Geveronga
 Geveronga was located in the area of what is now the neighborhood of Pico-Union, Los Angeles (pictured). | |
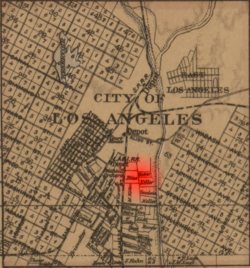 1877 map of the City of Los Angeles showing the area of Geveronga village in red | |
| Coordinates | 34°02′10″N 118°17′10″W / 34.036°N 118.286°W |
|---|---|
| History | |
| Abandoned | after destruction by the Spanish in 1781 |
| Cultures | Tongva |
| Associated with | Geverovit |
| Site notes | |
| Condition | destroyed, then built over |
Geveronga was a Tongva village located at what is now Pico-Union, Los Angeles, California along the Los Angeles River.[1][2] Part of the village area is also located on the campuses of the University of Southern California (USC) at its University Park Campus.[1] The USC History Department provided a map of the general location of Geveronga in its land acknowledgement in 2021.[1] People from the village were known as Geverovit (English: "People of Geveronga").[1]
Village[edit]
The village rested above the Los Angeles River floodplain along with the large village of Yaanga on what is known as Glendale Narrows.[1] It was described in historical accounts as being located near Yaanga and immediately adjoining the early Pueblo de Los Angeles settlement that would eventually grow into the city of Los Angeles.[3] Geveronga was a smaller and less influential village than Yaanga, which held the primary influence in this region of Tovaangar.[1]
Destruction[edit]
The village was dismantled in 1781, along with the original site of Yaanga, as part of the Anza Expedition by the Spanish Empire. Settlers came into the area and destroyed the village that year under a land claim to the area from King Carlos III in Spain for four Castilian leagues of land. The grant included a monopoly claim to the water rights of the Los Angeles River. It began much of the issues with Europeans taking water rights from Indigenous peoples of California.[1] At least 23 to 28 villagers from Geveronga were recorded to be baptized in the records of Mission San Gabriel.[4]
References[edit]
- ^ a b c d e f g "History Department Acknowledgement of the Tongva and Greater Indigenous Lands occupied by the University of Southern California". USC History Department. 2021. Archived from the original on March 2, 2024.
- ^ "Land Acknowledgement". USC Libraries. Retrieved 2023-01-08.
- ^ "Archaeological and Tribal Cultural Resources Assessment for The Villages at The Alhambra Project, Alhambra, Los Angeles County, California". 2019. pp. 12–13.
- ^ "Cultural and Paleontological Resources" (PDF). 2010. p. 104-05.
