Igua
| Igua Temporal range: Late Cretaceous
| |
|---|---|
| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | Squamata |
| Suborder: | Iguania |
| Clade: | †Gobiguania |
| Genus: | †Igua Borsuk-Białynicka and Alifanov, 1991 |
| Type species | |
| †Igua minuta Borsuk-Białynicka and Alifanov, 1991
| |
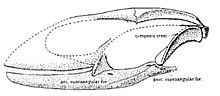
Igua is an extinct genus of iguanian lizards belonging to a group called Gobiguania that was endemic to the Gobi Desert during the Late Cretaceous. The type species Igua minuta was named in 1991 on the basis of a skull from the Barun Goyot Formation in Mongolia. The skull itself is very small, only 14 millimetres (0.55 in) long, and may have belonged to a juvenile given that it possesses a large fontanelle and that many of the bones are unfused. The snout-vent length of the individual (the total body length minus the tail) is estimated to have been 55 to 65 millimetres (2.2 to 2.6 in). Igua differs from related gobiguanians like Polrussia in having a more rounded skull. It is similar in appearance to the living genera Liolaemus and Tropidurus. The teeth are tricuspid and pleurodont, meaning they are attached to inner surfaces of the jaws.[1]
Below is a cladogram from Daza et al. (2012) showing the phylogenetic relationships of Igua:[2]
References[edit]
- ^ Borsuk-Białynicka, M.; Alifanov, V.R. "First Asiatic 'iguanid' lizards in the Late Cretaceous of Mongolia". Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. 36 (3): 325–342.
- ^ Daza, J. D.; Abdala, V.; Arias, J. S.; García-López, D.; Ortiz, P. (2012). "Cladistic Analysis of Iguania and a Fossil Lizard from the Late Pliocene of Northwestern Argentina". Journal of Herpetology. 46: 104–119. doi:10.1670/10-112. hdl:11336/61054. S2CID 85405843.

