page, which is now unavailable on the wiki. |
Vision Rehabilitation (often called vision rehab) is a term for a medical rehabilitation in order to improve vision or low vision. The rehabilitation is the process of restoring functional ability, quality of life, and independence in an individual who has lost function through illness or injury. In the case of vision rehabilitation, most rehabilitation services are focused on low vision.
Low vision is a visual impairment that cannot be corrected by regular eyeglasses, contact lenses, medication, or surgery, and it interferes with the ability to perform everyday activities.[1] The visual impairment is caused by various reasons including brain damage, vision loss, and etc.[2]
Basic Background[edit]
- Rehabilitation
- The rehabilitation does not undo or reverse the cause of damage, but seeks to promote function and independence through adaptation. Individuals can seek rehabilitation in a number of different domains, such as motor rehabilitation after a stroke or physical rehabilitation after a car accident.
- Low Vision
- The total of approximately 14 million Americans is suffering from low vision. The low vision is a condition where a level of vision is 20/70 or worse and it cannot be fully recovered with medical treatment, surgery, or conventional glasses. The low vision is clearly different from blindness since people with low vision have some useful sight. However, those people often have hard time accomplishing daily tasks as their vision deteriorates such as reading, cooking, driving, recognizing people's faces, and discerning color.The table below explains about the basic definitions of low vision and blindness.[3]
| Definition | Visual Activity | Visual Field |
|---|---|---|
| Moderate Visual Impairment | <20/60 to 20/160 | Not Considered |
| Severe Visual Impairment | ≤20/200 to 20/400 | Visual Field ≤20 degrees |
| Profound Visual Impairment | <20/400 to 20/1000 | Visual Field ≤10 degrees |
| Near-total Vision Loss | ≤20/1250 | |
| Total Blindness | No perception of light |
Causation[edit]
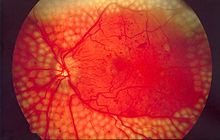
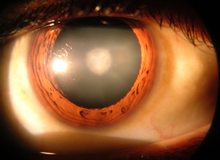
The low vision is not caused by a single disease. Multiple of diseases come together and impact to cause low vision or blindness. Despite the fact that the low vision mainly influences the elderly, it still can appear at any stage in life. Most people develop low vision as a result of eye conditions and diseases, including macular degeneration, diabetic retinopathy, glaucoma, cataracts, retinitis pigmentosa, and stroke.
Some causes of low vision, such as cataracts, are treatable and good vision can be restored. When diagnosed early, other conditions that lead to low vision, such as wet macular degeneration and glaucoma, can be halted or slowed - although vision lost is irreversible.[4] The impact of each of these eye diseases on functional vision is summarized in table below.[3]
| Disease | Clinical Presentation | Associated Disabilities |
|---|---|---|
| Age-related Macular Degeneration | Reduced visual acuity and Loss of central vision (central scotoma) | Difficulty reading, inability to recognize faces, distortion or disappearance of central vision, reduced color vision, reduced contrast perception, mobility difficulties related to loss of depth and contrast cues. |
| Diabetic retinopathy | Reduced visual acuity, Scattered central scotoma, Peripheral and mid-peripheral scotoma, and Macula edema | Difficulty with tasks requiring fine-detail vision such as reading, distorted central vision, fluctuating vision, loss of color perception, mobility problems due to loss of depth and contrast cues. In severe cases, total blindness can occur. |
| Glaucoma | Degeneration of the optic disc and Loss of peripheral vision (constricted visual field) | Mobility and reading problems due to restricted visual fields, people suddenly appearing in the visual field. In severe cases, total blindness can occur. |
| Cataract | Reduced visual acuity, Light scatter, Sensitivity to glare, and Image distortion | Remedied by lens extraction in 90% of cases. If not, difficulty with detail vision, difficulty with bright and changing light levels, reduced color vision, decreased contrast perception, mobility difficulties related to loss of depth and contrast cues. |


Treatments[edit]
Neurological Approach[edit]
Chemical Treatments[edit]
Gene Therapy[edit]
Occupational Therapy[edit]
Mechanical Approach[edit]
Mobility Training[edit]
Home Skills Training[edit]
Current Research[edit]
Useful Tips [5][edit]
- Identify yourself when you enter the room. Tell the person with visual impairment who else is accompanying you.
- Keep the environment organized and free of obstacles. Do not rearrange a person with visual impairment’s belongings without describing their new location.
- Ask the person what type of lighting allows for optimum use of vision. Use good contrast to assist the person in daily activities (i.e. pour dark coffee into a white cup, write very large with a bold black marker).
- When eating, describe the location of food items and utensils using a clock format. (i.e. “you have potato at 4:00, peas at 7:00 and meat at 12:00”).
- Use raised markers, high contrast tape, nail polish or “puffy” fabric paint to mark dials on appliances, thermostat, salt and pepper shakers, etc.
- Mobility: Have the person with visual impairment lightly hold your bent elbow. Walk smoothly, and both verbally and physically indicate steps or obstacles. Be sure to inquire as to which side is more comfortable for the person.
- Be creative! Rely on input from the person with visual impairment to assist him or her in being as independent as possible!
Clinical Studies[edit]
Since vision rehabilitation is focusing on low vision mainly, there are many clinical studies focused on low vision. However, there are still many mobility training and assisting devices for people with low vision.
| Study Title | Interventions | Conditions |
|---|---|---|
| Reading Performance with a Video Magnifier[6] | Behavioral: Video camera magnifier | Macular Degeneration |
| VA Low Vision Intervention Trials[7] | Low Vision Intervention | Low Vision |
| Clinical Trial of Peripheral Prism Glasses for Hemianopia[8] | Device: High power peripheral prism glasses, Device: Low power peripheral prism glasses | Homonymous Hemianopia |
| Project Magnify - A Comparison of Two Strategies to Improve Reading Ability[9] | Device: Optical Aids | Low Vision |
| Predictors of Driving Performance and Successful Mobility - Rehabilitation in Patients with Medical Eye Condition[10] | Procedure: Low Vision | Low Vision |
| The Use of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (TDCS) to Enhance the Rehabilitative Effect of Vision Restoration Therapy[11] | Behavioral: Vision Restoration Therapy (VRT); Device: Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) | Hemianopia; Quadrantanopia; Scotoma; Visual Field Loss |
| Low Vision Study Comparing EV Training vs. CCTV for AMD Rehabilitation [12] | Behavioral: Eccentric Viewing (EV) Training; Device: Closed Circuit Television (CCTV) | AMD |
| The Impact of Rehabilitation on Quality of Life in Visually Impaired [13] | Procedure: Blindness | Blindness |
| Wayfinding Information Access System for People with Vision Loss [14] | Device: RFID device | Blindness |
| Emergency Egress and Information System for Persons with Vision Loss [15] | Device: Electronic Badge | Blindness |
| Virtually Reality Mobility Training System for Veterans with Vision Loss[16] | Device: Virtual Sound System | Blindness |
| Evaluation of Eye Movement Tracking Systems for Visual Rehabilitation [17] | Procedure: Visual | Blindness |
| Vision Restoration Therapy (VRT) to Treat Non-Arteritic Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy [18] | Device: Vision Restoration Therapy (NOVAVISION) | Non-Arteritic Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy |
| Safety and Efficacy of ATG003 in Patients with Wet Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD) [19] | Drug: Mecamylamine; Drug: Placebo | Macular Degeneration |
| Low Vision Intervention Trail II (LOVIT II) [20] | Other: Interdisciplinary Low Vision Service; Other: Basic Low Vision Service | Central Vision Loss From Macular Diseases |
| Functional Vision in TBI [21] | Other: Vision Restoration Therapy; Behavioral: NVT Eye Scanning Therapy; Behavioral: Eccentric Viewing Training; Behavioral: Sham | Visually Impaired Persons; Brain Injuries |
| Low Vision Depression Prevention Trial for Age Related Macular Degeneration (VITAL) [22] | Behavioral: BA-LVR; Behavioral: ST-LVR | AMD; Depression |
| Restricted Useful Field View as a Risk Factor in Older Adults [23] | Procedure: Prevention of Falls | Visual Impairment |
| Improving Vision and Quality of Life in the Nursing Home [24] | Device: Spectacles; Procedure: Cataract Surgery | Refractive Error; Cataract |
| The Effect of Somatosensory Cue on Postural Stability in Blinded Persons [25] | Other: Observational | Visual Impairment |
| Use of "Smart Wheelchairs" to Provide Independent Mobility to Visual and Mobility Impairments [26] | Device: Smart Power Assistance Module (SPAM); Device: Smart Wheelchair Component System (SWCS) | Blindness; Wheelchair Users |
| Living Successfully with Chronic Eye Diseases [27] | Behavioral: Low Vision Self-Management Program | Chronic Diseases; Low Vision; Diabetic Retinopathy; Glaucoma; AMD |
| Yoga for Persons with Severe Visual Impairment (RPY) [28] | Behavioral: Yoga Intervention | Sleep Disturbance; Stress; Anxiety; Depression; Balance Impairment |
See Also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^ Liu, C.J., Brost, M.A., Horton, V.E, Kenyon, S.B., & Mears, K.E. (2013). "Occupational Therapy Interventions to Improve Performance of Daily Activities at Home for Older Adults with Low Vision:A Systematic Review". Journal of Occupational Therapy. 67 (3).
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Fletcher, K., & Barton, J.J.S. (2012). "Vision Rehabilitation: multidisciplinary care of the patient following brain injury". Perception. 41 (10): 1287-1288.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Vision Rehabilitation for Elderly Individuals with Low Vision or Blindness. USA: Department of Health & Human Services. 2004. p. 20.
- ^ "Low Vision and Visual Rehabilitation". University of Michigan. Retrieved 18 November 2013.
- ^ Wicker, Donna. "Helpful Hints for Families of the Visually Impaired" (PDF). Low Vision Services. Retrieved 18 November 2013.
- ^ Reading Performance With a Video Magnifier, http://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01670643
- ^ VA Low Vision Intervention Trial (LOVIT), http://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00223756
- ^ Clinical Trial of Peripheral Prism Glasses for Hemianopia, http://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00494676
- ^ Project Magnify - A Comparison of Two Strategies to Improve Reading Ability, http://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00366392
- ^ Predictors of Driving Performance and Successful Mobility - Rehabilitation in Patients with Medical Eye Condition, http://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00013377
- ^ The Use of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (TDCS) to Enhance the Rehabilitative Effect of Vision Restoration Therapy, http://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00921427
- ^ Low Vision Study Comparing EV Training vs. CCTV for AMD Rehabilitation, http://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00971464
- ^ The Impact of Rehabilitation on Quality of Life in Visually Impaired, http://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00013403
- ^ Wayfinding Information Access System for People with Vision Loss, http://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00829036
- ^ Emergency Egress and Information System for Persons with Vision Loss, http://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00262509
- ^ Virtually Reality Mobility Training System for Veterans with Vision, http://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00333879
- ^ Evaluation of Eye Movement Tracking Systems for Visual Rehabilitation, http://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00013429
- ^ Vision Restoration Therapy (VRT) to Treat Non-Arteritic Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy, http://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00140491
- ^ Safety and Efficacy of ATG003 in Patients with Wet Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD), http://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00414206
- ^ Low Vision Intervention Trail II (LOVIT II), http://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00958360
- ^ Functional Vision in TBI, http://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01214070
- ^ Low Vision Depression Prevention Trial for Age Related Macular Degeneration (VITAL), http://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00769015
- ^ Restricted Useful Field View as a Risk Factor in Older Adults, http://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00013351
- ^ Improving Vision and Quality of Life in the Nursing Home, http://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00347620
- ^ The Effect of Somatosensory Cue on Postural Stability in Blinded Persons, http://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00650676
- ^ Use of "Smart Wheelchairs" to Provide Independent Mobility to Visual and Mobility Impairments, http://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00333762
- ^ Living Successfully with Chronic Eye Diseases, http://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01879501
- ^ Yoga for Persons with Severe Visual Impairment (RPY), http://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01366677
