File:N-V center based thermal probe.jpg

Size of this preview: 467 × 600 pixels. Other resolutions: 187 × 240 pixels | 374 × 480 pixels | 598 × 768 pixels | 797 × 1,024 pixels | 1,644 × 2,112 pixels.
Original file (1,644 × 2,112 pixels, file size: 192 KB, MIME type: image/jpeg)
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 01:21, 16 March 2017 | 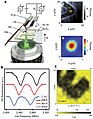 | 1,644 × 2,112 (192 KB) | Materialscientist | {{Information |Description=(a) Schematics of experimental setup. An electrical current circulates along the arms of a thermal AFM cantilever (phosphorous-doped Si) and heats up the end section above the tip (intrinsic Si). A high-NA objective excites a... |
File usage
The following pages on the English Wikipedia use this file (pages on other projects are not listed):
Global file usage
The following other wikis use this file:
- Usage on fr.wikipedia.org
- Usage on uk.wikipedia.org
